Office of Import Food Safety,
Inspection and Safety Division,
Department of Food Safety,
Pharmaceutical and Food Safety
Bureau, Ministry of Health, Labour
and Welfare
Results of Monitoring and Guidance
Based on the Imported Foods Monitoring and
Guidance Plan for FY 2014
August 2015
Department of Food Safety, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau,
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
Inspection Results of Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY
2014
Introduction
Foods, additives, apparatus, containers and packaging and toys (hereinafter referred to as "foods") imported by Japan in 2014 amounted to 32.41 million tons across 2.22 million import notifications. According to the "2014 Food Balance Sheet" published by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, the food self-sufficiency ratio in Japan is 40% (combined food self-sufficiency ratio by calorie intake), and 60% based on calorie intake is dependent on imports.
In order to ensure the safety of foods imported into Japan (hereinafter, "imported foods"), the government established the imported food monitoring and guidance plan in 2014 (hereinafter, "the Plan"). The program is based on the Guidelines for Monitoring and Guidance for Food Sanitation (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare Notification No. 301, 2003) as per the provisions of Article 23, paragraph 1 of the Food Sanitation Act (Act No. 233, 1947; hereinafter, "the Act"), and public comments were collected and risk communication carried out. The program was published in the Official Gazette as an official report according to the provisions of paragraph 3 of the same article, and monitoring and guidance for imported foods is being conducted based upon the Plan.
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare publish a recently compiled overview of the implementation of the monitoring and guidance for imported foods including an overview of the implementation of monitoring and inspections carried out under the Plan, the implementation of inspections of imported foods inspected or ordered, and an overview of the results thereof, monitoring and guidance to importers and the results thereof, and consultations in exporting countries.
1. Overview of the Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY 2014
1 What is the Imported Food Monitoring and Guidance Plan?
It is the plan (under Article 23 of the Act) for the implementation of monitoring and guidance of imported foods by the government.
Purpose: To further ensure the safety of imported foods by promoting intensive, effective and efficient import inspections and monitoring and guidance of importers.
2 Principles of Monitoring and Guidance for Imported Foods
Establishes a plan which aims to ensure sanitation at three stages, namely, in the exporting country, at the time of importation, and in domestic distribution, from the perspective of Article 4 (that is, food safety must be ensured internationally and domestically through appropriate measures at each stage of the food supply chain) of the Food Safety Basic Act (Act No. 48 of 2003).
3 Priority Items for Monitoring and Guidance
- Confirmation of legality with respect to the Act at time of import notification
- Monitoring*1 (FY 2014 Plan: 94,043 items across 168 food groups)
- Ordered inspection*2 (As of April 1st, 2014: 17 items from all exporting countries, and 75 items from 26 countries and 1 region)
- Regulations for comprehensive import bans*3
- Emergency measures based on overseas information
4 Promotion of safety measures in exporting countries
- Systematic collection of information on safety measures for foods exported to Japan and promotion of sanitation measures through on-site visits
- Request for the establishment of sanitation control measures such as stronger control for agricultural chemicals, enhancement the monitoring systems and implement of pre-export inspections, through bilateral talks and on-site visits
- Informing the responsible governmental agencies and food business operators of food safety regulations of Japan through seminars held in exporting countries.
5 Guidance on voluntary sanitation control by importers
- Pre-import guidance (known as import consulting)
- Guided inspections at pre-import, initial import and on a regular basis
- Guidance on preparation and storage of records
- Raising awareness of food safety amongst importers
*1: Systematic inspection using a statistical approach considering the import volume and violation ratio of each type of food.
*2: Inspection for products with a high probability of violation where an inspection is ordered for the importer, and import and distribution is not permitted without the results being in compliance with the law.
*3: Measures whereby the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare may prohibit sale or import of specific foods, etc. without inspection, in the case it is deemed necessary to prevent harm.
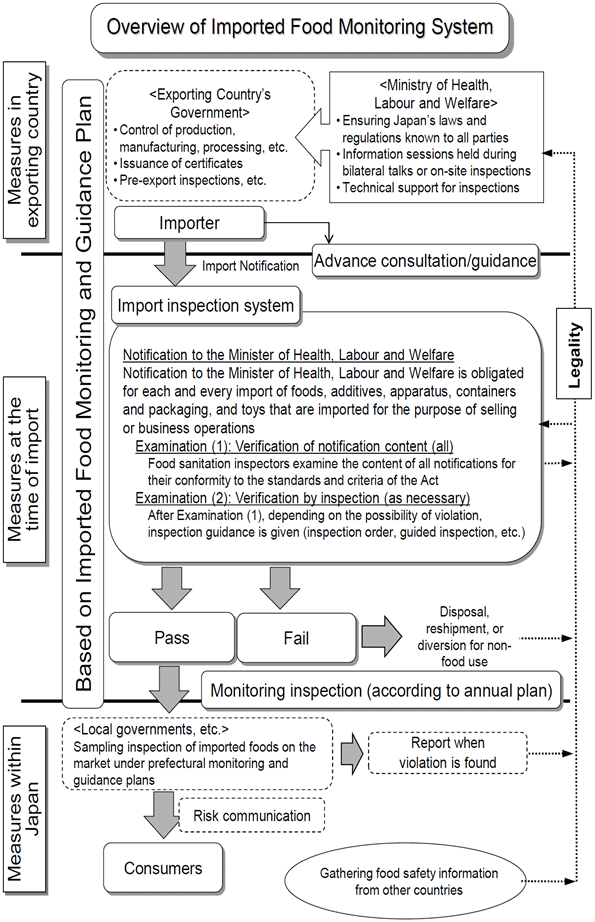
2. Results of Imported Food Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY 2014
Measures have been taken as described below by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and quarantine stations in accordance with Article 4 of the Food Safety Basic Act to ensure the safety of imported foods at every stage from production, manufacturing and processing in the exporting country to domestic distribution, based on the fundamental approach that it is necessary to take appropriate measures.
