健康・医療Food Additives
Food additives are used in the process of manufacturing foods or for the purpose of processing or preserving foods. They include preservatives, sweeteners, coloring agents and flavoring agents.
While food additives largely contribute to today’s distribution of a variety of foods, much caution is needed to ensure the safety of additives, which do not have a long history of human consumption unlike foods.
The MHLW consults the FSC and authorizes the use of them only when they do not have risks of harming human health.
The MHLW continuously takes adequate measures to review the safety of authorized food additives, for example, by surveying daily intake levels per person.
Historical background
In 1947, then Ministry of Health and Welfare (the present Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW)) enacted the Food Sanitation Act (FSA) as the first comprehensive Act for food safety/hygiene, and introduced a positive list system for food additives. Under the system, only additives designated as safe by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare may be used in foods. Since 1947, all food additives have been regulated by this act. However, designation system had been applied only to chemically synthesized additives until 1995 when the FSA was amended. Currently, all types of additives are equally subject to the designation system, synthetic or natural origin, with some exceptions.
Definition
The FSA, in the first Chapter, defines ''food additive'' as
(i) substances used in or on food in the process of manufacturing food, or
(ii) substances used for the purpose of processing or preserving food.
Consequently, ''food additive'' includes both substances remaining in the final products, such as food colors and preservatives, and substances not remaining in the final products, such as microorganism control agents and filtration aids.
Regardless of whether they are from natural origin, all substances used for the above purposes are categorized as food additives in Japan
The scope of food additives referred to by the FSA is different from that defined by the Codex Alimentarius Comission (CAC). The substances given below, which are not defined by the CAC as food additives, are all categorized as food additives in Japan.
(i) Processing aids,* like infiltration-supporting agents
(ii) Vitamins, minerals, and amino acids
(iii) Flavoring agents
* Processing aid means any substance or material, not including apparatus or utensils, and not consumed as a food ingredient by itself, intentionally used in the processing of raw materials, foods or its ingredients, to fulfill a certain technological purpose during treatment or processing and which may result in the non-intentional but unavoidable presence of residues or derivatives in the final product (CAC, Procedural Manual, “Section I : Definitions for the purpose of the Codex Alimentarius”)
Regulation
Designated additives and Existing food additives
Food additives that are permitted for use in food in Japan are limited to those listed at the following URLs, excluding natural flavoring agents, and ordinary foods used as food additives.
Notice: ONLY SUBSTANCES LISTED BELOW are allowed to use for food additives such as coloring, preservative, sterilizing, and manufacturing agents in Japan (excluding Natural flavoring agents and ordinary foods used as food additives).
●Designated Additives
Designated additives are those designated by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare as substances that are unlikely to harm human health based on Article 10 of the FSA.
http://www.ffcr.or.jp/zaidan/FFCRHOME.nsf/pages/list-desin.add-x
●Existing food additives.
Other than the designated additives, certain substances are permitted for use and distribution in Japan, as exception, without through the designation system as provide by the FSA for the reason that they are widely used in Japan and have a long history of consumption by humans. They are referred to as existing food additives and placed on the List of Existing Food Additives. This additive status was created in1995 when the FSA was revised and all additives (not only chemically synthesized substances but also natural origin) came to be subject to the designation system.
http://www.ffcr.or.jp/zaidan/FFCRHOME.nsf/pages/list-exst.add
●Standards for Use of Food Additives
Food additives with use standards (i.e., target foods and maximum use limits/residue limits) are shall meet these standards, when these substances are used.
http://www.ffcr.or.jp/zaidan/FFCRHOME.nsf/pages/stanrd.use
Other food additives
There are two substance categories that are exempted from the designation system: “natural flavoring agents” and “ordinary foods used as food additives.”
Examples of additives coming under these categories are placed on following lists.
●Natural flavoring agents
These substances are natural products that are obtained from animals and plants and used for flavoring food.(e.g., vanilla flavoring and crab flavoring). The amount used is generally very little.
http://www.ffcr.or.jp/zaidan/FFCRHOME.nsf/pages/list-nat.flavors
●Ordinary foods used as food additives
They are substance that are generally provided for eating or drinking as food and also used as food additives(e.g., strawberry juice and agar).
http://www.ffcr.or.jp/zaidan/FFCRHOME.nsf/pages/list-general.provd.add
Japan’s Specifications and Standards for Food Additives
The Food Sanitation Law requires the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare to prepare an official compilation of food additive specifications and standards. The compilation contains compositional specifications for individual additives as well as standards for manufacturing and use of these additives. The compilation is updated every several years to introduce new and improved test methods commensurate with the progress in science and technology, and to achieve international harmonization of standards. Japan’s Specifications and Standards for Food Additives is the English translation of the official compilation of food additives.
Japan's Standards and Specifications for Food Additives, 9th edition(2022)
https://dfa25.nihs.go.jp/jssfa/index.php
※Please note that the latest version(10th edition(2024)) is only available in Japanese.
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/kenkou_iryou/shokuhin/syokuten/kouteisho10e.html
For inquiry of individual products, please contact a quarantine station.
