健康・医療Radionuclides in Food
Immediately after the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in March 2011, the Government of Japan had taken comprehensive actions, such as establishing provisional regulatory values, monitoring of foods and materials for agricultural production, restriction of distribution of food with higher radionuclide levels than the regulatory values, and decontamination of farm land in order to ensure sufficient supply of safe foods distributed Japan, including foods to be exported. In April 2012, new limits were established for foods on a basis of intervention exemption level of 1 mSv/year, equivalent to the Codex Standard and monitoring results accumulated.
Since April 2012, the results of monitoring has indicated that the excess rates are decreasing and extremely low, 0.1% in FY2018, and majority of the detection (exceeding cases) is limited to wild harvest monitored at area where the distribution is already restricted. Non-compliance cases are hardly detected in food commodities prepared for the market. Estimations of exposure (effective dose) to radioactive cesium in foods are decreasing constantly and now around 0.1% of 1 mSv/year.
Japan continues to make utmost efforts for prompt and accurate information sharing regarding this issue. Also, Japan intends to respond to this issue in close cooperation with the relevant international organizations.
Abstract (Current Situation and Protective Measures for Radionuclides in Foods) (PDF[531KB])
JAPANESE PAGE
Basic Information
- Basic Information on Radiation Risk (Reconstruction Agency)
- Food and Radiation Q&A Mini (Consumer Affairs Agency)
](https://www.mhlw.go.jp/english/topics/2011eq/images/q_and_a_mini.jpg)
Limits

- The Ministerial Ordinance Partially Revising the Ministerial Ordinance on Milk and Milk Products Concerning Compositional Standards, etc.; the Notification on Designating the Radionuclides Designated by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare under the Provisions of Item(I)(1) of the Attached Table 2 of the Ministerial Ordinance on Milk and Milk Products Concerning Compositional Standards, etc.; and the Notification on Partial Revision of Specification and Standards for Food, Food Additives etc. (Notice No.0315 Articles 1 of the Department of Food Safety, March 15,2012) (PDF:28KB)
Rigorous Monitoring System
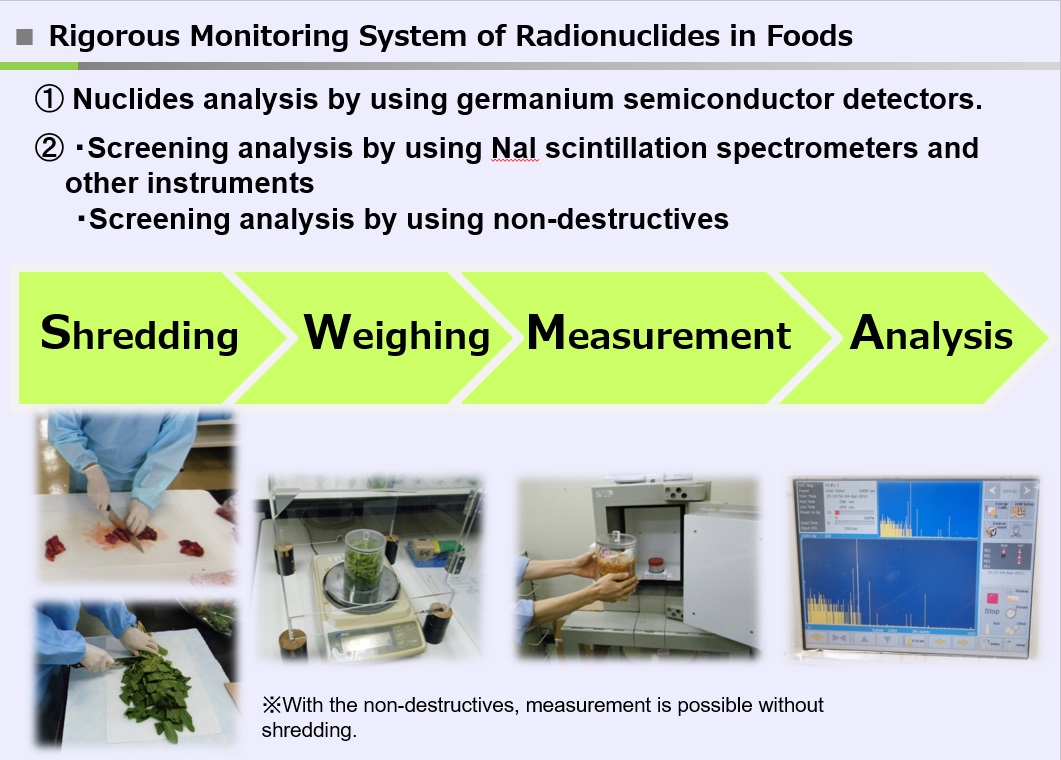
<Testing Methods>
- Testing Methods for Radionuclides in Food (Notice No.0315 Article 4 of the Department of Food Safety, March 15,2012) (PDF:105KB)
- Screening Method for Radioactive Cesium in Food Products (Administrative Notice, March 1, 2012) (PDF:637KB)
- Application of testing methods for radionuclides in food (Notice No.0315 Article 7 of the Standards and Evaluation Division, the Department of Food Safety, March 15,2012) (PDF:41KB)
- Monitoring of radionuclides in food are mainly conducted before shipment. Most of the food items exceeding the limits are derived from areas where restrictions of distribution have been instructed. Non-compliance cases are hardly detected in food commodities prepared for the market.
