Office of Import Food Safety, Food
Inspection and Safety Division,
Pharmaceutical Safety and
Environmental Health Bureau,
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
Results of Monitoring and Guidance
Based on the Imported Foods Monitoring and
Guidance Plan for FY 2016
August 2017
Food Inspection and Safety Division,
Pharmaceutical Safety and Environmental Health Bureau,
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
Inspection Results of Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY 2016
Introduction
Foods, additives, apparatus, containers and packaging and toys (hereinafter referred to as "foods") imported by Japan in 2016 amounted to 32.30 million tons across 2.34 million import notifications. According to the "2016 Food Balance Sheet" published by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, the food self-sufficiency ratio in Japan is 40% (combined food self-sufficiency ratio by calorie intake), and 60% based on calorie intake is dependent on imports.
In order to ensure the safety of foods imported into Japan (hereinafter, "imported foods"), the government established the Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan for 2016 (hereinafter, "the Plan"). The Plan is based on the Guidelines for Monitoring and Guidance for Food Sanitation (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Notification No. 301, 2003) as per the provisions of Article 23, paragraph 1 of the Food Sanitation Act (Act No. 233, 1947; hereinafter, "the Act"), and public comments were collected and risk communication was carried out. The Plan was published in the Official Gazette as an official report according to the provisions of paragraph 3 of the same article, and monitoring and guidance for imported foods has been conducted based upon the Plan.
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare published a recently compiled overview of the implementation of inspections of imported foods including monitoring and ordered inspections carried out under the Plan, the implementation of monitoring and guidance for importers, and the consultations with exporting countries.
Reference: "Monitoring of Imported Foods – For the Safety of Imported Food"
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/kenkou_iryou/shokuhin/yunyu_kanshi/index.html

1. Overview of the Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY 2016
1 What Is the Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan?
It is the plan for the implementation of monitoring and guidance for the import of foods by the Japanese government as stipulated by Article 23, paragraph 1 of the Act.
Purpose: To further ensure the safety of imported foods by the national government promoting intensive, effective and efficient monitoring and guidance for imported foods and importers.
2 Principles of Monitoring and Guidance for Imported Foods
Measures pertaining to ensuring food safety at three stages, namely, in the exporting country, at the time of importation, and in domestic distribution, shall be implemented from the perspective of Article 4 (that is, food safety shall be ensured internationally and domestically by taking the necessary measures appropriately at each stage of the food supply processes) of the Food Safety Basic Act (Act No. 48 of 2003).
3 Priority Items for Monitoring and Guidance
- Confirmation of legality with respect to the Act at the time of import notification
- Monitoring*1 (FY 2016 Plan: 95,929 cases)
- Ordered inspection*2 (As of April 1st, 2016: 17 items from all exporting countries, and 69 items from 31 countries and 1 region)
- Regulations for comprehensive import bans*3
- Emergency measures based on overseas information
- *1: Systematic inspection based on a statistical approach considering the import volume and violation rate for each type of food.
- *2: Inspection for products with a high probability of violation where an inspection is ordered for the importer. Import and distribution is not permitted without the results being in compliance with the Act.
- *3: Measures whereby the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare prohibits sale or import of specific foods, etc., without inspection, in a case where it is deemed necessary to prevent harm.
4 Promotion of Safety Measures in Exporting Countries
- Systematic collection of information on safety measures for foods exported to Japan and promotion of food safety measures through on-site visits
- Request for the establishment of sanitation control measures such as stronger control for agricultural chemicals, enhancement of the monitoring systems and implementation of pre-export inspections, through bilateral talks and on-site visits
- Informing the responsible governmental agencies and food business operators of food safety regulations of Japan through seminars held in exporting countries
5 Guidance on Voluntary Sanitation Control by Importers
- Pre-import guidance (known as import consulting)
- Guidance on voluntary inspections at import consulting, initial import and continued import
- Guidance on preparation and storage of records on the sanitation management of imported foods
- Raising awareness of food safety amongst importers
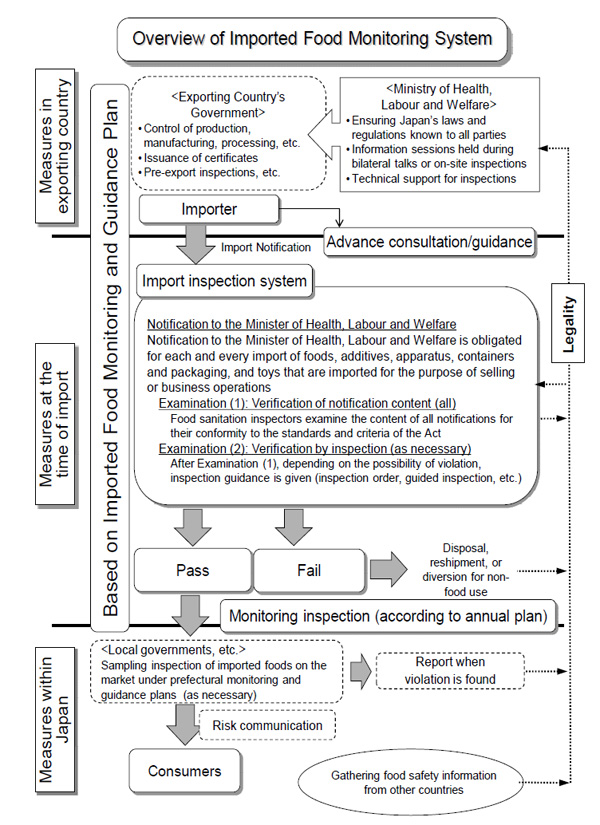
2. Results of Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY 2016
To ensure the safety of imported foods, measures have been taken as described below by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and at quarantine stations based on the fundamental approach stipulated by Article 4 of the Food Safety Basic Act that necessary measures for ensuring the safety of food shall be taken appropriately at each stage of food supply processes from production, manufacturing and processing in the exporting country to post-import domestic distribution.
(1) Examination of import notification in accordance with the provisions of Article 27 of the Act

Examination of notifications using
computer system
An examination on compliance with the Act was made primarily with the standards and criteria for foods under the provisions of Article 11 (1) and Article 18 (1) of the Act (hereinafter, “standards and criteria”), and inspections were carried out as required based on import notifications made under the provisions of Article 27 of the Act.
The number of import notifications made in FY 2016 was 2,338,765, and the weight of notified items was 32,300,000 tons. Among these imported notifications, inspections were carried out on 195,580 cases, of which 773 cases (running total of 803) were confirmed to be in violation of the Act, and steps were taken for their reshipment, disposal, etc. These accounted for 0.03% of the number of notifications (Table 1).
(2) Monitoring in accordance with the provisions of Article 28, paragraph 1 of the Act

Sampling at warehouse
Monitoring inspection is conducted for the purpose of broadly monitoring the safety status of various imported foods. In order to conduct intensive, effective and efficient monitoring, inspection numbers and inspection items are specified taking into account previous importation data and violation rates of each food type, ensuring the inspection number required to enable detection of violations to a certain degree of statistical reliability.
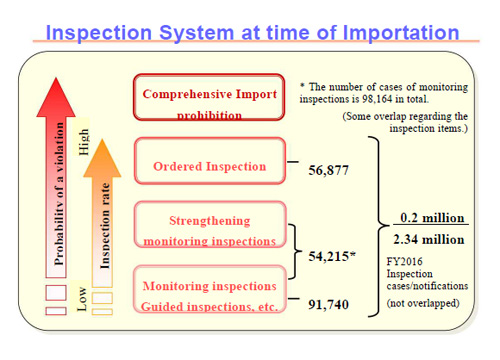
In FY 2016, monitoring inspection was conducted for 54,215 cases (98,164 cases compared to the planned cumulative total of 95,929 cases (implementation rate: approximately 102%)), and of which, 131 cases (running total of 136 cases) were confirmed to be in violation of the Act (Table 2), and steps were taken for recall, disposal, etc.
For foods found to be violating the Act during monitoring inspection, in order to grasp the management state of the exporting country, inspection was carried out by raising the inspection rate for the same exporting country and the same food type to 30% as necessary, and the monitoring system was changed to normal for cases where the possibility of foods in violation of the Act being imported is low (no cases of similar violation have been found after 1 year has elapsed since the date of starting the enhanced monitoring inspections or after carrying out inspections for 60 cases at least) (Table 3). Additionally, when a certain food of a certain country was found to be violating the Act multiple times pertaining to agricultural chemical residues or veterinary drug residues, the food was then subject to ordered inspection upon each and every importation for having a high probability of violation of the Act (Table 4). For foods in which chemicals feared to have adverse health effects (e.g., aflatoxin) were detected, inspection was immediately enhanced as subjects of ordered inspection (Table 5).
Regarding the inspection of agricultural chemical residues in processed food started in response to the cases of agricultural chemical poisoning due to frozen dumplings produced in China that occurred in January 2008, inspections were carried out on 11,065 cases in FY 2016 and no violation was found.
(3) Ordered inspection in accordance with the provisions of Article 26, paragraph 3 of the Act
In order to prevent harm to public health, subject countries and regions, foods and items of inspection have been specified, and ordered inspections have been carried out under the provisions of Article 26, paragraph 3 of the Act for imported foods that are considered to have a high probability of violating the Act.
As of March 31, 2017, 17 items from all exporting countries, and 69 items from 31 countries and 1 region were made subject to ordered inspection, and inspection was carried out for 56,877 cases (running total of 86,629 cases) in FY 2016. Of which, 235 cases (running total of 235 cases) were found to be in violation of the Act (Table 6), and steps were taken for re-shipment or disposal, etc.
(4) Violations
Breaking down violations by provision, 471 cases violated Article 11 of the Act (e.g., compositional standards for food (microbial, agricultural chemical residues, and veterinary drug residues) and standards for the use of additives in food), 206 cases violated Article 6 (e.g., adhesion of hazardous or toxic substances such as aflatoxin), 50 cases violated Article 18 (standards for apparatus or containers and packaging), 41 cases violated Article 10 (use of undesignated additives), 5 cases violated Article 9 (absence of health certificates of meat), which relates to health certificates of meat, and 2 cases violated Article 62 (mutatis mutandis application), which relates to criteria for toys (Table 7).
Breaking down violations by inspection type, violations of standards on microbes in frozen foods, etc., were found in 190 cases (24.6%) (Table 8-1), violations relating to existence of hazardous or toxic substances and contamination with pathogenic microbes in 176 cases (22.8%) (Table 8-2), violations of standards on agricultural chemical residues in 120 cases (15.5%) (Table 8-3), violations relating to the use of undesignated additives and violations of criteria on the use of additives in 108 cases (14.0%) (Table 8-4), violations on standards of apparatus, containers and packaging in 50 cases (6.5%) (Table 8-5), violations relating to decay and deterioration (e.g., generation of unpleasant smell or mold) in 46 cases (6.0%) (Table 8-6), violations of standards on veterinary drug residues in 44 cases (5.7%) (Table 8-7), and other violations in 42 cases (5.4%) (Table 8-8).
1. Violations of standards on microbes (Table 8-1)
By country, the rankings were China with 58 cases (28.9%), followed by Thailand with 26 cases (12.9%), and Vietnam with 22 cases (10.9%). The principle item in violation in these cases were microbial criteria (bacterial count, coliform bacteria, E. coli) as an index of contamination for frozen food with 139 cases (69.2%).
