Overview of Orphan Drug/Medical Device Designation System
Orphan Drug/Medical Device Designation
In Japan, drugs and medical devices can be designated as orphan drugs or medical devices based on the Article 77-2(PDF:87KB) of the Act on Securing Quality, Efficacy and Safety of Pharmaceuticals, Medical Devices, Regenerative and Cellular Therapy Products, Gene Therapy Products, and Cosmetics if they are intended for use in less than 50 000 patients in Japan and for which there is a high medical need. They are designated by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare based on the opinion of the Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Council (PAFSC).
Designation of orphan drugs/medical devices does not automatically lead to marketing approval.
The objectives and outline of the system are described below.
Background
Before the orphan drug/medical device system had established, drugs and medical devices to be used for the treatment of difficult-to-treat diseases and acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) had not been sufficiently developed despite the high medical needs because the number of patients was small. With the diversification of public healthcare needs, safe and quality medical products were required to be supplied to patients as soon as possible. Accordingly, based on rising public expectations and the changing circumstances of drug and medical-device research and development, it had been decided to take special measures to support and promote research activities for the development of orphan drugs/medical devices.
Designation criteria
The Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare may designate drugs and medical devices satisfying the following criteria as orphan drugs/medical devices after receiving applications for orphan designation from the applicants.
(1) Number of patients
The number of patients who may use the drug or medical device should be less than 50 000 in Japan.
- The number of patients could be estimated based on the report of Health and Labour Science Research or the data published by reliable scientific societies. The number of patients with a difficult-to-treat disease is sometimes difficult to estimate accurately due to lack of research on the patient population. Therefore, estimates from a variety of statistical data are generally used to indicate that the number of those patients is less than 50 000 in Japan. Submission of an estimate based on multiple statistical methods is recommended.
- Since financial year 2006, applicants may apply for orphan drug designation with the following new drugs if the estimated number of patients who may use the drug at the time of application is less than 50 000 in Japan.
- A vaccine to prevent an infectious disease rarely reported in Japan or that only reported overseas and the use of which is limited to a specific population, such as people who have visited the endemic area.
- A vaccine to prevent an emerging or re-emerging infectious disease associated with genetic mutation, of which an outbreak has not been reported at the time of designation but which may significantly affect the lives and health of Japanese people, and of which the time and size of epidemic are unpredictable.
(2) Medical needs
The drugs or medical devices should be indicated for the treatment of serious diseases, including difficult-to-treat diseases. In addition, they must be drugs or medical devices for which there are high medical needs satisfying one of the following criteria.
- There is no appropriate alternative drug/medical device or treatment
- High efficacy or safety is expected compared with existing products
(3) Possibility of development
There should be a theoretical rationale for the use of the product for the target disease, and the development plan should be appropriate.
- For example, in the case of application of an orphan drug, the possibility of development should be explained based on existing non-clinical and clinical data in the latter half of the phase I study or in the first half of the phase II study except when the product has already been approved overseas or sufficient clinical study data are available.
Incentives
For designated orphan drugs and medical devices, measures to support the research and development activities described below are taken.
(1) Subsidy payment
Orphan drug/medical device applicants can receive subsidies through the National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (NIBIO) to reduce the financial burden of product development. (The total budget for financial year 2010 was 650 million yen.)
(2) Guidance and consultation
Orphan drug/medical device applicants can receive guidance and consultation from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW), the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), and NIBIO on research and development activities. PMDA provides a priority consultation system for designated orphan drug/medical device. Lower user fee categories for PMDA’s consultation are applicable to designated orphan drugs.
Flow of Clinical Trial Consultation (PDF:123KB)
(3) Preferential tax treatment
Twelve percent of study expenses for orphan drug/medical device incurred during the NIBIO subsidy payment period (not including subsidies granted by NIBIO) can be reported as a tax credit.
(4) Priority review
Designated orphan drugs and medical devices will be subject to priority review for marketing authorization to ensure that they are supplied to clinical settings at the earliest possible opportunity. Categories of lower user fees are applicable to review for marketing authorization of designated orphan drugs.
(5) Extension of re-examination period
After orphan drug/medical device designation and approval, the re-examination period for the drugs will be extended up to 10 years for drugs and up to 7 years for medical devices.
Organization of the orphan drug/medical device designation system
The responsibilities of major regulatory authorities involved in the designation system are described below.
