COVID-19 Q&A
Q&A Links
- Q&A about Infection Prevention
- Q&A about Symptoms,Tests and Diagnosis
- Q&A about Self-isolation and Close Contact
- Q&A about Vaccines and Side Effects
- Q&A about Border Measures
- Q&A about COVID-19 in Japanese
Call Centers
MHLW Call Center (Toll Free)
-COVID-19 Vaccines: 0120-761-770
English, Chinese, Korean, Portuguese and Spanish: 9:00-21:00、Thai: 9:00-18:00、Vietnamese: 10:00-19:00
*Everyday including weekends and holidays. This service cannot provide medical advice.
Infection Prevention
【Q1】How to dispose of household garbage
(1) Cover an empty garbage container with a plastic garbage bag.
(2) Securely tie garbage bags to avoid direct contact.
(3) Wash your hands immediately after disposal.

Symptoms
【Q1】What should I do if I have a fever, cough or other symptoms?
Do not go to a medical institution right away; contact a COVID-19 Consultation Center (the name may vary depending on the region) first.
(1) At the very least, please contact Call center in any of the following situations.
-You have a severe symptoms such as breathing difficulty, intense tiredness (fatigue), or high fever: Symptoms vary from person to person. If you feel the symptoms are severe, contact Call center immediately.
-If you are at high risk of becoming severely ill(※) and have relatively mild cold symptoms, such as fever and cough. (※Elderly, People with underlying conditions such as diabetes, heart failure, or respiratory diseases (COPD, etc.), People on dialysis, People taking immunosuppressive agents or anti-cancer drugs.)
(2) Other than the above, people have been having relatively mild cold symptoms, such as fever and cough, that are persistent: Symptoms vary from person to person. If you feel the symptoms are severe, contact a Call Center immediately.
(3) Just in case, pregnant women, the same as people who are susceptible to severe illness, should contact your doctor or a COVID-19 Consultation Center. For children, it is advisable to see a pediatrician, and so please consult with a COVID-19 Consultation Center or your pediatric medical institution by telephone or other means.
(4) Take days off work or school and refrain from dining with others if you are feeling sick. Even if your fever is relieved by taking fever medicine, you may spread the infection.
【Q2】Is it safe to take antipyretic to treat symptoms?
No problem. Consult with your doctor or pharmacist in the following cases; ・If you are taking other medicine, while pregnancy or breastfeeding, or senior citizen. You might be limited medicines to take under medical care such as stomach and duodenal ulcers. ・If you have ever experienced allergic symptoms or asthma due to medication, etc. ・If symptoms are severe or long-lasting such as severe pain or high fever.
【Q3】I have a bad cough and cough up phlegm. How to stay calm?
When you lie down on your back for a long time, gravity causes phlegm to accumulate more sassily. Lying down on your stomach sometimes improve blood circulation.
【Q4】Can I get immunity or antibodies if I am infected with COVID-19?
It is known that antibodies and immunity against viral infections, such as measles, are produced after infection. It is also known that antibodies are produced in the body after infection with COVID-19, but at this moment, it is not clear how much antibody is produced, how long it will last, and whether immunity can be acquired or not.
Therefore, even if you find that you do not have antibodies to COVID-19, it does not mean that you are not infected with COVID-19 or that you have not been infected in the past.
Tests and Diagnosis
【Q1】What tests are being used to diagnose COVID-19?
Tests for diagnosing COVID-19 include PCR Test, Quantitative Antigen Test, and Qualitative Antigen Test. These tests are all designed to detect SARS-CoV-2 virus (which caused COVID-19) in one’s body and therefore can be used to see if someone is currently infected with the virus. Antibody tests are only used to see if a person has previously been infected with COVID-19. Antibody tests are not for use to diagnose acute infection.
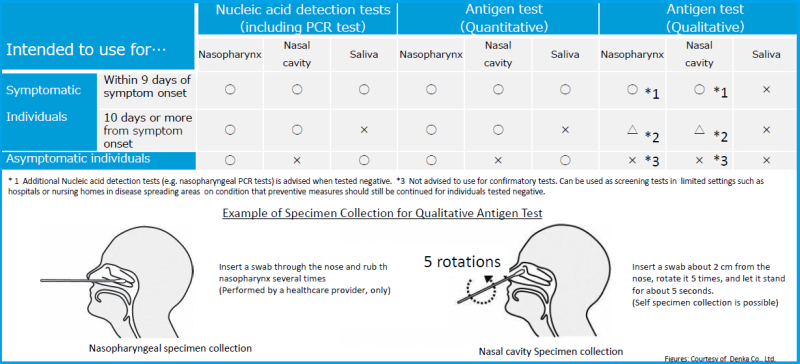
【Q2】How can I check if I am infected with COVID-19?
If you wish to be tested, you need to pay it for your own.
【Q3】I want to be diagnosed and receive prescription by phone or online
Considering the current situation, as a temporary special measure, diagnosis and prescriptions will be available by phone or online including initial consultation, at the doctor’s discretion. If you do not have a family doctor, please contact the nearest medical institution listed on our website (only in Japanese). Depending on your symptoms and condition, the doctor may advise you to have an in-person consultation at the doctor's discretion.
【Q4】How does the pulse oximeter work?
If Sp02 (blood oxygen saturation) level measured below 93% by the pulse oximeter, consult public health center or your family doctor immediately. It may not give an accurate reading if your hands are cold or swollen, or you have nail polish when you use it. There may be a slight error in measurements depending on the product.