2. Violations relating to existence of hazardous or toxic substances and contamination with pathogenic microbes (Table 8-2)
By country, the rankings were China and the USA with 47 cases (26.7%), followed by Italy with 16 cases (9.1%). The principle violation in these cases was adhesion of aflatoxin to peanuts in the USA and China, and detection of cyanides in pastry in Italy.
The most common material responsible for these violations was mycotoxin (aflatoxin) in 145 cases (82.4%), followed by cyanides in 12 cases (6.8%), and radioactive materials in 8 cases (4.5%). By product, the rankings were peanuts (including processed peanut products) with 72 cases (41.0%), followed by almonds (including processed almond products) and maize with 12 cases (6.8%).
3. Violations of standards on agricultural chemical residues (Table 8-3)
By country, the rankings were China with 26 cases (21.3%), followed by Venezuela with 15 cases (12.3%), and Ecuador with 10 cases (8.2%). The principle material responsible for violations in China was thiamethoxam in onion, and 2,4-D in cacao beans was responsible for all violations in Venezuela, while it was the principle material responsible for violations in Ecuador.
By product, the rankings were cacao beans with 32 cases (26.2%), followed by sesame seeds with 18 cases (14.8%), and onion and kiwi with 5 cases (4.1%).
4. Violations relating to the use of undesignated additives and violations of criteria on the use of additives (Table 8-4)
By country, the rankings were China with 27 cases (24.5%), followed by the USA with 11 cases (10.0%), and France and Vietnam with 7 cases (6.4%). The principle violation was the use of undesignated additives (cyclamic acid) in pastry and excessive sulfur dioxide residues in salt storage vegetables in China, the use of undesignated additives (TBHQ) in biscuits in the USA, the use of undesignated additives (potassium aluminum silicate) in chocolates in France, and excessive sulfur dioxide residues in seasoned dried products (fishes) and fruit preparations in Vietnam.
The principle materials responsible for violations relating to the use of undesignated additives were TBHQ in 16 cases (14.5%), followed by cyclamic acid in 11 cases (10.0%), and coloring agents (azorubine, quinoline yellow) in 6 cases (5.5%). The principle materials responsible for violations of criteria on the use of additives were sulfur dioxide in 39 cases (35.5%), followed by sorbic acid in 13 cases (11.8%), and sodium copper chlorophyllin in 5 cases (4.5%).
5. Violations on standards on apparatus, containers and packaging (Table 8-5)
By country, the rankings were China with 19 cases (34.5%), followed by Italy and Vietnam with 5 cases (9.1%).
6. Violations relating to decay and deterioration (e.g., generation of unpleasant smell or mold) (Table 8-6)
By country, the rankings were the USA with 14 cases (30.4%), followed by Thailand with 11 cases (23.9%), and Australia with 9 cases (19.6%). The principle product in violation in these cases was rice in the USA, rice in all cases in Thailand, and barley in Australia.
By product, the rankings were rice with 20 cases (43.5%), followed by wheat with 9 cases (19.6%), and soybeans with 7 cases (15.2%).
7. Violations of standards on veterinary drug residues (Table 8-7)
By country, the rankings were Vietnam with 35 cases (79.5%), followed by China with 4 cases (9.1%), and India with 3 cases (6.8%). The principle material responsible for violations in these cases was enrofloxacin in shrimp in Vietnam, methylene blue in eels, leucomalachite green in shrimp and enrofloxacin in softshell turtle and large yellow croaker in China, and furazolidone was responsible for all violations in shrimp in India.
By product, the rankings were shrimp with 32 cases (72.7%), followed by squid with 4 cases (9.1%), and thread-sail filefish with 3 cases (6.8%).
8. Other violations (Table 8-8)
The principle violations in other violation cases were violation of compositional standards for food additives in 15 cases, violation of compositional standards in mineral water in 11 cases, and detection of genetically modified papaya that has not undergone safety assessment in 6 cases.
(5) Comprehensive import ban in accordance with the provisions of Article 8, paragraph 1 or Article 17, paragraph 1 of the Act
When the violation of the Act is at a considerable degree and when deemed necessary for preventing occurrence of harm, the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare may ban the import or sale of specific foods from specific countries without requiring an inspection (comprehensive import ban).
According to the “Guidelines for the Banning of the Sale or Import of Specific Foods under Article 8 (1) and Article 17 (1) of the Food Sanitation Act” (SHOKUHATSU No. 0906001 dated September 6, 2002), request for improvement is made to the exporting country, etc., and investigation, etc., on the status of sanitation control in the exporting country is conducted for imported foods that exceed a 5% violation rate in the last 60 ordered inspections. As a result, in FY 2016, no foods were subject to such measures.
(6) Emergency measures based on information from overseas on food safety issues
The monitoring system at the time of importation has been enhanced and investigation into domestic distribution has been carried out, and appropriate measures including recalls of distributed goods and suspension of import notification were ordered after confirming a record of their import (Table 9), including possible contamination of frozen vegetable and frozen fruit with Listeria monocytogenes in the USA, possible contamination of gracilaria with Salmonella in the USA, and a fraudulent act in meat inspection for chicken meat in Brazil. The investigation was based on information on the overseas outbreaks of food poisoning or recall of food products in violation of laws that has been collected by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, the National Institute of Health Sciences, and the Food Safety Commission of Japan.
(7) Promotion of safety measures in exporting countries
1. Bilateral consultations and on-site inspection (Table 10)
Information on products in violation of the Act has been provided to the governments of exporting countries where the products were made subject to ordered inspection or enhanced monitoring inspections, and further, requests have been made through bilateral consultations for investigations into the causes of violations and for taking measures to prevent the recurrence of such violations. As a result of bilateral consultations, it was confirmed that recurrence prevention measures have been established in Taiwan for foods in which recycled waste oil was used.
To confirm the adequacy of safety measures during the production and processing stages in the exporting country, with regards to, for example, observance of the Japan export verification program for beef (as a measure against bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)) and promotion of sanitary measures in exporting countries relating to agricultural chemical residues, specialists were dispatched to carry out on-site inspection, etc., as necessary.
For Irish, Canadian, Swedish, American and Polish beef, observance of the Japan export verification program was confirmed by on-site inspection as a regular audit at facilities authorized for export to Japan.
For Filipino mango, in response to the cause unfolding and recurrence prevention measures on the agricultural chemical residues presented by the Filipino government, on-site inspection was carried out. As a result, it was confirmed that the cause was unfolded and recurrence prevention measures have been taken, and relevant exporters were re-registered as exporters exempted from ordered inspections.
For Paraguayan sesame seeds, in response to the cause unfolding and recurrence prevention measures on the agricultural chemical residues presented by the Paraguayan government, on-site inspection was carried out.
For South Korean flounders, on-site inspection was carried out in order to talk about measures pertaining to Kudoa septempunctata.
2. Inspections of exporting countries (Table 11)
To prevent occurrence of safety issues, information gathering has been systematically conducted as part of an investigation on safety measures in exporting countries, and on-site inspections have been carried out where necessary.
In FY 2016, inspections were carried out for India, Singapore, Norway and Malaysia into initiatives taken by the national government, producers and manufacturers of the exporting countries.
Along with the inspections, seminars on the import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan were held targeting government officials and/or food suppliers.
3. The Japan-China Food Safety Promotion Initiative
In May 2010, the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan and the Minister of General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (AQSIQ) of the People’s Republic of China signed a memorandum of understanding on the Japan-China Food Safety Promotion Initiative. As a result, the first ministerial meeting was held and working-level consultations and field studies were conducted. Both parties determined that bilateral exchange and cooperation should continue to be promoted in the field of safety for food exports and imports between the two countries.
For FY 2016, a working-level consultation was held, and the Chinese side provided an explanation on the sanitary measures for exported foods. The Japanese side requested the Chinese side to take effective and practical preventive measures in cooperation with agencies related to China’s domestic and exported food sanitation measures regarding aflatoxin in peanuts, agricultural chemical residues and shellfish poisons in bivalves and agricultural chemical residues in oolong tea and edamame, and to continue to ensure the safety of foods exported to Japan.
More details on the results, etc., of the Japan-China Food Safety Promotion Initiative are posted at the URL below.
4. Technical cooperation
In order to take measures against agricultural chemical residues in sesame seeds in Paraguay, in addition to dispatching long-term service specialists, specialists were dispatched from quarantine stations during the period from June 18 to July 4, 2016.
In order to provide support in establishing a system to swiftly gather and analyze information and to take measures for any food safety-related problems in Indonesia, long-term service specialists have been dispatched since August 2016.
Additionally, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, quarantine stations, quarantine and inspection centers for imported foods, etc., accepted trainees from governmental agencies of exporting countries and provided explanations on the import food monitoring systems, etc., in Japan, and exchanged opinions.
(8) Guidance on implementation of voluntary safety management by importer

Seminar at a Quarantine
Quarantine stations are to promote voluntary safety management of imported foods through seminars and pre-import guidance (import consulting), based on the Monitoring and Guidance Plan.
In FY 2016, a total of 88 seminars were held at training courses and workshops held by quarantine stations in Japan and related organizations, to which a total of 2,669 people attended.
Additionally, pre-import guidance (import consulting) was conducted for 24,180 cases, of which 410 cases (running total of 489 cases) were identified as not compliant with the Act (Table 12).
Breaking down the pre-import guidance (import consulting) cases which were not compliant with the Act by provision, 223 cases violated Article 11 of the Act, 210 cases violated Article 10, and 1 case violated Article 62 (Table 13).
By country, the rankings of violation cases were the USA with 87 cases (17.8%), followed by France with 60 cases (12.3%), and Italy with 38 cases (7.8%) (Table 14).
Where the pre-import guidance (import consulting) determined non-compliance with the Act, appropriate measures were taken to ensure compliance, and guidance was given to suspend import until improvements were made. After improvements were made and documentation demonstrating compliance with the Act was provided, guidance was given as necessary to confirm in advance the fulfillment of standards and criteria for said foods by, for instance, carrying out inspections.
In regard to undesignated additives (Article 10 of the Act), the number of violation cases identified at the time of importation was 41, while the number of non-compliance cases identified during pre-import guidance (import consulting) was 210, indicating that pre-import guidance (import consulting) promoted voluntary safety management by importers and prevented import of foods that violate the Act.
(9) Disclosure of information on violations of imported foods, and cooperation with prefectures
For cases violating the Act, details including the names of importers and imported foods in violation of the Act were published on the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare website, based on the provisions of Article 63 of the Act, in order to clarify the harm in terms of the food sanitation. The content of improvement measures, the cause of the violation, and the status of measures taken to rectify the matter (e.g., disposal) were published as identified.
For imported foods that were identified to be in violation of the Act during inspection at the time of importation yet had already passed customs, the relevant importer was instructed to promptly recall such imported foods in cooperation with the relevant prefectural governments.
When imported foods already on the domestic market were identified to be in violation of the Act during inspections by prefectural governments, the inspection system at the time of importation was enhanced as necessary (Table 15).