(1) Examination of import notification in accordance with Article 27 of the Act

Examination of notifications
using computer system
Examination of compliance with the Act was made, primarily with the standards and criteria for foods under the provisions of Article 11 (1) and Article 18 (1) of the Act (hereinafter, "standards and criteria"), and inspections were carried out as required at the time of importation, based on import notifications made under the provisions of Article 27 of the Act.
Looking at the notifications, inspections and violations made in FY 2014 (Table 1), there were 2,216,012 notifications, and the weight of notified items was 32,412,000 tons. Inspections were carried out on 195,390 items, of which 877 cases (running total 913 cases) were found to be in violation of the Act, and steps were taken for their reshipment, disposal, etc. These accounted for 0.04% of the number of notifications.
(2) Monitoring under Article 28 of the Act

Sampling at warehouse
Monitoring inspection numbers and inspection items to be carried out by quarantine stations were defined and planned for a total of 94,043 cases in FY 2014, considering previous importation data and violation rates for each food type, based on inspection numbers required to enable detection of violations to a statistically fixed degree of reliability.
In response to overseas cases of food poisoning and detection of pathogenic microorganisms in foods, inspections pertaining to pathogenic microorganisms were steadily enhanced.
Follow on the implementation of monitoring inspections at every quarantine station have been carried out, and the Plan reviewed during monitoring period to adjust inspections to the actual importation.
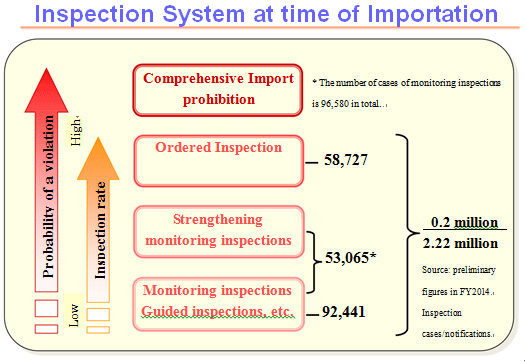
Looking at the Implementation of Monitoring Inspections for FY 2014 (Table 2), a total of 96,580 cases (actual number 53,065) were carried out compared to a total of 94,043 planned (an implementation rate of 103%), and of these, 140 cases were found to be in violation of the Act, and steps were taken for recall.
Inspections of the same food type are enhanced in response to the detection of violations of the Act during monitoring inspections, etc. (Table 3). Where multiple violations for agricultural chemical residues or veterinary drugs are detected in specific foods from the same country, or for foods which are expected to have a high probability of violation of the Act, such foods. will be subject to inspection upon each and every importation (Table 4). Foods in which aflatoxin or other bacteria are detected will be immediately subject to inspection (Table 5).
(3) Ordered inspection under Article 26 of the Act
Subject countries and regions, subject foods and items for inspection have been defined, and ordered inspection have been made under provisions of Article 26 of the Act for imported foods which have a high probability of violating the Act, to prevent harm to public health.
As of March 31st, 2015, 17 items from all exporting countries, and 79 items from 32 countries and 1 region were subject to ordered inspection, and the record of ordered inspection for FY 2014 (Table 6) shows 58,727 cases (running total 95,346) were implemented, of which 251 cases (running total 255) were found to be in violation of the Act and steps were taken for re-shipment or disposal, etc.
(4) Violations (*total number of cases in violation)
Breaking down the 913 cases of violation by provision (Table 7), violations of Article 11 of the Act, which relates to microbial criteria, standards for agricultural chemical residues, and standards for the use of additives in food, were the most common at 539 cases (59.0% as a proportion of 913 violations), followed by violations of Article 6, which relates to contamination with hazardous or toxic substances such as aflatoxin, at 245 cases (26.8%), violations of Article 18, which relates to standards for apparatus or containers and packaging, at 70 cases (7.7%), violations of Article 10, which relates to the use of undesigenated additives, at 54 cases (5.9%), violations of Article 9, which relates to the health certificates of meat, at 3 cases (0.3%), and violations of Article 62 (mutatis mutandis application), which relates to criteria for toys, at 2 cases (0.2%).
Breaking down the violations by inspection type, the most common were violations relating to microbial criteria in frozen foods, etc. (Table 8-1) at 207 cases (22.7%% as a proportion of 913 violations), followed by violations relating to agricultural chemical residues (Table 8-2) at 195 cases (21.4%), violations relating to hazardous or toxic substances or pathogenic microorganisms (Table 8-3) at 163 cases (17.9%), violations relating to undesignated additives used and additives in violations of usage standards (Table 8-4) at 119 cases (13.0%), violations relating to decay, deterioration, generation of mold and unpleasant smell (Table 8-5) at 82 cases (9.0%), violations relating to apparatus, containers and packaging (Table 8-6) at 70 cases (7.7%), violations relating to veterinary drugs (Table 8-7) at 42 cases (4.6%), and violations relating to criteria for toys (Table 8-8) at 2 cases (0.2%).
Breaking down the violations relating to microbial criteria (Table 8-1) by country, the rankings were China with 70 cases (33.8% as a proportion of all 207 violations relating to microbial criteria), Thailand with 28 cases (13.5%) and South Korea with 22 cases (10.6%). The principle violation in these cases were, for all countries, microbial criteria (bacterial count, coliform bacteria, E.coli) in frozen foods.