Restriction of Distribution and/or Consumption of Contaminated Food
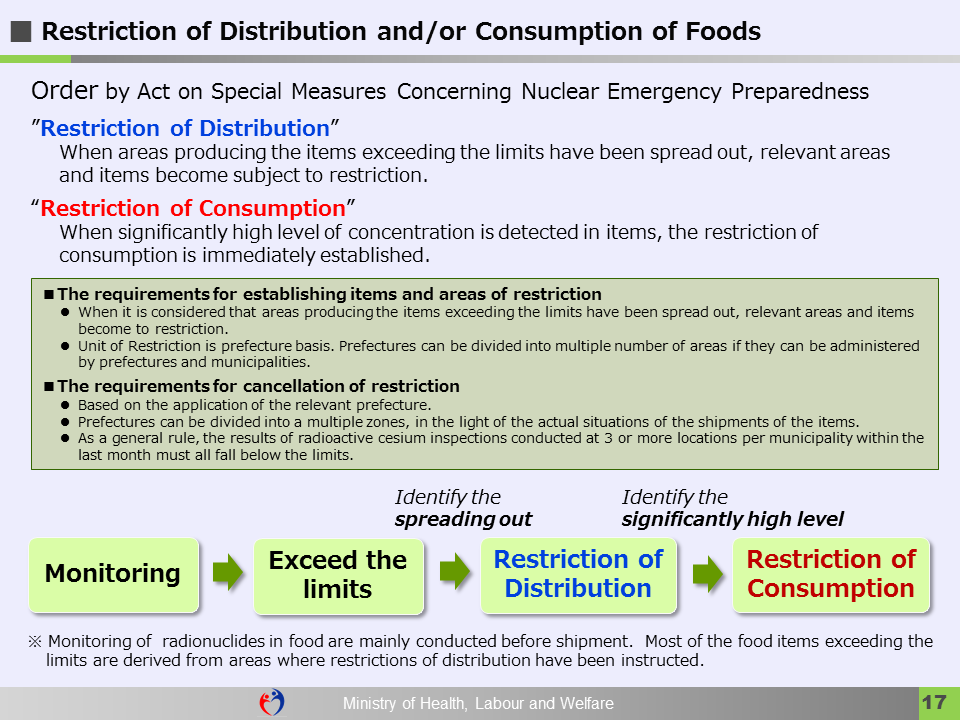
<Inspection and Instruction to Restrict Distribution/Cancellation>
- The Revision of the "Concepts of Inspection Planning and the Establishment and Cancellation of Items and Areas to which Restriction of Distribution and/or Consumption of Foods concerned Applies" (31 March 2025)(PDF[411KB])
- The instructions associated with food by Director-General of the Nuclear Emergency Response Headquarters (PDF[996KB])
Estimations of effective dose from radionuclides in foods
Please refer to the Consumer Affairs Agency website for recent test results below
https://www.caa.go.jp/policies/policy/standards_evaluation/food_pollution/criterion