(10) Provision of information to the people
Regarding risk communication on the safety of foods, in January 2017, in Tokyo and Osaka, Japan, information was provided to consumers, food business operators, etc., about the situation of guidance on monitoring of imported foods, content of the Monitoring and Guidance Plan, etc., and opinions were exchanged.
| Notifications (cases) |
Imported Weight (thousand tons) |
Inspections*1 (cases) |
Proportion*2 (%) |
Violations (cases) |
Proportion*2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2,338,765 | 32,300 | 195,580 (56,877)*3 |
8.4 | 773 (235)*3 |
0.03 (0.41)*3 |
| (FY 2015) 2,255,019 |
31,900 | 195,667 | 8.7 | 858 | 0.04 |
*1 Inspections by authorities, registered inspection organizations and foreign official laboratories, deducting duplicates.
*2 Proportion as compared to notifications.
*3 Number of ordered inspections.
| Food Groups | Inspected Substances*1 | Planned Number in FY | Actual Number | Violations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Livestock Foods Beef, pork, chicken, horse meat, other poultry meat, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. | 1,879 | 2,008 | 1 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals | 1,191 | 1,658 | 0 | |
| Additives | 118 | 135 | 0 | |
| Pathogenic microorganisms | 657 | 644 | 0 | |
| Standards for constituents | 415 | 373 | 0 | |
| Radiation irradiation | 29 | 29 | 0 | |
| Removal of SRMs | - | 2,326 | 5 | |
| Processed Livestock Foods Natural cheeses, processed meat products, ice cream, frozen (meat) products, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. | 2,182 | 2,218 | 0 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals | 1,697 | 1,807 | 0 | |
| Additives | 1,247 | 1,400 | 1 | |
| Pathogenic microorganisms | 3,584 | 3,649 | 0 | |
| Standards for constituents | 1,937 | 2,171 | 3 | |
| Mycotoxins | - | 3 | 0 | |
| Aquatic Foods Bivalves, fish, crustacea(shrimps, crabs), etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. | - | 2 | 2 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals | 2,572 | 2,750 | 3 | |
| Additives | 1,134 | 1,905 | 1 | |
| Pathogenic microorganisms | 297 | 311 | 0 | |
| Standards for constituents | 1,074 | 1,431 | 0 | |
| Radiation irradiation | 354 | 357 | 0 | |
| Processed Aquatic Foods Processed fish products (fillet, dried or minced fish, etc.), Frozen food(aquatic animals, fish), processed marine product eggs, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. | 34 | 31 | 0 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals | 4,234 | 4,919 | 5 | |
| Additives | 4,111 | 4,941 | 0 | |
| Pathogenic microorganisms | 1,894 | 2,278 | 0 | |
| Standards for constituents | 4,661 | 4,928 | 1 | |
| Radiation irradiation | 4,930 | 4,879 | 36 | |
| Agricultural foods Vegetables, fruit, wheat, maize, pulses, peanuts, nuts, seeds, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. | - | 7 | 0 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals | 2,559 | 3,085 | 1 | |
| Additives | 9,190 | 10,112 | 30 | |
| Pathogenic microorganisms | 474 | 499 | 0 | |
| Standards for constituents | 1,495 | 1,353 | 0 | |
| Mycotoxins | 355 | 416 | 0 | |
| Genetically modified food | 2,273 | 2,360 | 1 | |
| Radiation irradiation | 469 | 454 | 0 | |
| Processed agricultural food Frozen food(vegetables), processed vegetable products, processed fruit products, spice, instant noodles, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. | 119 | 143 | 0 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals | 598 | 716 | 0 | |
| Additives | 6,800 | 8,076 | 11 | |
| Pathogenic microorganisms | 4,551 | 5,273 | 2 | |
| Standards for constituents | 956 | 1,550 | 1 | |
| Mycotoxins | 2,648 | 3,087 | 9 | |
| Genetically modified food | 2,774 | 2,915 | 3 | |
| Radiation irradiation | 252 | 312 | 0 | |
| Other foods Health foods, soups, seasonings, confectionery, cooking oil and fat, frozen food, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. | 424 | 436 | 0 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals | - | 2 | 0 | |
| Additives | 1,074 | 1,155 | 0 | |
| Standards for constituents | 3,344 | 3,492 | 3 | |
| Mycotoxins | - | 5 | 0 | |
| Genetically modified food | 598 | 465 | 5 | |
| Radiation irradiation | 955 | 1,102 | 0 | |
| Beverages Mineral waters, soft drinks, alcoholic drinks, etc. |
Residual agricultural chemicals | - | 6 | 0 |
| Additives | 118 | 156 | 0 | |
| Standards for constituents | 1,075 | 1,231 | 0 | |
| Mycotoxins | 657 | 659 | 1 | |
| Genetically modified food | 178 | 169 | 0 | |
| Additives / Apparatus, containers and packaging / Toys | Standards for constituents | 1,762 | 1,775 | 11 |
| Total (gross) | 95,929※2 | 98,164 Implementation rate of 102% |
136※3 | |
※1:Examples of inspected substances
- ・Antibacterial substances, etc.: antibiotics, synthetic antimicrobials, hormone drugs, etc.
- ・Residual agricultural chemicals: organophosphorous, organochlorine, carbamates, pyrethroid, etc.
- ・Additives: preservatives, coloring agents, sweeteners, antioxidants, antimold agents, etc.
- ・Pathogenic microorganisms : enterohemorrhagic E.coli O26, O103, O104, O111, O121, O145 and O157, Listeria monocytogenes etc.
- ・Standards for constituents, etc.: Items stipulated in the standards for constituents (bacterial count, coliform bacteria, etc.), shellfish poisons (diarrhetic shellfish poison and paralytic shellfish poison), etc.
- ・Mycotoxin: aflatoxin, deoxynivalenol, patulin, etc.
- ・Genetically modified organisms (GMOs): genetically modified foods, etc. that have not been assessed for safety.
- ・Radiation irradiation: with or without of irradiation
※2:10,000 cases of the total cases planned for the FY were part of enhanced monitoring.
※3:Total number of item-by-item inspections
| Country/Region | Subject Food | Inspected Substances |
|---|---|---|
| China | Asparagus | Ametryn |
| Green soybeans | Paclobutrazol | |
| Taro(limited to Colocasia esculenta) | Chlorpyrifos | |
| Ginger | Thiamethoxam | |
| Flowering fern | Acetochlor | |
| Rape flower | Haloxyfop | |
| Chinese chive | Triazophos, metalaxyl and mefenoxam | |
| Garlic sprouts | Chlorpyrifos | |
| Welsh onions | Tebufenozide | |
| Hard clam | Prometryn | |
| Spinach | Indoxacarb | |
| Matsutake mushroom | Chlorpyrifos | |
| Eel | Pendimethaline, Methylene blue | |
| Cultured shrimp | Furazolidone, Malachite green | |
| Large yellow croaker | Enrofloxacin | |
| Lychees | 4-CPA, Diflubenzuron | |
| India | Cardamom immature fruit | Triazophos |
| Cumin seeds | Iprobenfos | |
| Egg | Enrofloxacin | |
| Chickpea | Aflatoxin, Glyphosate | |
| Fenugreek seeds | Aflatoxin | |
| Fennel seed | Iprobenfos, Profenofos | |
| Thailand | Red hot pepper | Triazophos, Propiconazole |
| Shrimp (for raw consumption) | Vibrio parahaemolyticus (MPN)*2 | |
| Okra | Imidacloprid, Pyridaben | |
| Coriander | Profenofos | |
| Fresh lime leaves | Profenofos | |
| Balsam pear | Metalaxyl and mefenoxam | |
| Vietnam | Green hot pepper | Difenoconazole, Propiconazole |
| Red hot pepper | Difenoconazole | |
| Shrimp | Oxytetracycline, Chloramphenicol | |
| Bee larva | Oxytetracycline | |
| Cultured shrimp | Sulfamethoxazole | |
| Philippines | Sea urchin (for raw consumption) | Vibrio parahaemolyticus (MPN)*2 |
| Banana | Imidacloprid, Cypermethrin | |
| Papaya | Cypermethrin | |
| Mango | Azoxystrobin | |
| Italy | Chestnut | Aflatoxin |
| Corns | Aflatoxin | |
| Pistachio processed products | Aflatoxin | |
| Ecuador | Cacao beans | Diuron, Pyrimethanil, Malathion |
| South Korea | Ark shell (for raw consumption) | Vibrio parahaemolyticus (MPN)*4 |
| Perilla | Diniconazole | |
| Freshwater clam | Endosulfan | |
| Chile | Grape | Profenofos |
| Grape leaves | Indoxacarb | |
| Blueberry | Streptomycin | |
| France | Parsnip | Cyprodinil |
| Pigeon meat | Oxytetracycline | |
| Apple juice and Apple juice concentrate | Patulin | |
| U.S.A. | Corns (popcorn only) | Pirimiphos-methyl |
| Chicken | Ethoxyquin | |
| Propolis | Chloramphenicol | |
| Australia | Rape or colza seeds | Fenitrothion |
| Apple juice and Apple juice concentrate | Patulin | |
| Guana | Cacao beans | Imidacloprid, Chlorpyrifos |
| Spain | Processed almond products | Aflatoxin |
| Pistachio processed products | Aflatoxin | |
| Nepal | Red pepper | Ethion, Triazophos |
| Belgium | Chicory | Metalaxyl and mefenoxam |
| Parsnip | Difenoconazole | |
| Argentina | Chia seed | 2,4-D |
| Iran | Pistachio | Imidacloprid |
| United Kingdom | Parsnip | Tebuconazole |
| Egypt | Calendula (Calendula officinalis) | Profenofos |
| Austlia | Horseradish | Difenoconazole |
| Netherlands | Cabbage | Pencycuron |
| Canada | Propolis | Chloramphenicol |
| Greece | Honey | Coumaphos |
| Costa Rica | Banana | Gibberellin |
| Colombia | Cacao beans | Fipronil |
| Syria | Pistachio processed products | Aflatoxin |
| Taiwan | Carrot | Acephate |
| Pakistan | Rose Petal | Triazophos |
| Brazil | Mango | Cypermethrin |
| Peru | Quinoa | Fipronil |
| Bolivia | Chia seed | 2,4-D |
| South Africa | Grapefruit | Epoxiconazole |
| Mexico | Immature kidney beans | Flonicamid |
| Mozambique | Sesame seed | 2,4-D |
| Morocco | Chaste tree berries(Vitex agnus-castus) | Aflatoxin |
| Rumania | Egg | Furazolidone |
*1 Include the Items which were rescinded from inspection orders. Exclude items which were moved to inspection orders.
*2 Item which all (100%) import declarations were inspected as a measure to enhance inspections during the summer period, (Jun-Oct 2016).