Breaking down the violations relating to agricultural chemical residues (Table 8-2) by country, the rankings were China with 49 cases (25.1% as a proportion of all 195 violations relating to agricultural chemical residues), Ghana with 45 cases (23.1%) and South Korea with 16 cases (8.2%). The principle products in violation in these cases were onions from China (thiamethoxam), cacao beans from Ghana (cypermethrin) and red chili peppers from South Korea (difenoconazole).
Breaking down the violations relating to hazardous or toxic substances or pathogenic microorganisms (Table 8-3) by country, the rankings were the USA with 43 cases (26.4% as a proportion of all 163 violations relating to hazardous or toxic substances or pathogenic microorganisms), China with 28 cases (17.2%) and Italy with 26 cases (16.0%). The principle products in violation in these cases were almonds from the USA (contamination with aflatoxin), peanuts from China (contamination with aflatoxin) and uncooked meat products from Italy (Listeria monocytogenes).
Breaking down the violations relating to additives (Table 8-4) by country, the rankings were China with 15 cases (12.6% as a proportion of all 119 violations relating to additives), Italy with 12 cases (10.1%) and Germany with 11 cases (9.2%). The principle products in violation in these cases were processed salted bamboo shoots from China (violation of standard of use (bleach)), fruit vinegar from Italy (violation of standard of use (antioxidant)) and liquors from Germany (use of undesignated additives).
Breaking down the violations relating to decay, deterioration, generation of mold and unpleasant smell (Table 8-5) by country, the rankings were the USA with 19 cases (23.2% as a proportion of all 82 violations relating to decay, deterioration, generation of mold and unpleasant smell), Thailand with 18 cases (22.0%) and Colombia with 10 cases (12.2%). The principle products in violation in these cases were wheat from the USA, rice from Thailand, and coffee beans from Colombia.
Breaking down violations relating to apparatus, containers and packaging (Table 8-6) by country, the rankings were China with 36 cases (51.4% as a proportion of all 70 violations relating to apparatus, containers and packaging) and Malaysia with 8 cases (11.4%). The principle materials in violation in these cases were synthetic resins, which accounted for 37 cases.
Breaking down the violations relating to veterinary drugs (Table 8-7) by country, the rankings were Vietnam with 26 cases (61.9% as a proportion of all 42 violations relating to veterinary drugs), India with 10 cases (23.8%) and China with 5 cases (11.9%). The principle products in violation in these cases were shrimp from Vietnam (enrofloxacin), shrimp from India (furazolidone) and octopus from China (furazolidone).
Breaking down the violations relating to criteria for toys (Table 8-8) by country, the rankings were only China with 2 cases (100% as a proportion of all 2 violations relating to criteria for toys). The materials in violations in these cases were synthetic resin and combined materials (phthalates).
(5) Emergency measures based on information from overseas on food safety issues
The monitoring system at the time of importation has been enhanced and an investigation into domestic distribution has been carried out and appropriate measures including recalls were ordered where there was a record of their import regarding issues in FY 2014 (Table 9), including Diethylstilbestrol contamination of pork in Denmark, enterohemorrhagic E. coli O26 contamination of natural cheeses in France and contamination of Datura seeds in blended cereals in Switzerland and Germany. The investigation was based on information on the overseas outbreaks of food poisoning and the recall of food products in violation of the Act that has been collected by the National Institute of Public Health and Food Safety Commission of the Cabinet Office.
Further, on the matter of agricultural chemical poisoning due to frozen dumplings produced in China that occurred in January 2008, inspections for agricultural chemical residues in processed food were carried out on a total of 12,678 samples throughout FY 2014, which resulted in the finding of 1 case of violation in frozen fish meat paste produced in Myanmar (chlorpyrifos). As a result, the monitoring system has been enhanced.
(6) Promotion of sanitation measures in exporting countries

Okra farm in Thailand
In FY 2014, information on products in violation of the Act has been provided to the governments of exporting countries where the products are subject to ordered inspection or strengthening monitoring inspections and further, requests have been made through bilateral consultations for investigations into the causes of violations and for taking measures to prevent the recurrence of such violations.
As part of this promotion, when it was necessary to confirm the adequacy of sanitation measures during the production or processing stages in the exporting country, with regards to the issues of, for example, agricultural chemical residues or bovine spongiform encephalopathy (hereinafter, "BSE"), specialists were dispatched to the exporting countries and audit of sanitation measures taken in the countries was also carried out (Table 10).
On-site inspections for meat products and unheated meat products from Spain were carried out from October 8 to 10, 2014, to verify the control systems of Listeria monocytogenes.
On-site inspections for Italian unheated meat, natural cheeses and gorgonzola cheese were carried out from October 13 to 17, 2014, to verify the control systems of Listeria monocytogenes.
On-site inspections for Thai asparagus, okra, banana, mango and mangosteen were carried out from February 8 to 14, 2015, to verify the control systems for agricultural chemical residue.
On-site inspections for Polish beef were carried out from June 23 to 27, 2014, at beef production facilities in Poland authorized for export to Japan to confirm the preparation state for enforcing a Japan export verification program.
Regular audit for USA beef was carried out from November 2 to 13, 2014, at beef production facilities in the USA authorized for export to Japan to verify and inspect observance of the Japan export verification program.
Regular audit for Canadian beef was carried out from March 22 to 28, 2015, at beef production facilities in Canada authorized for export to Japan to verify and inspect observance of the Japan export verification program.