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/english/topics/importedfoods/1-2.html
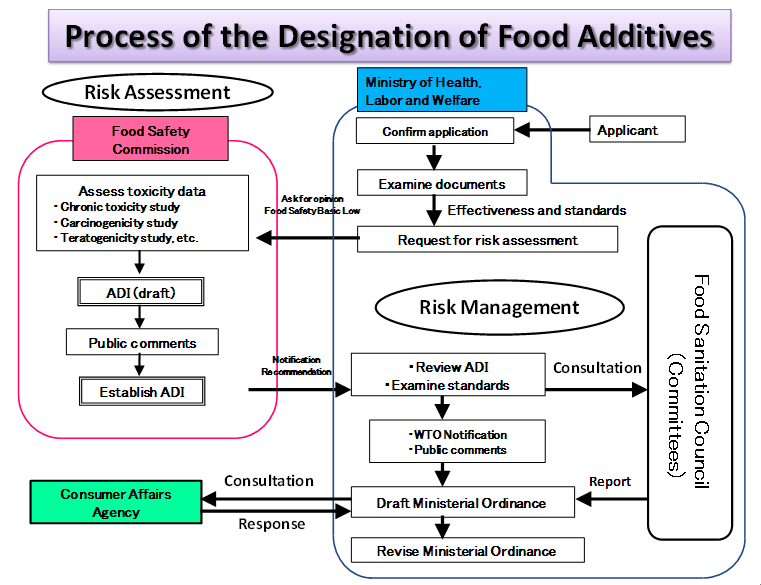
Application for designation of food additives or revision of standards
The designation of food additives and the revision of standards for food additives both require risk assessment by the Food Safety Commission of Japan (FSCJ) and review by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) based on the risk assessment by the FSCJ.
- Revision of Guidelines for the Designation of Food Additives and Revision of Standards for Use of Food Additives (PDF:497KB)[497KB]
- Guidelines for the Designation of Flavoring Agents(PDF:163KB)
Those wishing to apply for designation of food additives or revision of standards for food additives should collect documents required for the application and submit them together with the application form to the MHLW. For details for application procedure, please consult "The Procedure for Preparing Application Documents for Designation of Food Additives and Revision of Use Standards for Food Additives" (食品添加物の指定及び使用基準改正要請資料作成に関する手引) and guidelines for FSCJ’s risk assessment.
- The procedure is available at
https://www.nihs.go.jp/dfa/FADCC/dfa_e_fadccsite/e005_fadcc_guideline.html - Notification for the standard period is available at
The standard period required to designate food additives (PDF:63KB)
FSCJ(English Page)
Guidelines(provisional translation) for FSCJ’s risk assessment are available at
https://www.fsc.go.jp/hyouka/index.data/guidelines_for_food_additives_revised_2021.pdf
https://www.fsc.go.jp/hyouka/index.data/guidelines_for_flavoring_revised_2021.pdf
https://www.fsc.go.jp/hyouka/index.data/guidelines_for_enzymes_revised_2021.pdf
https://www.fsc.go.jp/hyouka/index.data/guidelines_for_fortification_revised_2021.pdf
Risk Assessment by FSCJ available at
https://www.fsc.go.jp/english/evaluationreports/additives_e3.html
For consultation of application for designation of food additives or revision of standards, please contact Food Additive Designation Consultation Center (FADCC) of National Institute of Health Sciences.
https://www.nihs.go.jp/dfa/FADCC/dfa_e_fadccsite/e000_index.html
Data of average intake of individual food―additional data to the survey report on food intake and frequency (食品摂取頻度・摂取量調査の特別集計業務 報告書追加資料)
―is available at (PDF:899KB) (xls:1,004KB)
Notice: If the applicant lives overseas, he or she should establish a contact person in Japan for responsible handling of the application.
Materials required for assessments of food additives.
(Guideline for Assessment of the Effect of Food on Human Health Regarding Food additives (Excerpt))
| Items | Designation |
Revision of |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Information on the additive subject to assessment | |||
|
1. Name and usage |
Required | Required | |
|
2. Origin or process of discovery |
Required | * | |
|
3. Usage in other countries |
Required | Required | |
|
4. Assessments by international organizations and other organizations |
Required | * | |
|
5. Physiochemical properties |
Required | * | |
|
6. Suggestions for usage standards |
Required | Required | |
|
7. Others |
* | * | |
|
|
|||
|
Findings regarding safety |
|||
|
1. Tests for disposition in organisms |
Required | * | |
|
2. Toxicity |
|||
| (1) Subchronic toxicity studies and chronic toxicity studies | Required | * | |
| (2) Carcinogenicity studies | Required | * | |
| (3) Toxicity/carcinogenicity combination studies with one-year repeated-dose administration |
Required | * | |
| (4) Reproductive toxicity studies | Required | * | |
| (5) Prenatal developmental toxicity studies | Required | * | |
| (6) Genotoxicity studies | Required | * | |
| (7) Allergenic potential studies | Required | * | |
| (8) General pharmacological studies | Required | * | |
| (9) Other studies | * | * | |
|
3. Findings in humans |
Required | * | |
|
4. Estimation of daily intake, etc. |
Required | Required | |
|
|
|||
Note 1. When requesting a division of usage standards for a food additive for which assessment of the effect of the food on health has already been carried out by FSCJ, the materials required for “Revision of standard” should be submitted. When requesting a division of usage standards for a food additive for which assessment of the effect of the food on health has not been carried out by FSCJ, documents required for designation should be submitted, in principle.
Note 2. Materials marked “Required” should be submitted whenever applicable. Materials marked with an asterisk (*) should be submitted as necessary (when there is a new finding, for example).
Note 3. When a combination test for chronic toxicity and carcinogenicity is carried out using one rodent species, a chronic toxicity test and carcinogenicity test on another rodent species can be omitted.