*3 Item which 30% of import declarations were inspected as a measure to enhance inspections during the summer period, (Jun-Oct 2016)
| Country/Region | Subject Food | Inspected Substances |
|---|---|---|
| China | Cumin seeds | Profenofos |
| Immature peas | Diniconazole | |
| Egypt | Calendula (Calendula officinalis) | Chlorpyrifos |
| South Korea | Oriental melon | Chlorfenapyr |
| Spain | Non glutinous rice | Tebuconazole |
| Thailand | Boiled crab (manufactures limited) | Vibrio parahaemolyticus |
| Chile | Kiwi fruit | Fenhexamid |
| USA | Celery | Bifenthrin |
| Vietnam | Shrimp | Sulfadiazine |
| Peru | Cacao beans | 2, 4-D |
| Country/Region | Subject Item | Inspected Substances |
|---|---|---|
| South Korea | Kimchi(manufactures limited) | Enterohemorrhagis Escherichia coliO103 |
| Cultured olive flounder (culturing farm limited) | Kudoa septempunctata | |
| China | Foods (manufactures limited) | Cyclamic acid |
| Lotus seeds | Aflatoxin | |
| Turkey | Dried apple | Aflatoxin |
| Pistachio processed products | Aflatoxin | |
| France | Soft or semi-hard natural cheese (manufactures limited) | Listeria monocytogenes |
| Country/Region | Major subject foods | Major Inspected Substances | Inspections | Violations | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Exporting Countries (17 items) |
Dried figs, Chili peppers, Nuts, Mixed spices, Peanuts | Aflatoxin | 11,759 | 106 | |
| Manioc, beans containing cyanide | Cyanide | 399 | 3 | ||
| Salted salmon roe | Nitrite | 278 | 0 | ||
| Pufferfish | Identification of fish species | 0 | 0 | ||
| China (15 items) |
Vegetables(green soybeans, onion, spinach etc.), Lychees, Oolong tea, Cumin seed | Diflubenzuron, Thiamethoxam, Fipronil, Difenoconazole, etc. | 19,465 | 11 | |
| Bivalve | Paralytic shellfish poison, Diarrhetic shellfish poison | 9,432 | 0 | ||
| Eel, Soft-shelled turtle, Hard clam | Enrofloxacin, Oxolinic acid, Sulfadimidine, Prometryn | 3,115 | 4 | ||
| All processed products | Cyclamic acid | 829 | 0 | ||
| Lotus seed | Aflatoxin | 8 | 0 | ||
| Thailand (7 items) |
Vegetables(okra, green asparagus etc.), Fruits (mango, banana etc.) |
Chlorpyrifos, Cypermethrin, Propiconazole, EPN, etc. | 2,253 | 0 | |
| Boiled crab | Vibrio parahaemolyticus (MPN) | 32 | 0 | ||
| India (7 items) |
Cultured shrimp | Furazolidone | 1,508 | 3 | |
| Cumin seed, Chili peppers, Chickpea, Black tea | Glyphosate, Triazophos, Profenofos, Hexaconazole | 200 | 5 | ||
| Cassia torea, Fenugreek seed | Aflatoxin | 168 | 3 | ||
| South Korea (6 items) |
Bivalves | Paralytic shellfish poison, Diarrhetic shellfish poison | 130 | 0 | |
| Chili pepper, Tomatos, Paprika, Cherry tomatos | Chlorpyrifos, Fluquinconazole, | 77 | 0 | ||
| Cultured olive flounder | Enrofloxacin, Oxytetracycline | 6 | 0 | ||
| Italy (5 items) |
Pistachio, Processed almond products | Aflatoxin | 417 | 2 | |
| Non glutinous rice | Pirimiphos-methyl | 31 | 0 | ||
| Natural cheese | Listeria monocytogenes、Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O26 | 25 | 1 | ||
| USA (4 items) |
Corns, Pistachio | Aflatoxin | 2,966 | 13 | |
| Celery | Bifenthrin | 395 | 2 | ||
| Other (23 countries and 1 region ; total 35 items) | 33,128 | 82 | |||
| Total | (Gross)*1 (Actual) *2 |
86,629 56,877 |
235 235 |
||
*1 Gross number of inspection cases by inspected substances.
*2 Number of notification cases for which inspections were carried out
| Provision violated | Violations (cases) | Proportion(%) | Brief details of Violation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Article 6 (Foods and additives prohibited to distribute) |
206(Gross) 206(Actual) |
25.7 | Aflatoxin contamination in almonds, dried fig, walnut, cassia seed, spice, sesami seed, chia seeds, corns, lotus seeds, job's tears, pistachio, brazil nuts, dried apple, peanut, etc.; detection of cyanide from seeds of flax, cassava, etc; detection of Enterohemorrhagis Escherichia coli from kimchi; detection of methanol from brandy; decay, deterioration and fungus formation due to accidents during the transport of barley, rice, coffee bean, wheat, soybeans, etc. |
| Article 9 (Limitation on distribution, etc. of diseased meat) |
5(Gross) 5(Actual) |
0.6 | No health certificate attached |
| Article 10 (Limitation of distribution, etc. of additives) |
42(Gross) 41(Actual) |
5.2 | Use of unspecified additives such as TBHQ, Azorubin, Dipotassium inosinate, Quinoline Yellow, dipotassium guanylate, Potassium aluminium silicate, Cyclamic acid, Sodium ethoxide, Potassium iodate, carbon monoxide. |
| Article 11 (Standards and criteria for foods and additives) |
493(Gross) 471(Actual) |
61.4 | Violation of standards for constituents for vegetables or frozen vegetables (excess of standards on residual agricultural chemicals), violation of standards for constituents for animal foods, aquatic foods and processed products (excess of standards on residual veterinary drugs, excess of standards on residual agricultural chemicals), violation of standards for constituents for other processed products (coliform bacteria test, etc.), violation of criteria on use of additives (sucralose, sorbic acid, SO₂ etc.), and violation of standards for constituents for additives, detection of radioactive substance, detection of genetically modified food that has not undergone safety assessment. |
| Article 18 (Standards and criteria for apparatus, containers and packaging) |
55(Gross) 50(Actual) |
6.8 | Violation of materials standards for raw materials |
| Article 62 (Mutatis mutandis application for toys) |
2(Gross) 2(Actual) |
0.2 | Violations of standards for toys |
| Total | 803(Gross) *1 773(Actual) *2 |
||
*1 Gross number of inspection cases by inspected substances.
*2 Number of notification cases for which inspections were carried out
| Country of production | Item category | Violation details | Cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Frozen food (fish) | Bacterial count (5), Coliform bacteria (3), E.coli (2) | 58 |
| Frozen food (vegetable) | Coliform bacteria (3), E.coli (3), Bacterial count (2) | ||
| Frozen food (shellfish) | Bacterial count (4), Coliform bacteria (3) | ||
| Fish paste product | Coliform bacteria (5) | ||
| Frozen food (squid) | E.coli (3), Bacterial count (2) | ||
| Frozen food (marine animal) | Bacterial count (2), Coliform bacteria (2) | ||
| Frozen food (other foods) | Bacterial count (2), Coliform bacteria, E.coli | ||
| Hermetically packaged, Pressure and heat sterilized food product | Possible microbes (4) | ||
| Frozen food (meat) | Coliform bacteria (2), E.coli | ||
| Heat processed meat product | Coliform bacteria, E.coli | ||
| Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption | Bacterial count, Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen food (shrimp) | Bacterial count | ||
| Frozen food (bean) | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Boild crab | Bacterial count | ||
| Boild octopus | Bacterial count | ||
| Thailand | Frozen food (squid) | Coliform bacteria (4), Bacterial count (2) | 26 |
| Frozen food (shrimp) | Coliform bacteria (4), E.coli (2) | ||
| Frozen food (vegetable) | Bacterial count (4), Coliform bacteria (2) | ||
| Frozen food (fish) | Coliform bacteria, E.coli | ||
| Fish paste product | Coliform bacteria (2) | ||
| Ice milk | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen food (grain) | E.coli | ||
| Frozen food (fruit) | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Vietnam | Frozen food (shrimp) | Coliform bacteria (4), Bacterial count (2), E.coli (2) | 22 |
| Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption | Coliform bacteria (3), Bacterial count | ||
| Frozen food (vegetable) | Coliform bacteria (2), Bacterial count | ||
| Frozen food (other foods) | Bacterial count, E.coli | ||
| Frozen food (fish) | E.coli | ||
| Fish paste product | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen food (shellfish) | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen food (squid) | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Hermetically packaged, Pressure and heat sterilized food product | Possible microbes | ||
| Philippines | Frozen food (fruit) | Coliform bacteria (6), Bacterial count | 15 |
| Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption | Bacterial count (2), Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen food (fish) | Coliform bacteria (3) | ||
| Boild octopus | Coliform bacteria (2) | ||
| Italy | Flavoured Ice | Bacterial count (2), Coliform bacteria | 12 |
| Frozen food (other foods) | Coliform bacteria (2), Bacterial count | ||
| Powdered soft drink | Bacterial count、Coliform bacteria | ||
| Ice milk | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Ice cream with milk-solids | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen food (vegetable) | E.coli | ||
| Mineral water | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Indonesia | Frozen food (shrimp) | E.coli (4), Bacterial count (2), Coliform bacteria | 12 |
| Frozen food (fish) | E.coli | ||
| Boild octopus | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen food (vegetable) | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Powdered soft drink | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Fruits juice for raw material | Coliform bacteria | ||
| South Korea | Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption | Coliform bacteria (2), Bacterial count | 12 |
| Boild crab | Bacterial count (2) | ||
| Frozen food (other foods) | Coliform bacteria (2) | ||
| Powdered soft drink | Bacterial count (2) | ||
| Frozen food (fish) | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen food (marine animal) | Bacterial count | ||
| Hermetically packaged, Pressure and heat sterilized food product | Possible microbes | ||
| Taiwan | Frozen food (vegetable) | Bacterial count (2), Coliform bacteria (2) | 10 |
| Hermetically packaged, Pressure and heat sterilized food product | Possible microbes (2) | ||
| Ice cream with milk-solids | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen food (other foods) | Bacterial count | ||
| Flavoured Ice | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Powdered soft drink | Coliform bacteria | ||
| India | Frozen food (grain) | Bacterial count, E.coli | 4 |
| Frozen food (vegetable) | E.coli | ||
| Frozen food (other foods) | Bacterial count | ||
| Netherlands | Frozen food (other foods) | Coliform bacteria (3), Bacterial count | 4 |
| France | Heat processed meat product | E.coli | 4 |
| Ice cream | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Frozen food (other foods) | Bacterial count | ||
| Soft drink | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Australia | Frozen food (vegetable) | Bacterial count (2) | 3 |
| Frozen food (fruit) | Bacterial count | ||
| Peru | Frozen food (fruit) | Bacterial count, Coliform bacteria | 3 |
| Frozen food (vegetable) | Bacterial count | ||
| Malaysia | Frozen food (shrimp) | Coliform bacteria | 3 |
| Frozen food (squid) | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Instant coffee | Coliform bacteria | ||
| Spain | Powdered soft drink | Bacterial count | 2 |
| Frozen food (vegetable) | E.coli | ||
| USA | Soft drink | Coliform bacteria | 2 |
| Frozen food (grain) | Bacterial count | ||
| United Kingdom | Boild crab | Bacterial count | 1 |
| Switzerland | Powdered soft drink | Bacterial count | 1 |
| Germany | Powdered soft drink | Bacterial count | 1 |
| Turkey | Frozen food (vegetable) | E.coli | 1 |
| Japan | Frozen food (other foods) | Coliform bacteria | 1 |
| Brazil | Fruits juice for raw material | Coliform bacteria | 1 |
| Belgium | Frozen food (grain) | E.coli | 1 |
| South Africa | Powdered soft drink | Coliform bacteria | 1 |
| Myanmar | Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption | Coliform bacteria | 1 |
| Total | (Gross) *1 | 201 | |
| (Actual) *2 | 190 |
*1 Gross number of inspection cases by inspected substances.