Specialists were dispatched to the USA to confirm the adequacy of the sanitation control systems for genetically modified products as part of sanitation control training organized by the governments of exporting countries.
(7) Promotion of pre-inspection sanitation measures in exporting countries
As a new preventative initiative, systematic information gathering and, when required, on-site inspections have been conducted in many exporting countries since FY 2009 regarding information etc. on sanitation measures at the exporting countries.
For FY 2014, these activities were conducted in Argentina, Chile and Paraguay. In addition, initiatives of the governments, producers, and manufacturers of exporting countries were investigated (Table 11).
(1) Argentina
Descriptions were given by a representative from the Argentine government on the food sanitation regulations in Argentina, and inspection and opinion exchange were carried out. Further, a seminar on import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan was held targeting government officials etc.
Additionally, on-site inspections were carried out at salmon processing facilities and beef slaughterhouse and processing facilities, for the conditions of control.
(2) Chile
Descriptions were given by a representative from the Chilean government on the food sanitation regulations in Chile, and inspection and opinion exchange were carried out. Further, a seminar on import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan was held targeting government officials etc.
Additionally, on-site inspections were carried out at pig farms, slaughterhouses and salmon farms/processing facilities for the conditions of veterinary drug control etc.
(3) Paraguay
Descriptions were given by a representative from the Paraguayan government on the food sanitation regulations in Paraguay, and opinion exchange was carried out. Further, a seminar on import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan was held targeting the Paraguayan government officials, food suppliers, etc.
Additionally, on-site inspections were carried out for the conditions of chemical residues control of sesame seeds, pertaining to those exported to Japan.
(8) The Japan-China Food Safety Promotion Initiative
In May 2010, both the Minister of the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan and the Minister of General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (AQSIQ) of the People's Republic of China signed a memorandum of understanding on the Japan-China Food Safety Promotion Initiative (hereinafter referred to as “Memorandum”). As a result, the first ministerial meeting was held and working-level consultations and field studies were conducted. Both parties determined that bilateral exchange and cooperation should continue to be promoted in the field of safety for food exports and imports between two countries.
For the FY2014, a special working-level consultation was held in August (in China) for the case of processed food produced using expired chicken.
At the special working-level consultation, the Chinese side explained the situation of production problems in the food processed using expired chicken and the efforts to ensure the safety of domestic and exported food. The Japanese side requested the Chinese side to take effective preventive measures based on the final results of investigation in cooperation with agencies related to China’s domestic and exported food sanitation measures, and to continue to ensure the safety of foods exported to Japan.
More details on the results, etc., of the Japan-China Food Safety Promotion Initiative are posted at the URL below.
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/kenkou_iryou/shokuhin/yunyu_kanshi/exporter/index.html
(9) Comprehensive import ban regulations under Articles 8 and 17
Article 8 and Article 17 of the Food Sanitation Act provide measures for the comprehensive banning of imports, as a method of enabling the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare to comprehensively ban the import or sale of specific foods from specific countries without requiring an inspection. According to the "Guidelines for the Banning of the Sale or Import of Specific Foods under Article 8 (1) and Article 17 (1) of the Food Sanitation Act" (SHOKUHATSU No. 0906001 dated September 6th, 2002), before invoking measures for a comprehensive import ban on items that exceed a 5% violation rate in the latest 60 ordered inspection, the status of sanitation controls is confirmed with the exporting country, and a request is made for improvements. In FY 2014, no imported foods were subject to any such measures or requests.
(10) Guidelines for implementation of voluntary sanitation controls by importer

Seminar at a Quarantine Station
At the seminar held by quarantine stations, importers are advised that the safety of imported foods is confirmed in advance by obtaining necessary materials from the producer or manufacturer. Additionally, in the case that foods be imported to Japan for the first time, or there are some violations in similar foods, importers are recommended to have consultation with quarantine statations in advance, based on the Plan..
Officers from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and quarantine stations were dispatched to training courses and workshops held by related organizations in order to raise awareness of food sanitation with importers, and as a result importers in general understand the details. Looking at the figures for pre-import guidance given by Offices of Imported Food Consultation (known as import consultations) in quarantine stations in FY 2014 (Table 12), a total of 24,360 cases by product received import consultations, of which 257 cases (total 358) were identified as non-compliant with the Act in advance.
Breaking down the cases which were non-compliant with the Act by the specific provision (Table 13), violations of Article 11 which relates to standards and criteria for food including standards for agricultural chemical residues and standards for usage of additives were the most common with 186 cases (52.0% as a proportion of all 358 violations), followed by violations of Article 10 which relates to the use of undesignated additives with a total of 162 cases (45.3%).
Breaking this down by country (Table 14), the USA had the most cases at 117 (32.7%), followed by Taiwan with 32 cases (8.9%), then by Italy with 26 cases (7.3%). The principle violation in these cases was the use of undesignated additives in health foods from the USA, the use of preservatives in other than target foods in jams from Taiwan and the use of preservatives in other than target foods in sauces from Italy.
Where the import consultation determined non-compliance with the Act, appropriate measures were taken to ensure compliance, and guidance was given to suspend import until improvements were made. After improvements were made and documentation showing compliance with the Act provided, guidance was given as needed to carry out in advance checks such as inspections for fulfillment of standards and criteria for said foods.
(11) Disclosure of information on violations of imported foods, and cooperation with prefectures
Details of violations including the names and imported foods of importers in violation of the Act were listed and published on the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare website, based on provisions of Article 63 of the Act, in order to clarify the food sanitation risk. Along with the names, etc. of parties in violation, measures taken to rectify matters, the cause of the violation, and method of disposal were also identified and published.