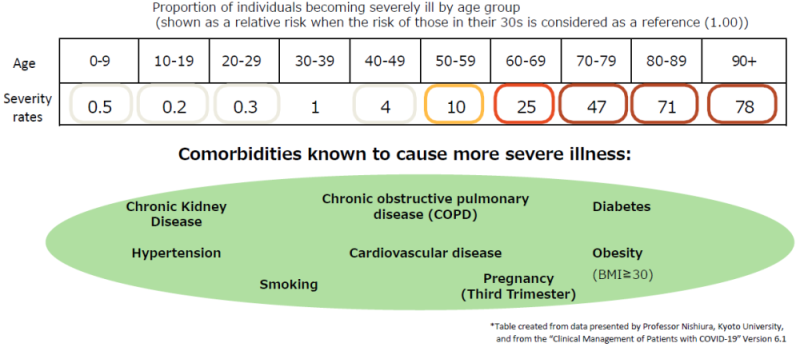
【Q5】Who is at increased risk for severe illness and death among diagnosed with COVID-19?
Among those diagnosed with COVID19, the elderly, those with underlying medical conditions, and some pregnant women in their third trimesters are more likely than others to develop severe illness or die. Comorbidities known to cause more severe illness include: Chronic, Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases (COPD ), Chronic Kidney Diseases, Diabetes, Hypertension, Cardiovascular diseases, Obesity, and Smoking.
Full vaccination (two doses) is effective in preventing severe illness.
【Q6】What is the definition of "severe illness"?
-Severe illness : People who needs hospitalize to ICU(intensive care unit) using a ventilator facing crisis of life
-Moderate illness : People who has shortness of breath or pneumonia
-Moderate illnessⅡ: People who needs oxygen apply
-Moderate illnessⅠ: People who doesn’t need oxygen apply
-Minor : People who can breathe on their own without problem even if it’s hard
If your SpO2 level measured under 93% by your pulse oximeter, consult to your doctor even with no symptoms.
Self-isolation and Close Contact
【Q1】How can I end isolation?
【Symptomatic】1) 7 whole days after the first sign of symptoms and 2) 24 hours free of any symptoms or 2 consecutive negative results on a COVID-19 test taken at least 24 hours apart, after being free of symptoms.
【Asymptomatic】7 whole days after the day the positive specimen was collected. Or 5 days if the test kit is negative on the 5th day.
【If Symptoms appear after a negative result】The patient may end isolation 10 days after the onset of symptoms.
【Q2】How long family member needs quarantine?
We consider a family member as a close contact person. Stay home and quarantine for 7days after patient develops symptoms. During that period, stay away from people you live with, wash your hands, wear a well-fitting mask and sanitize the place you might touch, and dispose the garbage properly. Even after the period is over, you are encouraged to check your health and avoid social gathering until the patient is recovered.
Vaccines
【Q1】What are the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccines approved in Japan?
The vaccines are effective in preventing the onset, infection and severe illness from COVID-19. Although the protection from infection and symptom onset may gradually decrease over time, it has been reported that the effectiveness in preventing serious symptoms remains comparatively high.
【Q2】 I had COVID-19 before. Should I still get the vaccine?
Yes, people infected with COVID-19 in the past can be vaccinated. At this point, two doses are given for primary vaccine series as usual.
【Q3】 Can I still get the vaccine if I am pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant?
Yes, you can get the vaccine. People who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning to become pregnant are also eligible. Vaccination is recommended regardless of the time of pregnancy.
【Q4】 I have a chronic illness, can I get the vaccine?
Yes. Vaccination is recommended for people with pre-existing conditions and the elderly, as they are more susceptible to severe illness. However, it is best to avoid vaccination when the illness is worsening. There are also some precautions that should be taken depending on the disease you are suffering from, so please consult your doctor.
【Q5】Why do we need an updated (bivalent) booster shot?
COVID-19 vaccines are highly effective in preventing the onset of illness, but it has been suggested that their effectiveness in preventing infection gradually declines as time passes. From the perspective of preventing the development of severe disease, the spread of infection and the onset of illness, it is recommended that people who have completed their primary vaccination series and aged 5 years and older now will be offered an updated (bivalent) booster shot.
【Q6】How effective are the booster shots?
Compared to the original (monovalent) COVID-19 vaccination, the updated (bivalent) vaccination has produced equivalent or better neutralizing antibody titers and neutralizing antibody response rates.
The updated booster shot is expected to be more effective in preventing severe disease, infection and the onset of illness than original one.
【Q7】Can I still get a first dose even booster shot started?
The free COVID-19 vaccination program is scheduled to continue until March 31st, 2024. Within this period, you can get your first dose.
【Q8】Who is eligible for the updated booster (bivalent) dose?
From May 8th, 2023 on, people at high risk of serious illness (the elderly, people with underlying medical conditions), health care workers, etc., and children between the ages of 5 and 11 are eligible for the updated booster (bivalent) dose.
Side Effects of vaccination
【Q1】Who should I consult about side effects after COVID-19 vaccination?
Talk to your doctor or contact point for consultation about long-term side effects. Each prefecture has set up contact points for you, including people who do not have a medical institution nearby, to ask for advice. They also ensure their local system for smooth access to specialized hospital/medical facilities when deemed necessary.