*2 Number of violation cases for which inspections were carried out
| Country/Region of Production | Item Category | Violation Details | Cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Peanut | Aflatoxin (44) | 47 |
| Other foods | Aflatoxin | ||
| Lotus seeds | Aflatoxin | ||
| Job's tears | Aflatoxin | ||
| USA | Peanut | Aflatoxin (17) | 47 |
| Corn | Aflatoxin (12) | ||
| Almond | Aflatoxin (6) | ||
| Pistachio nut | Aflatoxin (4) | ||
| Walnut | Aflatoxin (2) | ||
| Peanut butter | Aflatoxin (2) | ||
| Confectionery | Aflatoxin | ||
| Dried fig | Aflatoxin | ||
| Cereal flour | Cyanide | ||
| Preparations of nuts and seeds | Cyanide | ||
| Italy | Western confectionery | Cyanide (4) | 16 |
| Almond | Aflatoxin (2) | ||
| Natural cheese | Listeria monocytogenes (2) | ||
| Unheated meat product | Listeria monocytogenes (2) | ||
| Health food | Radioactive substance | ||
| Chocolate | Cyanide | ||
| Hot pepper(spice) | Aflatoxin | ||
| Unheated meat product | Salmonella spp. | ||
| Pistachio nut | Aflatoxin | ||
| Macaroni | Cyanide | ||
| Pakistan | Mixed spice | Aflatoxin (8) | 9 |
| Hot pepper(spice) | Aflatoxin | ||
| France | Fruit preparation | Radioactive substance | 7 |
| Seed paste | Aflatoxin | ||
| Natural cheese | Listeria monocytogenes | ||
| Mix powder for bread | Cyanide | ||
| Brandy | Methanol | ||
| Blueberry jam | Radioactive substance | ||
| Processed herb and spices | Aflatoxin | ||
| Indonesia | Confectionery | Cyanide (2) | 5 |
| Nutmeg | Aflatoxin (2) | ||
| Dressing | Aflatoxin | ||
| Australia | Almond | Aflatoxin | 5 |
| Almond oil | Aflatoxin | ||
| Preparations of nuts and seeds | Aflatoxin | ||
| Mixed spice | Aflatoxin | ||
| Peanut | Aflatoxin | ||
| Thailand | Job's tears | Aflatoxin (3) | 5 |
| Hot pepper processed products | Aflatoxin | ||
| Boiled crab(for raw consumption) | Vibrio Parahaemolyticus | ||
| South Africa | Peanut | Aflatoxin (5) | 5 |
| Sri Lanka | Hot pepper(spice) | Aflatoxin (2) | 4 |
| Curry powder | Aflatoxin | ||
| Cassava processed products | Cyanide | ||
| India | Cassia seed | Aflatoxin (3) | 3 |
| Finland | Dried fruits | Radioactive substance (3) | 3 |
| Iran | Dried fig | Aflatoxin (2) | 2 |
| Spain | Brandy | Methanol | 2 |
| Western confectionery | Aflatoxin | ||
| Turkey | Pistachio nut | Aflatoxin | 2 |
| Dried fig | Aflatoxin | ||
| New Zealand | Almond oil | Aflatoxin (2) | 2 |
| Laos | Job's tears | Aflatoxin (2) | 2 |
| Argentina | Peanut | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Ukraine | Blueberry | Radioactive substance | 1 |
| South Korea | Kimchi | Enterohemorrhagic E.coli O103 |
1 |
| Singapore | Peanut | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Taiwan | Peanut | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Germany | Dried apple | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Nigeria | Sesami seed | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Philippines | Boiled octopus | Vibrio Parahaemolyticus | 1 |
| Brazil | Brazil nut | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Belgium | Fruit preparation | Radioactive substance | 1 |
| Total | (Gross) *1 154 (Actual) *2 153 |
||
*1 Gross number of Itemized cases violations
*2 Item number of the consultation to be a violation of the law
| Country of Production | Item Category | Violation Details | Cases*1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Value | Uniformity Standard | |||
| China | Onion | Thiamethoxam(5) | 26 | |
| Short-neck clam | Prometryn(3) | |||
| Green soybeans | Difenoconazole(2), Paclobutrazol | |||
| Cumin | Profenofos(3) | |||
| Taro | Chlorpyrifos(3) | |||
| Snap peas | Diniconazole(3) | |||
| Eel | Pendimethalin | |||
| Garlic sprout | Chlorpyrifos | |||
| Welsh onion | Tebufenozide | |||
| Spinach | Indoxacarb | |||
| Immature pea | Diniconazole | |||
| Lychee | 4-CPA | |||
| Venezuela | Cacao bean | 2,4-D (15) | 15 | |
| Ecuador | Cacao bean | 2,4-D (6), Pyrimethanil(3), Malathion | 10 | |
| Myanmar | Sesame seed | Imidacloprid(9) | 9 | |
| India | Cumin | Profenofos(4) | Iprobenfos(IBP) | 8 |
| Cardamom | Triazophos | |||
| Hot pepper | Triazophos | |||
| Fennel | Iprobenfos(IBP) | |||
| USA | Celery | Bifenthrin(4) | 8 | |
| Cacao bean | 2,4-D (2) | |||
| Corn | Pirimiphos methyl(2) | |||
| Chile | Kiwi fruit | Fenhexamid(5) | 6 | |
| Blueberry | Streptomycin | |||
| France | Calendula | Chlorpyrifos(2) | 5 | |
| Parsnip | Cyprodinil | |||
| Grape leaves | Indoxacarb | |||
| Rose petal | Triazophos | |||
| Thailand | Okra | Pyridaben(2) | 4 | |
| Red hot pepper | Propiconazole | |||
| Coriander | Profenofos | |||
| Tanzania | Sesame seed | Imidacloprid(4) | 4 | |
| Burkina Faso | Sesame seed | Imidacloprid(4) | 4 | |
| Ghana | Cacao bean | Cypermethrin | Fenvalerate(2) | 3 |
| Iran | Pistachio nut | Imidacloprid(2) | 2 | |
| South Korea | Oriental melon | Chlorfenapyr(2) | 2 | |
| Cote d'ivoire | Cacao bean | 2,4-D (2) | 2 | |
| Spain | Non glutinous rice | Tebuconazole(2) | 2 | |
| Philippines | Banana | Cypermethrin, Imidacloprid | 2 | |
| Peru | Cacao bean | 2,4-D (2) | 2 | |
| Nepal | Hot pepper | Ethion | Triazophos | 2 |
| UAE | Oolong tea | Fipronil | 1 | |
| Costa Rica | Banana | Gibberellin | 1 | |
| Colombia | Coffee bean | Chlorpyrifos | 1 | |
| Sri Lanka | Oolong tea | Fipronil | 1 | |
| Germany | Calendula | Chlorpyrifos | 1 | |
| Paraguay | Sesami seed | Carbaryl(NAC) | 1 | |
| Total | (Gross) *1 | 122 | ||
| (Actual) *2 | 120 | |||
*1 Gross number of Itemized cases violations
*2 Item number of the consultation to be a violation of the law
| Country/Region of Production | Item Category | Violation Details | Cases* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undesignated additive | Compositional standard | |||
| China | Pickles (vegetable) | Cyclamic acid | Sucralose (2) | 27 |
| Confectionery | Cyclamic acid (3) | |||
| Instant noodles | Cyclamic acid、TBHQ | Polysorbate | ||
| Salted vegetable | Sulfur dioxide (3) | |||
| Health food | Cyclamic acid | Sulfur dioxide | ||
| Fruit in syrup | Cyclamic acid | Sulfur dioxide | ||
| Kashiwaba | Sulfur dioxide (2) | |||
| Dried vegetable | Cyclamic acid | Sulfur dioxide | ||
| Boiled vegetable | Sulfur dioxide | |||
| Seasonings | Cyclamic acid | |||
| Biscuits | TBHQ | |||
| Vegetable preparation | TBHQ | |||
| Salted mushroom | Sulfur dioxide | |||
| Dried japanese plum | Cyclamic acid | |||
| Chestnut in syrup | Sulfur dioxide | |||
| USA | Biscuits | TBHQ (5) | 11 | |
| Health food | Sodium ethoxide | Sorbic acid (2) | ||
| Vegetable protein | Sulfur dioxide | |||
| Natural cheese | Natamycin | |||
| Dried plum | Sorbic acid | |||
| France | Chocolate | Potassium aluminium silicate (3)、Quinoline Yellow | Iron sesquioxide | 7 |
| Soup | Cyclamic acid | |||
| Mix spice | Iron sesquioxide | |||
| Vietnam | Seasoning dried product of fish | Sulfur dioxide (2) | 7 | |
| Fruit preparation | Sulfur dioxide (2) | |||
| Pickles (vegetable) | Sorbic acid | |||
| Biscuits | TBHQ | |||
| Salt | Potassium iodate | |||
| India | Biscuits | Sulfur dioxide (3) | 6 | |
| Vegetable preparation | TBHQ | |||
| Frozen food (cereal) | TBHQ | |||
| Sugar | Sulfur dioxide | |||
| Belgium | Chocolate | Azorubin | Sorbic acid (3)、Copper chlorophyll, Sodium copper chlorophyllin | 6 |
| Italy | Pistachionut paste | Sodium copper chlorophyllin (2) | 5 | |
| Wine | Sorbic acid (2) | |||
| Seasonings | Sulfur dioxide | |||
| Bangladesh | Fruit juice drink | Sulfur dioxide (2)、Sorbic acid (2) | 5 | |
| Biscuits | Sulfur dioxide | |||
| Philippines | Pickles (olive) | Dipotassium inosinate、Dipotassium guanylate | 4 | |
| Unheated meat products | Sorbic acid | |||
| Seasonings | Sorbic acid | |||
| Brazil | Processed agricultural products | Sulfur dioxide | 4 | |
| Seasonings | TBHQ | |||
| Candies | TBHQ | |||
| Vinegar | Sulfur dioxide | |||
| Malaysia | Fruit juice drink | Sulfur dioxide (3) | 4 | |
| Soy sauce | Benzoic acid | |||
| Indonesia | Frozen tuna | Carbon monoxide (2) | 3 | |
| Snakes meat processed | Sulfur dioxide | |||
| Thailand | Fruit in syrup | Sulfur dioxide | 3 | |
| Fruit preparation | Sulfur dioxide | |||
| Snack food | Azorubin | |||
| Taiwan | Tapioca starch | Sulfur dioxide (2) | 2 | |
| Philippines | Biscuits | TBHQ | 2 | |
| Soup | TBHQ | |||
| Romania | Western confectionery | Sodium copper chlorophyllin (2) | 2 | |
| Russian federation | Biscuits | Azorubin | 2 | |
| Other foods | Azorubin | |||
| United Kingdom | confectionery | Iron sesquioxide | 1 | |
| Sri Lanka | Fruit juice drink | Benzoic acid | 1 | |
| Serbia | Vegetable protein | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Tajikistan | Dried apricot | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Turkey | Dried apricot | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| New Zealand | Vegetable oil | TBHQ | 1 | |
| Panama | Chili sauce | Nisin | 1 | |
| Finland | Chocolate | Quinoline Yellow | 1 | |
| South Africa | Dried apricot | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Mexico | Frozen food (fruit) | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Total | (Gross) *1 (Actual) *2 |
42 41 |
68 67 |
110 108 |
*1 Gross number of Itemized cases violations
*2 Item number of the consultation to be a violation of the law
| Country/Region of Production | Material type | Violation Details | Cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Synthetic resin | Evaporation residue(9)、Lead(2)、Antimony、Caprolactam、 Formaldehyde、Potassium permanganate consumption |
19 |
| Combination | Evaporation residue、Cadmium | ||
| Rubber | Zinc(2) | ||
| Italy | Synthetic resin | Lead、Heavy Metals | 5 |
| Metal | Lead(2) | ||
| Rubber | Zinc | ||
| Vietnam | Porcelain | Lead(3) | 5 |
| Synthetic resin | Cadmium | ||
| Combination | Lead | ||
| United Kingdom |
Synthetic resin | Evaporation residue(2)、Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (2) | 4 |
| Korea | Synthetic resin | Evaporation residue、Potassium permanganate consumption | 4 |
| Rubber | Zinc(2) | ||
| Thailand | Rubber | Zinc(2) | 3 |
| Porcelain enamel | Cadmium | ||
| Taiwan | Synthetic resin | Evaporation residue(2)、Caprolactam | 3 |
| Germany | Porcelain | Lead(2) | 3 |
| Combination | Evaporation residue | ||
| India | Synthetic resin | Evaporation residue(2) | 2 |
| Indonesia | Porcelain enamel | Cadmium(2) | 2 |
| France | Synthetic resin | Caprolactam | 2 |
| Combination | Cadmium | ||
| USA | Synthetic resin | Dibutyltin Compounds | 1 |
| Sweden | Porcelain | Cadmium | 1 |