Imported foods which had already passed customs at the time they were identified as being in violation were promptly recalled with the cooperation of the relevant prefectural governments. Imported foods discovered to be in violation through domestic market inspections by prefectural governments (Table 15) led to enhanced inspections where required.
Table 1 – Notifications, Inspections, and Violations (FY 2014)
Notifications
(cases) |
Imported Weight
(thousand tons) |
Inspections*1
(cases) |
Proportion*2
(%) |
Violations
(cases) |
Proportion*2
(%) |
| 2,216,012 |
32,412 |
195,390
(58,727)*3 |
8.8 |
877
(251)*3 |
0.04
(0.43)*3 |
| (FY 2013) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 2,185,480 |
30,982 |
201,198 |
9.2 |
1,043 |
0.05 |
*1 Inspections by authorities, registered inspection organizations and foreign official laboratories, deducting duplicates.
*2 Proportion as compared to notifications.
*3 Number of inspection orders.
Table 2 – Implementation of Monitoring Inspections (FY 2014)
| Food Groups |
Inspected Substances*1 |
Number Planned in FY |
Actual Number |
Violations |
Livestock Foods
Beef, pork, chicken, horse meat, other poultry meat, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. |
1,909 |
2,059 |
1 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals |
1,191 |
1,694 |
0 |
| Additives |
118 |
147 |
0 |
| Pathogenic microorganisms |
686 |
663 |
0 |
| Standards for constituents |
295 |
375 |
0 |
| Radiation irradiation |
29 |
30 |
0 |
| Removal of SRMs |
2,500 |
1,490 |
0 |
Processed Livestock Foods
Natural cheeses, processed meat products, ice cream, frozen (meat) products, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. |
2,266 |
2,297 |
0 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals |
1,697 |
1,848 |
0 |
| Additives |
1,247 |
1,422 |
0 |
| Pathogenic microorganisms |
3,584 |
3,530 |
4 |
| Standards for constituents |
1,547 |
1,675 |
2 |
| Mycotoxins |
- |
9 |
0 |
Seafood products
Bivalves, fish, shellfish (shrimps, crabs), etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. |
2,752 |
2,724 |
1 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals |
1,613 |
2,132 |
0 |
| Additives |
297 |
289 |
0 |
| Pathogenic microorganisms |
1,074 |
1,542 |
0 |
| Standards for constituents |
539 |
489 |
0 |
| Radiation irradiation |
34 |
29 |
0 |
Processed seafood
Processed fish products (fillet, dried or minced fish, etc.), Frozen food(seafood, fish), processed marine product eggs, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. |
3,757 |
4,605 |
4 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals |
3,904 |
5,034 |
4 |
| Additives |
1,927 |
2,479 |
1 |
| Pathogenic microorganisms |
4,063 |
4,413 |
2 |
| Standards for constituents |
2,867 |
2,966 |
29 |
| Mycotoxins |
- |
7 |
0 |
| Radiation irradiation |
- |
9 |
0 |
Agricultural foods
Vegetables, fruit, wheat, maize, pulses, peanuts, nuts, seeds, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. |
2,979 |
3,022 |
0 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals |
9,129 |
10,838 |
45 |
| Additives |
774 |
782 |
0 |
| Pathogenic microorganisms |
1,495 |
1,388 |
0 |
| Standards for constituents |
355 |
405 |
1 |
| Mycotoxins |
2,871 |
2,821 |
3 |
| Genetically modified food |
235 |
468 |
0 |
| Radiation irradiation |
119 |
135 |
0 |
Processed agricultural food
Frozen food(processed vegetables), processed vegetable products, processed fruit, spice, instant noodles, etc. |
Antibacterial substances, etc. |
598 |
599 |
0 |
| Residual agricultural chemicals |
8,148 |
9,118 |
6 |
| Additives |
4,222 |
5,137 |
1 |
| Pathogenic microorganisms |
956 |
1,257 |
0 |
| Standards for constituents |
2,499 |
2,869 |
12 |
| Mycotoxins |
2,594 |
2,798 |
1 |
| Genetically modified food |
427 |
181 |
1 |
| Radiation irradiation |
424 |
438 |
0 |
Other foods
Health foods, soups, seasonings, confectionery, cooking oil, frozen food, etc. |
Residual agricultural chemicals |
1,434 |
1,578 |
0 |
| Additives |
2,685 |
2,954 |
4 |
| Pathogenic microorganisms |
- |
12 |
0 |
| Standards for constituents |
598 |
426 |
2 |
| Mycotoxins |
1,135 |
1,158 |
0 |
| Radiation irradiation |
- |
5 |
0 |
Beverages
Mineral waters, soft drinks,
alcoholic drinks, etc. |
Residual agricultural chemicals |
358 |
403 |
0 |
| Additives |
1,374 |
1,520 |
0 |
| Standards for constituents |
657 |
726 |
2 |
| Mycotoxins |
118 |
123 |
0 |
Additives
Apparatus, containers and packaging
Toys |
Standards for constituents |
1,433 |
1,462 |
14 |
Total (gross)
6,530 cases of the total cases planned for the FY were part of enhanced monitoring. |
94,043 |
96,580
Implementation rate of 103% |
140※2 |
※1:Examples of inspected substances
・Antibacterial substances, etc.: antibiotics, synthetic antimicrobials, hormone drugs, etc.
・Residual agricultural chemicals: organophosphorous, organochlorine, carbamates, pyrethroid, etc.
・Additives: preservatives, coloring agents, sweeteners, antioxidants, antimold agents, etc.