(1) Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW)
- Review and designation of orphan drugs/medical devices
- Review and approval of orphan drugs/medical devices
- Pre-designation consultation for orphan drugs/medical devices
- Payment for the operational cost of NIBIO
(2) Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA)
- Priority scientific consultation for clinical trials and dossiers for marketing authorization of orphan drugs/medical devices
(3) National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (NIBIO)
- Subsidy payment to the applicant
- Accreditation for research expenses to be used by the applicant
- Provision of guidance and consultation to the applicant
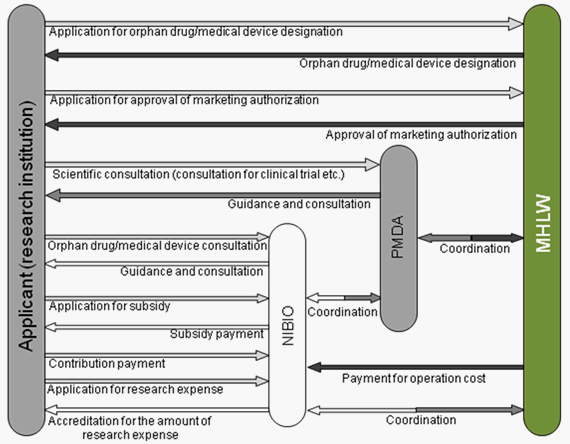
Figure Organization of orphan drug/medical device designation system
Orphan drug/medical device designation procedure
Applications for orphan drug/medical device designation can be submitted at any time. After the receipt of application, the designation will be determined based on the discussion at Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Council (PAFSC).
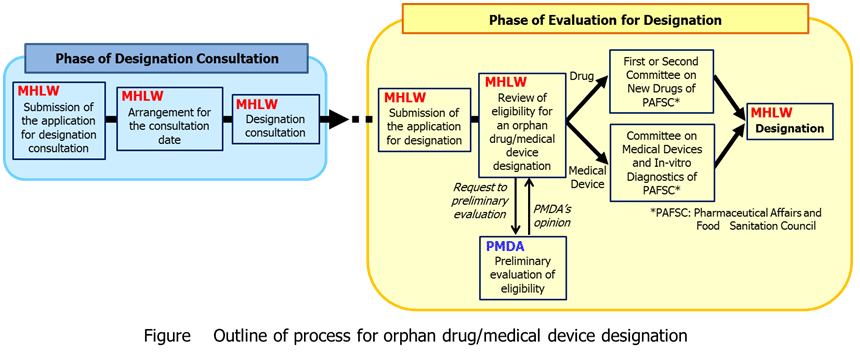
Preparation for designation consultation
(1) Application for consultation
- Applicants who wish to obtain an orphan drug/medical device designation may apply for a designation consultation at any time.
- Applicants should submit a consultation application to the administrator of the orphan drug/medical device designation at the Evaluation and Licensing Division, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, MHLW.
- Applications should be sent by post or fax. Use of the Application Form for Orphan Drug/Medical Device Designation Consultation (Attachment 1 (pdf:109KB,Word:39KB)) is recommended. For consultation regarding a specific product, attachment of the Summary of the Orphan Drug/Medical Device (Attachment 2(pdf:50KB,Word:36KB)) is desirable.
- Fill out the forms in Japanese (as for any consultation). Please refer to brief instructions for the Application Form for Orphan Drug/Medical Device Designation Consultation.[203KB]
Contact point
- Orphan drugs
Administrator of Orphan Drug Designation
Evaluation and Licensing Division
Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, MHLW
1-2-2
Kasumigaseki
Chiyoda-ku
Tokyo 100-8916
JAPAN
Fax +81-3-3597-9535 - Orphan medical devices
Administrator of Orphan Medical Device Designation
Office of Medical Devices Evaluation
Evaluation and Licensing Division
Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, MHLW
1-2-2
Kasumigaseki
Chiyoda-ku
Tokyo 100-8916
JAPAN
Fax +81-3-3597-0332
(2) Arrangement for the consultation date
The date of consultation will be notified by the administrator of the orphan drug/medical device designation via telephone, fax or e-mail as soon as possible after the application for consultation is submitted.
Designation consultation
(1) Consultation for application of orphan drug/medical device designation
- Consultation will be held before application of orphan designation.
- Consultation will be held at the Evaluation and Licensing Division, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, MHLW.
- Consultation will be provided in a 30-minute session in principle.
- The number of consultation attendees will not be specified. However, the number should be appropriate for the extent of consultation items.
(2) Important notes
- Prepare a draft of documents necessary for the application for designation (hereinafter referred to as “draft documents for designation”) in advance.