| Malaysia | Rubber | Zinc | 1 |
| Total | (Gross) *1 | 55 | |
| (Actual) *2 | 50 | ||
*1 Gross number of Itemized cases violations
*2 Item number of the consultation to be a violation of the law
| Country of Production | Item Category | Cases |
|---|---|---|
| USA | Rice (7) | 14 |
| Wheat (6) | ||
| Soybean | ||
| Thailand | Rice (11) | 11 |
| Australia | Barley (5) | 9 |
| Wheat (2) | ||
| Rice (2) | ||
| Canada | Soybean (2) | 4 |
| Barley | ||
| Wheat | ||
| Brazil | Soybean (4) | 4 |
| Colombia | Coffee bean (2) | 2 |
| Indonesia | Seaweed | 1 |
| Ethiopia | Coffee bean | 1 |
| Total | 46 | |
| Country of Production | Item Category | Violation details | Cases*1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excess of standard values | Do not contain | Non-detectable | |||
| Vietnam | Shrimp | Enrofloxacin (13), Sulfadiazine(7) | Furazolidone (as AOZ) (7), Sulfamethoxazole |
35 | |
| Squid | Chloramphenicol(4) | ||||
| File fish | Chloramphenicol(3) | ||||
| China | Eel | Methylene blue | 4 | ||
| Shrimp | Leucomalachite green | ||||
| Soft-shelled turtle | Enrofloxacin | ||||
| Large yellow croaker | Enrofloxacin | ||||
| Indea | Shrimp | Furazolidone (as AOZ) (3) |
3 | ||
| France | Pigeon meat | Oxytetracycline | 1 | ||
| USA | Propolis | Chloramphenicol | 1 | ||
| Total | (Gross) *1 | 44 | |||
| (Actual) *2 | 44 | ||||
*1 Gross number of Itemized cases violations
*2 Item number of the consultation to be a violation of the law
| Country of Production | Material type | Violation Details | Cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Mineral water | Compositional standard(5) | 10 |
| Food additive | Compositional standard(3) | ||
| Unheated meat products | manufacturing standard(2) | ||
| China | Food additive | Compositional standard(4) | 6 |
| Toys | Compositional standard(2) | ||
| Thailand | Food additive | Compositional standard(3) | 5 |
| Mineral water | Compositional standard | ||
| Pickled in syrup | Unauthorised genetically modified papaya positive | ||
| Australia | Natural cheeses(including Papaya) | Unauthorised genetically modified papaya positive((3) | 4 |
| Flavoured Ice | manufacturing standard | ||
| Spain | Dried meat products | Water activity(2) | 3 |
| Mineral water | Compositional standard | ||
| Denmark | Beef offal | Non-attachment of health certificate(2) | 3 |
| Food additive | Compositional standard | ||
| France | soft drinks | manufacturing standard(2) | 3 |
| Mineral water | Compositional standard | ||
| Malaysia | Mineral water | Compositional standard(2) | 3 |
| Food additive | Compositional standard | ||
| Ireland | Beef offal | Non-attachment of health certificate(2) | 2 |
| Germany | Food additive | Compositional standard(2) | 2 |
| Vietnam | Frozen food (including Papaya) | Unauthorised genetically modified papaya positive(2) | 2 |
| Italy | Unheated meat products | stroage standard | 1 |
| Indonesia | Food additive | Compositional standard | 1 |
| Canada | Dried meat products | Water activity | 1 |
| Brunei | Mineral water | Compositional standard | 1 |
| Poland | Beef offal | Non-attachment of health certificate | 1 |
| Japan | soft drinks | stroage standard | 1 |
| Total | (Gross) *1 | 49 | |
| (Actual) *2 | 42 | ||
*1 Gross number of Itemized cases violations
*2 Item number of the consultation to be a violation of the law
| Month of enhancement | Subject country or region | Subject food and details | Background and status |
|---|---|---|---|
| May | USA | Frozen vegetable and frozen fruit (Possible contamination with Listeria monocytogenes) |
Information was received stating that in the USA possible contamination with Listeria monocytogenes was found in frozen vegetable and frozen fruit and relevant products were recalled. When an import notification was made for such recall products, steps were taken for reshipment, etc. |
| December | USA | Gracilaria (Possible contamination with Salmonella) |
Information was received stating that in the USA possible contamination with Salmonella was found in gracilaria and relevant gracilaria was recalled. When an import notification was made for such recall products, steps were taken for reshipment, etc. |
| March | Brazil | Chicken meat, etc. (Fraudulent act in meat inspection) |
Information was received stating that in Brazil some facilities were subject to suspension of operation or special inspections associated with a fraudulent act in meat inspection. When an import notification was made for products of relevant facilities, the import procedure was suspended. When an import notification was made for products of other facilities, steps were taken for enhanced inspections at the time of importation. |
| Subject item (Inspection order item, etc.) |
Bilateral talks | Date of on-site inspection, etc. |
|---|---|---|
| Taiwan, Foods (recycled waste oil) |
In September 2014, recycled waste oil was mixed into cooking oil and sold as food ingredient and food using relevant oil was recalled, and consultation began. In March 2017, based on completion of the recall of relevant products and reports on recurrence prevention measures, etc., the monitoring system was changed to normal. | – |
| The Philippines, Mango (agricultural chemical residues) |
In March 2015, violations relating to agricultural chemical residues were found in cargo exported from exporters exempted from ordered inspections, and consultation began. In February 2016, on-site inspections were carried out and it was confirmed that the cause was unfolded and recurrence prevention measures have been taken, and the relevant exporters were re-registered as exporters exempted from ordered inspections. | February 2016 |
| Paraguay, Sesame (agricultural chemical residues) |
In August 2013, relevant products were made subject to ordered inspections, and consultation began. Measures against agricultural chemical residues were taken by the Paraguayan government, and on-site inspections were carried out in March 2016. Talks are continuing. | March 2016 |
| South Korea, Flounder (Kudoa septempunctata) |
Consultation began in April 2013. On-site inspections were carried out in December 2016 for verification of observance of a Japan export verification program and discussions about the cause and improvements. Talks are continuing. | December 2016 |
| Poland, Beef (BSE) |
In November 2016, on-site inspections were carried out and observance of a Japan export verification program at facilities authorized for export to Japan was confirmed. | November 2016 |
| Sweden, Beef (BSE) |
In December 2016, on-site inspections were carried out and observance of a Japan export verification program at facilities authorized for export to Japan was confirmed. | December 2016 |
| USA, Beef (BSE) |
In December 2016, on-site inspections were carried out and the state of preparation for enforcing a Japan export verification program at facilities planned to be authorized for export to Japan was confirmed. | December 2016 |
| Ireland, Beef (BSE) |
In February 2017, on-site inspections were carried out and observance of a Japan export verification program at facilities authorized for export to Japan was confirmed. | February 2017 |
| Canada, Beef (BSE) |
In March 2017, on-site inspections were carried out and observance of a Japan export verification program at facilities authorized for export to Japan was confirmed. | March 2017 |
| India | |
|---|---|
| Subject of inspection | System investigation of foods exported to Japan in India |
| Relevant law |
|
| Summary | Descriptions were given by representatives of the export regulation authorities of the Indian government, Food Safety and Standards Authority of India, etc., about the food sanitation regulations in India, and opinions were exchanged. A seminar on import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan was held targeting government officials. Additionally, on-site inspections were carried out at spice manufacturing facilities, fish paste processing facilities and shrimp culture farms for the conditions of control, etc., and at export inspection institutions. |
| Singapore | |
| Subject of inspection | System investigation of foods exported to Japan in Singapore |
| Relevant law |
|
| Summary | Descriptions were given by representatives of the Agri-Food & Veterinary Authority of Singapore about the food sanitation regulations in Singapore, and opinions were exchanged. A seminar on import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan was held targeting government officials and food suppliers. Additionally, on-site inspections were carried out at cocoa powder manufacturing facilities, pastry manufacturing facilities, and meat processing facilities, for the conditions of control, etc. |
| Malaysia | |
| Subject of inspection | System investigation of foods exported to Japan in Malaysia |
| Relevant law |
|
| Summary | Descriptions were given by representatives of the Food Safety and Quality Division, Ministry of Health Malaysia about the food sanitation regulations in Malaysia, and opinions were exchanged. A seminar on import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan was held targeting government officials and food suppliers. Additionally, on-site inspections were carried out at syrup manufacturing facilities and chocolate manufacturing facilities, for the conditions of control, etc., and at export inspection institutions. |
| Norway | |
| Subject of inspection | System investigation of foods exported to Japan in Norway |
| Relevant law |
|
| Summary | Descriptions were given by representatives of the Norwegian Food Safety Authority about the food sanitation regulations in Norway, and opinions were exchanged. A seminar on import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan was held targeting government officials and food suppliers. Additionally, on-site inspections were carried out at salmon culture farms and seafood processing facilities, for the conditions of control, etc. |
| FY2012 | FY2013 | FY2014 | FY2015 | FY2016 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Import consultations implemented | 13,962 | 12,492 | 11,826 | 13,086 | 12,352 |
| Import consultations on item-by-item basis | 27,825 | 23,903 | 24,360 | 24,377 | 24,180 |
| Violations on item-by-item basis | 372 | 354 | 257 | 364 | 410 |
* Offices of Imported Food Consultation are set up in each quarantine station in Otaru, Sendai, Narita Airport, Tokyo, Yokohama, Niigata, Nagoya, Osaka, Kansai Airport, Kobe, Hiroshima, Fukuoka, and Naha.