・Pathogenic microorganisms (enterohemorrhagic E.coli O26, O103, O104, O111, O121, O145 and O157, Listeria monocytogenes etc.)
・Standards for constituents, etc.: Items stipulated in the standards for constituents (bacterial count, coliform bacteria, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, etc.), shellfish poisons (diarrhetic shellfish poison and paralytic shellfish poison), etc.
・Mycotoxin: aflatoxin, deoxynivalenol, patulin, etc.
・Genetically modified organisms (GMOs): genetically modified foods, etc. that have not been assessed for safety.
・Radiation irradiation: with or without of irradiation
※2:Total number of item-by-item inspections
Table 3 – Items Subject to Enhanced Monitoring Inspections in FY 2014*1(As of March 31, 2015*2)
Country/Region |
Subject Food |
Inspected Substances |
| China |
Constricted tagelus |
Prometryn |
| Sea urchin (for raw consumption) |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus(MPN) *3 |
| Chinese pepper (Zanthoxylum bungeanum) |
Aflatoxin |
| Arrowhead |
Paclobutrazol |
| Sesame seed |
Dicofol |
| Taro |
Chlorpyrifos |
| Octopus |
Furazolidone |
| Carrot |
Triadimenol |
| Immature peas |
Diniconazole, Pyridaben |
| Cultured shrimp |
Sulfamethoxazole |
| Lychee |
4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid |
| Allium Wakegi |
Difenoconazole |
| Thailand |
Green soybeans |
Triazophos |
| Feverweed |
Cypermethrin |
| Okra |
Isoprothiolane |
| Holy Basil |
EPN, Chlorpyrifos |
| Pandanus palm leaf |
2,4-D |
| Immature peas |
Flusilazole |
| South Korea |
Arch shell (for raw consumption) |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus (MPN)*4 |
| Eel |
Ofloxacin |
| Green pepper |
Tricyclazole, hexaconazole |
| New Zealand |
Green peas |
Haloxyfop |
| Carrot |
Methamidophos |
| USA |
Celery |
Bifenthrin |
| Blueberry |
Buprofezin |
| Argentina |
Chia seed |
Pirimiphos-methyl |
| Indonesia |
Boiled crab (for raw consumption) |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus*3 |
| Ethiopia |
Fresh coffee beans |
Chlorpyrifos |
| Australia |
Cotton seeds |
Aflatoxin |
| Guatemala |
Broccoli |
Profenofos |
| Colombia |
Fresh coffee beans |
Chlorpyrifos |
| Taiwan |
Carrot |
Methamidophos |
| Philippines |
Sea urchin (for raw consumption) |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus (MPN)*5 |
| France |
Guinea fowl meat |
Brotizolam |
| Vietnam |
Cultued shrimp |
Sulfadiazine |
| Bolivia |
Sesame seed |
Haloxyfop |
| Honduras |
Fresh coffee beans |
Chlorpyrifos |
| Mexico |
Avocado |
Acephate |
| Rumania |
Apple juice and Apple juice concentrate |
Patulin |
*1 Enhanced monitoring inspections in FY 2014 were normally conducted on 30% of all import notifications after violations have been detected. Items which had rescinded frominspection orders as a result of import or inspection results were also handled in the same way. However, if no similar violations were detected within 60 enhanced monitoring inspections or within 1 year, the items in question were subjected to the normal inspection state.
*2 Excludes items included in Table 4.
*3 Item which 30% of import declarations were inspected as a measure to enhance inspections during the summer period, (Jun-Oct 2014)
*4 Item which all (100%) import declarations were inspected as a measure to enhance inspections during the summer period, (Jun-Oct 2014).
*5 Item which 30% of import declarations were inspected first, and then it has been enhanced to inspect all (100%) import declarations after detection of violation of Food Sanitation Act as a measure to enhance inspections during the summer period. (Jun-Oct 2014)
Table 4 – Items Transferred to Inspection Order after Enhanced Monitoring Inspections in FY 2014
Country/Region |
Subject Food |
Inspected Substances |
| South Korea |
Green hot pepper |
Difenoconazole, Fluquinconazole |
| Tomato |
Fluquinconazole |
| Thailand |
Feverweed |
Chlorpyrifos |
| Durian |
Metalaxyl and mefenoxam |
| India |
Chickpea |
Glyphosate |
| Netherlands |
Cabbage |
Pencycuron |
| Ghana |
Cacao beans |
Cypermethrin, Fenvalerate |
| China |
Onion |
Thiamethoxam |
| Bangladesh |
Cumin seeds |
Profenofos |
| Philippines |
Mangos |
Phenthoate |
| Burkina Faso |
Sesame seed |
Imidacloprid |
| Vietnam |
Filefish |
Chloramphenicol |
Table 5 – Items Immediately transferred to Inspection Order in FY 2014
Country/Region |
Subject Item |
Inspected Substances |
| Italy |
Unheated meat products (manufactures limited) |
Listeria monocytogenes |
| Pistachio processed products |
Aflatoxin |
| Spain |
Unheated meat products (manufactures limited) |
Listeria monocytogenes |
| Pistachio processed products |
Aflatoxin |
| France |
Soft or semi-hard natural cheese (manufactures limited) |
Enterohemorrhagis Escherichia coli 026 |
| Unheated meat products (manufactures limited) |
Listeria monocytogenes |
| Iran |
Pistachio processed products |
Aflatoxin |
| India |
Fenugreek |
Aflatoxin |
| South Korea |
Cultured olive flounder (culturing farm limited) |
Kudoa septempunctata |
| Syria |
Pistachio processed products |
Aflatoxin |
| Switzerland |
Unheated meat products (manufactures limited) |
Listeria monocytogenes |
| Taiwan |
Foods (manufactures limited) |
Cyclamic acid |
| China |
Foods (manufactures limited) |
Cyclamic acid |
| Nigeria |
Sesame seed |
Aflatoxin |
| Paraguay |
Chia seed |
Aflatoxin |
| Philippines |
Tuna fillet for raw consumption ( manufactures limited) |
Salmonella spp. |
* Item shifted to promptly inspection order due to consecutive violations.