- Attach a list of references to the draft documents for designation as necessary.
- Prepare 5 copies.
- Ensure the copies arrive no later than 1 week before the day of consultation in principle.
Process of designation
(1) Submit an original and a copy of the application for designation to the Evaluation and Licensing Division, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, MHLW after the consultation if no specific problems are identified. The application will be accepted when it is complete with all necessary documents. Incomplete applications cannot be accepted. The application will not be accepted when the product fails to satisfy the designation criteria. Use the Application Form descrived below for application of orphan designation. Fill out the forms in Japanese.Please refer to brief instructions for the Application Form of Orphan Drug Designation[254KB].
(2) The Evaluation and Licensing Division, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, MHLW will review an orphan drug/medical device designation after receiving the application for designation.
(3) If a designation can be determined, Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Coucil (PAFSC) will be consulted.
(4) A designation will be granted in principle if the First or Second Committee on New Drugs of PAFSC (or the Committee on Medical Devices and In-vitro Diagnostics for orphan medical devices) approves of the designation.
(5) The designation notice will be sent to the applicant after all the procedures are completed. The designation [the name of drug (ingredient), expected indication(s), name and address of applicant and date of designation] will be published in a government gazette as a MHLW Ministerial Notification.
Applications of orphan drug/medical device designation
- Application form (Drug(pdf:83KB,Word:40KB) and Medical device(pdf:92KB,Word:40KB))
- Form (Article 250, Ministerial Ordinance for Enforcement of the Pharmaceutical Affairs Act)
Application for Orphan Drug Designation [Form 107(1)][83KB], Application for Orphan Medical Device Designation [Form 107(2)][91KB] - Number of copies to be submitted
One original and two copies - Submit to:
Evaluation and Licensing Division, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, MHLW
- Form (Article 250, Ministerial Ordinance for Enforcement of the Pharmaceutical Affairs Act)
- Attachments to the application
- Data on the number of patients
Objective statistical data on the number of patients in Japan for whom the drug or medical device will be indicated. - Data on medical needs
-Data on the diseases such as etiology and symptoms
-Data on the current status such as availability of similar drugs/medical devices and treatment - Data on the theoretical rationale for the use of the drugs/medical devices Related data in a draft dossier of application for marketing authorization, which is available at the time of application for orphan drug/medical device
- Development plan (data on the possibility of development)
Data on the outline of the development plan, including the current development status, expected test items, duration of the study and necessary expenses
- Data on the number of patients
- Preparation of Summary of the Orphan Drug/Medical Device
The Summary of the Orphan Drug/Medical Device should be prepared for Committee meetings and publication. See Attachment 2(pdf:50KB,Word:36KB) for the specific form.Please refer to brief instructions for the form[152KB].
Withdrawal of orphan drug/medical device designation
Notification of research discontinuation
- Discontinuation notice
- Form (Article 252, Ministerial Ordinance for Enforcement of the Pharmaceutical Affairs Act) Orphan Drug/Medical Device Research/Marketing/Manufacturing Discontinuation Notice (Form 108)
- Number of copies to be submitted
One original and two copies - Submit to:
Evaluation and Licensing Division, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, MHLW
The withdrawal of orphan drug/medical device designation will be notified after the Evaluation and Licensing Division, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, MHLW receives the discontinuation notice and reports to Pharmaceutical Affairs and Food Sanitation Council (PAFSC).
Withdrawal of designation
The orphan drug/medical device designation may be withdrawn if any of the following applies.
- The requirement for the number of patients is not satisfied.
- The requirement for medical needs is not satisfied because of approval for other similar medical products or other reasons.
- Any false statement is found in the application for designation.
- The orphan drugs/medical devices have not been developed or marketed without a justifiable reason.
- The applicant violates any laws or ordinances related to pharmaceutical affairs or related regulatory measures.
Related Sites Links
- Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency(PMDA)
- National Institute of Biomedical Innovation (NIBIO)
- European Medicines Agency(EMA)
- European Medicines Agency(EMA)-Orphan designation
- U.S. Food and Drug administration(FDA)
- U.S. Food and Drug administration(FDA)-Orphan Drug Act
This page was modified with permission from Handbook of orphan drugs 2009, edited by Study group of orphan drugs, Jiho.Inc., 2009: p1-6
To see the charts(pdf file), it requires a software "Acrobat Reader".
You can get Acrobat Reader for free, please click on the next button. Get Adobe Reader