* Figures include only advance consultations implemented prior to import in Office of Imported Food Consultation
| Provision | Violations (cases) | Proportion(%) | Details of major violations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Article 10 (Limitation on distribution, etc. of additives, etc.) |
250(Gross) *1 210(Actual) *2 |
51.1 | Use of Potassium aluminium silicate, Iodinated salt, Azorubin, Carboxymethylcellulose, Isobutane, Amidated pectin, Sodium lauryl sulfate, Croscarmellose sodium, Zinc oxide, Iodine, TBHQ, Magnesium lactate, Iron oxide, Quinoline yellow, Patent Blue V, L-Cysteine, Polyethylene glycol monostearate, Sodium ethylate, Potassium iodate, Formaldehyde, Black PN, Dimethyl dicarbonate, etc. |
| Article 11 (Standards and criteria for foods and additives) |
238(Gross) *1 223(Actual) *2 |
48.7 | Non-compliance with manufacturing standard of soft drink(inadequate sterilization), use of sodium benzoate in alcoholic beverages(use to inhibited foods), use of excessive amount of calcium carbonate in health food, etc. |
| Article 62 (Mutatis mutandis application for toys) |
1(Gross) *1 1(Actual) *2 |
0.2 | Violations of criteria for toys or their raw materials |
| Total | 489 (Gross) *1 410 (Actual) *2 |
||
*1 Gross number of Itemized cases violations
*2 Item number of the consultation to be a violation of the law.
| Country of Production | Item | Violation details | Cases※2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA | Health food | Use of unspecified additives(Croscarmellose Sodium(6), D-α-Tocopherol Succinate(3), Zinc oxide(3), Copper oxide(2), Para-aminobenzoic acid(2), Potassium iodide(2), Manganese ascorbate, N-Acetyl-L-cysteine, Complexes of chromium and amino acid, Complexes of selenium and amino acid, Complexes of molybdenum and amino acid, β-alanine, Chromium chloride, L-glutathione, Chromium oxide, Choline bitartrate, Zeaxanthin, Selenium, Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose acetate succinate, Methanol) Use to inhabited foods(Ferrous gluconate, Sorbic acid) Use of excessive amounts(Calcium carbonate) |
35 | 87 |
| Alcoholic beverages | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate(11)) | 11 | ||
| Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(TBHQ(5)) Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(6)) |
11 | ||
| Cereal preparations | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(8)) | 8 | ||
| Powdered soft drink | Use of unspecified additives(Magnesium lactate(6), Magnesium citrate) | 7 | ||
| Additives | Use of unspecified additives(Azorubine(4), Argon, Manganese gluconate) | 6 | ||
| Seasoning | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(2)) | 2 | ||
| Confectionery mix | Use to inhabited foods(L-Cysteine monohydrochloride) | 1 | ||
| Canning | Use to inhabited foods(Sulfur dioxide) | 1 | ||
| Soft drink | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate) | 1 | ||
| Other foods | Use to inhabited foods(Chlorine dioxide) | 1 | ||
| Milk product | Use to inhabited foods(Liquid paraffin) | 1 | ||
| Processed vegetables product | Use of unspecified additives(Ethyl cellulose) | 1 | ||
| Oils and fats | Use of unspecified additives(Argon) | 1 | ||
| France | Chocolate | Use of unspecified additives(Potassium aluminium silicate(13), Azorubine(3), Patent Blue V(3), Brown HT(2), Black PN(2), Quinoline yellow) Use to inhabited foods(Iron sesquioxide(13), Potassium sorbate(5)) |
42 | 60 |
| Frozen food (confectionery) | Use of unspecified additives(Amidated pectine(4), L-Cysteine) Use to inhabited foods(L-Cysteine monohydrochloride, Iron sesquioxide) |
7 | ||
| Canning | Non-compliance with manufacturing standard (radiation exposure(4)) | 4 | ||
| Additives | Use of unspecified additives(Oak chips, Quinoline yellow) | 2 | ||
| Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(Patent Blue(2)) | 2 | ||
| Alcoholic beverages | Use of unspecified additives(Quinoline yellow) | 1 | ||
| Processed fruits product | Use of unspecified additives(Azorubine) | 1 | ||
| Seasoning | Residue of excessive amounts of additives (Potassium pyrosulfite) | 1 | ||
| Italy | Additives | Use of unspecified additives(Isobutane(10), Potassium aluminium silicate(10)) | 20 | 38 |
| Alcoholic beverages | Use of unspecified additives(Azorubine(3), Patent Blue V(2), L-Malic acid) | 6 | ||
| Confectionery | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(4)) | 4 | ||
| Soft drink | Non-compliance with manufacturing standard(inadequate sterilization) Use of unspecified additives(D-Glucuronolactone, Quinine hydrochloride dihydrate) |
3 | ||
| Seasoning | Use to inhabited foods(Sorbic acid(2), Potassium sorbate) | 3 | ||
| Meat products | Non-compliance with manufacturing standard(inadequate use of sodium nitrite(2)) | 2 | ||
| Australia | Health food | Use of unspecified additives(Iron oxide(5), Croscarmellose Sodium(4), Sodium ethylate(4), D-α-Tocopherol Succinate(2), Sodium lauryl sulfate(2), Quinoline yellow, Zinc citrate, Iron oxide red, Iron oxide black, Choline bitartrate, Ferrous fumarate, Potassium iodate) Use to inhabited foods(Sodium selenite) Use of excessive amounts(Calcium phosphate) |
26 | 27 |
| Soft drink | Use of unspecified additives(Redbark cinchona extract obtained from undefined substances) | 1 | ||
| Vietnam | Seasoning | Use of unspecified additives(Carmin, Brown HT) Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate(4), Benzoic acid(2), Sorbic acid, Potassium sorbate) Use of excessive amounts(Nisin) |
11 | 26 |
| Soft drink | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(9)) | 9 | ||
| Instant noodle | Use to inhabited foods (Sodium benzoate, BHA, BHT) | 3 | ||
| Noodles | Use to inhabited foods(Food Yellow no.4, Food Yellow no.5) | 2 | ||
| Frozen food (fish) | Use of unspecified additives(Diphosphorus pentoxide) | 1 | ||
| Taiwan | Health food | Use of unspecified additives(Sodium lauryl sulfate(6)) | 6 | 21 |
| Soft drink | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(4)) Non-compliance with manufacturing standard(inadequate sterilization) |
5 | ||
| Confectionery | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate, Potassium sorbate) | 2 | ||
| Syrup | Use of excessive amounts(Acesulfame potassium(2)) | 2 | ||
| Pickled vegetables | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(2)) | 2 | ||
| Processed agricultural product | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(2)) | 2 | ||
| Seasoning | Use to inhabited foods(Disodium glycyrrhizinate) | 1 | ||
| Frozen food (other foods) | Use of excessive amounts(Propylene glycol) | 1 | ||
| South Africa | Alcoholic beverages | Use of unspecified additives(Polyethylene glycol monostearate(5)) Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate(12)) |
17 | 18 |
| Chocolate | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium stearoyl lactylate) | 1 | ||
| Spain | Alcoholic beverages | Use of unspecified additives(Potassium aluminium silicate(3)) Use to inhabited foods(Iron sesquioxide(2), Ester gum) |
6 | 17 |
| Frozen dough | Use of unspecified additives (L-Cysteine(4)) | 4 | ||
| Soft drink | Use of unspecified additives (Dimethyl dicarbonate(3)) | 3 | ||
| Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives (Amidated pectine) Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate) |
2 | ||
| Chocolate | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate, Potassium sorbate) | 2 | ||
| Thailand | Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(Iodine, Iodinated salt) Use to inhabited foods(Sodium propionate(2)) Use of excessive amounts(Propylene glycol(2)) |
6 | 17 |
| Processed seaweed product | Use of unspecified additives(Iodine(4)) | 4 | ||
| Processed fruits product | Residue of excessive amounts of additives (Sodium pyrosulfite, Sulfur dioxide) | 2 | ||
| Soft drink | Non-compliance with manufacturing standard(inadequate sterilization) Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate) |
2 | ||
| Health food | Use of unspecified additives(Butylene glycol) | 1 | ||
| Processed Livestock product | Use to inhabited foods(Color) | 1 | ||
| Frozen food (confectionery) | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium stearoyl lactylate) | 1 | ||
| South Korea | Health food | Use of unspecified additives(Zinc oxide(3), DL-Isoleucine, DL-Valine) Use of excessive amounts(Calcium carbonate, Propylene glycol) |
7 | 16 |
| Seasoning | Use to inhabited foods(Ethyl p-hydroxybenzoate(4), Calcium disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate) Use of excessive amounts(Silicone resin(2)) |
7 | ||
| Soft drink | Use of unspecified additives(Zinc oxide) | 1 | ||
| Frozen dough | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium stearoyl lactylate) | 1 | ||
| United Kingdom | Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(Iodinated salt(4)) | 4 | 14 |
| Additives | Use of unspecified additives(Potassium aluminium silicate(3)) Non-compliance with manufacturing standard(Peracetic acid composition) |
4 | ||
| Alcoholic beverages | Use of unspecified additives(Azorubine, Quinoline yellow) | 2 | ||
| Health food | Use of unspecified additives(Zinc citrate) Violation of standards on use of additives (Silicon dioxide) |
2 | ||
| Flour paste | Use of unspecified additives(Quinoline yellow, Methyl p-hydroxybenzoate) | 2 | ||
| Germany | Health food | Use of unspecified additives(Iron oxide(2), Chromium chloride, Sodium cyclamate, Potassium iodate) Use to inhabited foods(Sodium selenite) |
6 | 14 |
| Meat products | Use of unspecified additives(Potassium iodate(3)) | 3 | ||
| Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(Copper chlorophyllin(2)) | 2 | ||
| Soft drink | Use of unspecified additives(Synthetic caffeine(2)) | 2 | ||
| Additives | Use of unspecified additives(Lutein) | 1 | ||
| Philipines | Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(Iodinated salt(4)) Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(4)) |
8 | 12 |
| Meat products | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(2)) | 2 | ||
| Processed fruits product | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate) | 1 | ||
| Chocolate | Use of excessive amounts(Sodium benzoate) | 1 | ||
| Armenia | Alcoholic beverages | Use of unspecified additives(Carboxy methyl cellulose(11)) | 11 | 11 |
| India | Spice | Use of unspecified additives(Iodinated salt(8)) | 8 | 11 |
| Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(Flavour) | 1 | ||
| Instant noodle | Use of unspecified additives(Iodinated salt) | 1 | ||
| Seasoning | Use of unspecified additives(Iodinated salt) | 1 | ||
| Newzealand | Milk product | Use of unspecified additives(Azorubine) Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(8)) |
9 | 11 |
| Processed Livestock product | Use to inhabited foods(Disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetate(2)) | 2 | ||
| Finland | Soft drink | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(7)) | 7 | 11 |
| Processed fruits product | Use of unspecified additives(Amidated pectine(4)) | 4 | ||
| Malaysia | Instant noodle | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate(5)) | 5 | 11 |
| Powdered soft drink | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium stearoyl lactylate(4)) | 4 | ||
| Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(Flavour) | 1 | ||
| Other foods | Use of unspecified additives(Azorubine) | 1 | ||
| Singapore | Seasoning | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(6)) Use of excessive amounts(Sodium benzoate(2)) |
8 | 8 |
| Zimbabwe | Seasoning | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate(4), Potassium sorbate(4)) | 8 | 8 |
| Russia | Processed fruits product | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate(5)) | 5 | 8 |
| Sugar | Use of unspecified additives(Formaldehyde(3)) | 3 | ||