Table 6 – Major Items subject to Inspection Orders and Inspection Outcomes (FY 2014)
Country/Region |
Major subject foods |
Major Inspected Substances |
Inspections |
Violations |
All Exporting Countries
(17 items) |
Dried figs, Chili peppers, Nuts Peanuts. |
Aflatoxin |
11,224 |
77 |
| Manioc, beans containing cyanide |
Cyanide |
397 |
5 |
| Salted salmon roe |
Nitrite |
295 |
2 |
China
(19 items) |
Eel, Shrimp, Soft-shelled turtle |
Enrofloxacin, Chlortetracycline, Sulfadimidine, Malachite green, Sulfamethoxazole, etc. |
7,624 |
3 |
Vegetables, Fruits
(spinach, onion, green soybeans, lychees etc.), Bivalve, Oolong tea, Sesame seed |
Acetochlor, Indoxacarb, Diflubenzuron, Thiamethoxam, Prometryn, Difenoconazole, etc. |
18,580 |
29 |
| All processed products |
Cyclamic acid |
586 |
0 |
| Bivalve |
Paralytic shellfish poison, Diarrhetic shellfish poison |
7,615 |
3 |
| Lotus seed,Chinese pepper (Zanthoxylum bungeanum) |
Aflatoxin |
37 |
1 |
South Korea
(13 items) |
Cultured olive flounder |
Enrofloxacin, Oxytetracycline |
16 |
0 |
| Chili pepper, Freshwater clam, Cherry tomatos |
Endosulfan, Fluquinconazole, Difenoconazole |
178 |
7 |
| Arch shell |
Vibrio parahaemolyticus (MPN) |
2 |
0 |
| Bivalves |
Paralytic shellfish poison, Diarrhetic shellfish poison |
144 |
0 |
Thailand
(11 items) |
Vegetables, Fruit
(okra, green asparagus, mango, banana, mangosteen, etc.) |
Chlorpyrifos, Cypermethrin, Profenofos, Propiconazole, EPN, etc. |
2,508 |
1 |
India
(9 items) |
Cultured shrimp |
Furazolidone |
1,278 |
10 |
| Cumin seed, Chili peppers, Chickpea, Black tea |
Glyphosate, Triazophos, Profenofos, Hexaconazole |
125 |
9 |
| Cassia torea, Chickpea, Fenugreek seed |
Aflatoxin |
121 |
0 |
Italy
(7 items) |
Gorgonzola cheese, Natural cheese, Unheated meat products |
Listeria monocytogenes |
1,726 |
11 |
| Pistachio, Chestnut, Corns |
Aflatoxin |
502 |
6 |
USA
(6 items) |
Food to contain natural cheese mainly, Unheated meat products |
Listeria monocytogenes |
18 |
0 |
| Corns, Pistachio |
Aflatoxin |
2,928 |
16 |
Taiwan
(5 items) |
Carrot |
Acephate |
55 |
0 |
| All processed products |
Cyclamic acid |
76 |
0 |
| Filleted tilapia |
Carbon monoxide |
3 |
0 |
| Other (29 countries ; total 55 items) |
39,308 |
75 |
| Total |
|
|
95,346 |
255 |
Table 7 – Violations by Legal Provision (FY 2014)
| Provision violated |
Violations (cases) |
Proportion(%) |
Brief details of Violation |
Article 6
(Foods and additives prohibited to distribute) |
245 |
26.8 |
Aflatoxin contamination in corns, peanuts, almonds, dried fig, Job's tears, pistachionuts, chili peppers, nutmeg, walnuts, sesame seed, fenugreek, chestnut, lotus seed, etc.; contamination of toxic fish; detection of diarrhetic shellfish toxin; detection of cyanide; detection of Listeria monocytogenes from unheated meat products, natural cheese*3; decay, deterioration and fungus formation due to accidents during the transport of rice, wheat, rapeseed, soybeans, etc. |
Article 9
(Limitation on distribution, etc. of diseased meat) |
3 |
0.3 |
No health certificate attached |
Article 10
(Limitation of distribution, etc. of additives) |
54 |
5.9 |
Use of unspecified additives such as TBHQ, Quinoline Yellow, Patent blue V, Cyclamic acid, Azorubin, Methyl p-hydroxy benzoate, Iodized salt, Acid blue 3 sodium salt, amidated pectin, boric acid, potassium iodate, carbon monoxide, Methylene chloride, etc. |
Article 11
(Standards and criteria for foods and additives) |
539 |
59.0 |
Violation of standards for constituents for vegetables or frozen vegetables (violation of standards on residual agricultural chemicals), violation of standards for constituents for marine products and processed products thereof (violation of standards on residual veterinary drugs, violation of standards on residual agricultural chemicals), violation of standards for constituents for other processed products (Coliform bacteria test, etc.), violation of standards on use of additives (sulfur dioxide, sorbic acid, benzoic acid etc.), and violation of standards for constituents for additives, detection of radioactive substance |
Article 18
(Standards and criteria for apparatus, containers and packaging) |
70 |
7.7 |
Violation of criteria for apparatus, containers and packaging
Violation of materials criteria for raw materials |
Article 62
(Mutatis mutandis application for toys) |
2 |
0.2 |
Violations of criteria for toys or their raw materials |
Total |
913(Gross)*1
877(Actual)*2 |
|
*1 Gross number of inspection cases by inspected substances.