| China | Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(Zinc lactate) Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate, Potassium sorbate) |
3 | 7 |
| Instant noodle | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium stearoyl lactylate(2)) | 2 | ||
| Seasoning | Use to inhabited foods(Sorbic acid) | 1 | ||
| Processed vegetables product | Residue of excessive amounts of additives(Sulfur dioxide) | 1 | ||
| Denmark | Processed aquatic product | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate(4), Potassium sorbate) | 5 | 5 |
| Croatia | Alcoholic beverages | Use to inhabited foods(Ester gum(2)) | 2 | 4 |
| Syrup | Use of unspecified additives(Azorubine, Black PN) | 2 | ||
| Estonia | Frozen food (fish) | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate, Saccharin, Potassium sorbate) | 3 | 3 |
| Mexico | Alcoholic beverages | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate) | 1 | 3 |
| Frozen food (fruit) | Violation of standards on use of additives (Peracetic acid) | 1 | ||
| Frozen food (cereals) | Use to inhabited foods(L-Cysteine monohydrochloride) | 1 | ||
| Indonesia | Processed seed product | Use of unspecified additives(TBHQ) | 1 | 2 |
| Toys | Non-compliance with manufacturing standard(use of unspecified additives) | 1 | ||
| Netherlands | Alcoholic beverages | Use of unspecified additives(Potassium ascorbate) Use of excessive amounts(Potassium sorbate) |
2 | 2 |
| Swizerland | Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(Carbon black) | 1 | 2 |
| Sugar | Use to inhabited foods(Sorbic acid) | 1 | ||
| Turkey | Seasoning | Non-compliance with manufacturing standard (radiation exposure) | 1 | 2 |
| Confectionery mix | Non-compliance with manufacturing standard (radiation exposure) | 1 | ||
| Brazil | Health food | Use of unspecified additives (Polyethylene glycol) | 1 | 2 |
| Soft drink | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate) | 1 | ||
| Belgium | Confectionery | Use of unspecified additives(Flavour) | 1 | 2 |
| Soft drink | Non-compliance with manufacturing standard(inadequate sterilization) | 1 | ||
| Poland | Soft drink | Use of unspecified additives (Magnesium citrate, Pantothenic acid) | 2 | 2 |
| Israel | Additives | Use of unspecified additives(Levan obtained from undefined substances) | 1 | 1 |
| Canada | Confectionery | Use to inhabited foods (Sodium propionate) | 1 | 1 |
| Greece | Processed vegetables product | Use to inhabited foods(Sodium benzoate) | 1 | 1 |
| Sweden | Frozen food (other foods) | Use to inhabited foods(Potassium sorbate) | 1 | 1 |
| Pakistan | Soft drink | Use of unspecified additives(Carboxy methyl cellulose) | 1 | 1 |
| Paraguay | Processed fruits product | Use of excessive amounts(Potassium sorbate) | 1 | 1 |
| Undetermined | Seasoning | Use of unspecified additives(Iodine) | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 489 | |||
*Gross number of cases violations
| Country of Production | Item | Violation Details | Cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| South Korea | Cultured olive flounder | Kudoa septempunctata(3) | 3 |
| Thailand | Okra | Imidacloprid | 3 |
| Confectionery | TBHQ | ||
| Curry | TBHQ | ||
| USA | Beef | No health certificate attached | 2 |
| Orange | Propiconazole | ||
| Sri Lanka | Cocktail onion(pickles) | Benzoic acid | 1 |
| China | Seasoned bamboo shoots | Dehydroacetic acid | 1 |
| New Zealand | Mozzarella cheese | Unauthorised genetically modified rennet | 1 |
| South Africa | Grapefruit | Imazalil | 1 |
| Total | 12 | ||
*Gross number of cases violations.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Nitrite | Additive (color fixative agent) |
| Acesulfame potassium | Additive (sweetener) |
| Acetochlor | Agricultural chemical (anilide herbicide) |
| Acephate | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Sodium selenite | Additive (nutrient) |
| Azoxystrobin | Agricultural chemical (strobilurin fungicide) |
| Aflatoxin | Mycotoxin produced by the fungus Aspergillus, etc. |
| Ametryn | Agricultural chemical (triazine herbicide) |
| Benzoic acid | Additive (preservative) |
| Sodium benzoate | Additive (preservative) |
| Genetic modification | Technology such as fragmentation of bacterial genes, followed by arrangement of the gene sequences or introducing the arranged genes into other organism’s genes. |
| Iprobenfos | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Imazalil | Additive (antibiotical agent) |
| Imidacloprid | Agricultural chemical (Neonicotinoid insecticide) |
| Ester Gum | Additive (gum base) |
| Ethion | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Calcium Disodium Ethylenediaminetetraacetate | Additive (antioxidizing agent) |
| Ethoxyquin | Feed additive (antioxidant agents) |
| Epoxiconazole | Agricultural chemical (triazole fungicide) |
| Endosulfan | Agricultural chemical (organochlorine insecticide) |
| Enrofloxacin | Veterinary drug (new quinolone synthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Oxytetracycline | Veterinary drug (tetracycline antibiotical agent) |
| Oxolinic acid | Veterinary drug (synthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Peracetic acid formulation | Additive (antimicrobial) |
| Carbaryl | Agricultural chemical (carbamate insecticide) |
| Kudoa septempunctata | Kind of parasite that causes food poisoning. (Myxosporidia) |
| Coumaphos | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Disodium glycyrrhizate | Additive (sweetener) |
| Glyphosate | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous herbicide) |
| Ferrous gluconate | Additive (color stabilizer) |
| Chloramphenicol | Veterinary drug (chloramphenicol antibiotical agent) |
| Chlorpyrifos | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Chlorfenapyr | Agricultural chemical (pesticides containing pyrrole ring) |
| Diarrhetic shellfish toxin | Shellfish toxin (mainly refers to toxins produced by a harmful plankton accumulated in clams, toxic clams cause diarrhetic poisoning) |
| Saccharin | Additive (sweetener) |
| Salmonella spp. | Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium that is ubiquitous in the intestines of animals as well as in nature, such as rivers, sewage and lakes. It contaminates meat, mostly poultry and eggs, and causes acute abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever and vomiting.) |
| Iron sesquioxide | Additive (coloring agent) |
| Cyanide | Harmful or poisonous compound (cyanide-related compounds (e.g., cyanogenic glycoside) ) found in vegetables such as some varieties of beans. |
| Diniconazole | Agricultural chemical (triazole fungicide) |
| Difenoconazole | Agricultural chemical (triazole fungicide) |
| Diflubenzuron | Agricultural chemical (urea insecticide) |
| Cyproginil | Agricultural chemical (heterocyclic insecticide) |
| Cypermethrin | Agricultural chemical (pyrethroid insecticide) |
| Gibberellin | Agricultural chemical (growth regulator) |
| Tartrazine, Sunset Yellow FCF | Additive (coloring agent) |
| Silicone resin | Additive (anti-foaming agent) |
| Sucralose | Additive (sweetener) |
| Sodium stearoyl lactylate | Additive (emulsifier) |
| Streptomycin | Aminoglycoside antibiotics |
| Sulfadiazine | Veterinary drug (synthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Sulfadimidine | Veterinary drug (synthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Sulfamethoxazole | Veterinary drug (synthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Sorbic acid | Additive (preservative) |
| Potassium sorbate | Additive (preservative) |
| Calcium carbonate | Additive (nutrient) |
| Thiamethoxam | Agricultural chemicals (neonicotinoid insecticide) |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium living in seawater (estuaries, coastal areas, etc.) that commonly contaminates fish and shellfish, and causes abdominal pain, watery diarrhea, fever and vomiting.) |
| Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli ( E.coli ) O26, O104, O157 etc. | Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium that normally lives in the intestines of animals. It contaminates foods and drinking water by way of faces and urine, and causes acute abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea together with large amounts of blood after early cold-like symptoms.) |
| Tetracycline antibiotic | A general term for antibiotics which have constant spectrum (ex.Oxytetracycline, Chlorotetracycline, Tetracycline etc.) |
| Dehydroacetic acid | Additive (preservative) |
| Tebuconazole | Agricultural chemical (triazole fungicide) |
| Tebufenozide | Agricultural chemical (benzoilhydrazide insecticide) |
| Sodium copper chlorophyllin | Additive (coloring agent) |
| Triazophos | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Nisin | Additive (preservative) |
| Sulfur dioxide | Additive (antioxidant agents) |
| Chlorine dioxide | Additive (wheat flour treatment agent) |
| Silicon dioxide | Additive (production agent) |
| Pactobutrazole | Agricultural chemical (triazole growth regulator) |
| Patulin | Mycotoxin (produced by the fungi such as Penicillium and Aspergillus) |
| Haloxyfop | Agricultural chemical (herbicide) |
| Bifenthrin | Agricultural chemical (pyrethroid insecticide) |
| Pyridaben | Agricultural chemical (insecticide) |
| Pirimiphos methyl | Agricultural chemical (insecticide) |
| Pyrimethanil | Agricultural chemical (anilinopyrimidine fungicide) |
| Potassium pyrosulfite | Additive (antioxidant agents) |
| Sodium pyrosulfite | Additive (antioxidant agents) |
| Fipronil | Agricultural chemical (phenylpyrazole synergist) |
| Fenitrothion | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Fenvalerate | Agricultural chemical (pyrethroid insecticide) |
| Fenhexamid | Agricultural chemical (hydroxyanilide fungicide) |
| Bisphthalate | Plasticizer |
| Furazolidone | Veterinary drug (nitrofuran synthetic antibacterial agent) ; generates AOZ when metabolized |
| Fluquinconazole | Agricultural chemical (fungicide) |
| Flonicamid | Agricultural chemical (pyridinecarboxamide insecticide) |
| Sodium propionate | Additive (preservative) |
| Propiconazole | Agricultural chemical (triazole fungicide) |
| Propylene glycol | Additive (softening agents) |
| Profenophos | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Prometryn | Agricultural chemical (triazine herbicide) |
| Hexaconazole | Agricultural chemical (triazole fungicide) |
| Pencicron | Agricultural chemical (urea fungicide) |
| Paralytic shellfish poison | Shellfish poison (mainly refers to toxins produced by a harmful plankton accumulated in clams, toxic clams cause paralytic poisoning) |
| Malachite green | Veterinary drug (triphenylmethane synthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Marathion | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Metalaxyl | Agricultural chemical (anilide fungicide) |
| Methylene blue | Veterinary drug (insecticide) |
| Mefenoxam | Agricultural chemical (anilide fungicide) |
| Listeria monocytogenes | Pathogenic microorganism (A normal flora in the natural environment that contaminates daily products and processed meat products, and causes influenza-like symptoms including tiredness and fever) |
| Liquid paraffin | Additive (production agent) |
| Calcium phosphate | Additive (nutrient) |
| Leucomalachite green | Metabolite of malachite green |
| 2,4-D | Agricultural chemical (phenoxy acid herbicide) |
| 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid | Agricultural chemical (growth regulator) |
| BHA (butylatedhydroxyanisole) | Additive (antioxidant agent) |
| BHT (butylhydroxytoluene) | Additive (antioxidant agent) |
| BSE (bovin spongiform encephalopathy) | An indolent malignant central neurological disease in cattle that causes a spongy degeneration in the brain tissues and symptoms including astasia. |
| EPN | Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| L-cysteine hydrochloride | Additive (nutrient) |