*2 Number of notification cases for which inspections were carried out
*3 Violation in the reference value before the revision of standard
Table 8-1 – Violations by Country, Item and Violation details for Microbial Criteria (FY 2014)
Country of production |
Item category |
Violation details |
Cases* |
| China |
Frozen food (vegetable) |
E.coli(7), Coliform bacteria(7),
Bacterial count(2) |
70 |
| Frozen food (other foods) |
Bacterial count(3), Coliform bacteria(3),
E.coli(3), |
| Frozen food (fish) |
Bacterial count(6), Coliform bacteria(3),
E.coli |
| Heat processed meat product |
Coliform bacteria(4), E.coli(3) |
| Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption |
Coliform bacteria(5) |
| Frozen food (squid) |
Bacterial count(4), Coliform bacteria,
E.coli |
| Fish paste product |
Coliform bacteria(2) |
| Boiled crab |
Bacterial count(2) |
| Boiled octopus |
Bacterial count , Coliform bacteria |
| Frozen food (shellfish) |
Bacterial count , Coliform bacteria |
| Frozen food (marine animal) |
Bacterial count , Coliform bacteria |
| Frozen food (animal product) |
Bacterial count , Coliform bacteria, E.coli |
| Frozen food (agricultural food product) |
Bacterial count , Coliform bacteria |
| Hermetically packaged, Pressure and heat sterilized food product |
Possible microbes |
| Frozen food (bean) |
Bacterial count |
| Thailand |
Frozen food (shrimp) |
Bacterial count(3), Coliform bacteria(2),
E.coli(2) |
28 |
| Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption |
Coliform bacteria(5) |
| Heat processed meat product |
E.coli(4) |
| Frozen food (squid) |
Bacterial count(2), Coliform bacteria(2) |
| Fish paste product |
Coliform bacteria(3) |
| Frozen food (other foods) |
Bacterial count(2) |
| Hermetically packaged, Pressure and heat sterilized food product |
Possible microbes |
| Frozen food (fish) |
E.coli |
| Frozen food (marine animal) |
Coliform bacteria |
South Korea |
Chilled fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption |
Coliform bacteria(5),
Vibrio parahaemolyticus (MPN) |
22 |
| Fish paste product |
Coliform bacteria(4) |
| Frozen food (shellfish) |
Coliform bacteria(2), Bacterial count, E.coli |
| Hermetically packaged, Pressure and heat sterilized food product |
Possible microbes(3) |
| Powdered soft drink |
Coliform bacteria |
| Mineral water |
Coliform bacteria |
| Frozen food (fish) |
Coliform bacteria |
| Frozen food (marine animal) |
Bacterial count |
| Frozen food (other foods) |
Bacterial count |
| Vietnam |
Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption |
Coliform bacteria(3), Bacterial count(2) |
18 |
| Frozen food (squid) |
Coliform bacteria (2), E.coli |
| Frozen food (shrimp) |
Coliform bacteria (2), E.coli |
| Frozen food (fruit) |
Coliform bacteria (3) |
| Frozen food (vegetable) |
Coliform bacteria (2) |
| Fish paste product |
Coliform bacteria |
| Frozen food (shellfish) |
Bacterial count |
| Philippines |
Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption |
Coliform bacteria(4), Bacterial count(2),
Vibrio parahaemolyticus (MPN) |
15 |
| Fish paste products |
Coliform bacteria(3) |
| Fruits juice for raw material |
Coliform bacteria(2) |
| Frozen food (fruit) |
Coliform bacteria(2) |
| Frozen food (other foods) |
Coliform bacteria |
| Indonesia |
Frozen food (shrimp) |
Bacterial count(2), E.coli(2) |
12 |
| Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption |
Coliform bacteria(2), Bacterial count |
| Boiled crab |
Bacterial count, Coliform bacteria |
| Boiled octopus |
Bacterial count, Coliform bacteria |
| Frozen food (marine animal) |
Coliform bacteria |
| France |
Frozen food (other foods) |
Coliform bacteria(2), Bacterial count |
9 |
| Butter |
Coliform bacteria(2) |
| Frozen food (fruit) |
Bacterial count, Coliform bacteria |
| Powdered soft drink |
Coliform bacteria |
Frozen food (other agricultural food
product) |
Coliform bacteria |
| Italy |
Ice cream |
Coliform bacteria(3) |
6 |
| Heat processed meat product |
Clostridium |
| Frozen food (fish) |
E.coli |
| Frozen food (vegetable) |
E.coli |
| Chile |
Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption |
Coliform bacteria(3), Bacterial count |
4 |
| Brazil |
Flavoured Ice |
Coliform bacteria(2), Bacterial count |
4 |
| Heat processed meat product |
E.coli |
| India |
Frozen food (shrimp) |
Bacterial count |
3 |
Frozen food (other agricultural food
product) |
Coliform bacteria |
| Frozen food (other foods) |
Bacterial count |
| Taiwan |
Fruits juice for raw material |
Coliform bacteria |
3 |
| Frozen food (fruits juice) |
Coliform bacteria |
| Frozen food (other foods) |
Bacterial count |
| Poland |
Powdered soft drink |
Bacterial count(2) |
2 |
| Netherlands |
Frozen food (vegetable) |
E.coli |
1 |
| Spain |
Powdered soft drink |
Coliform bacteria |
1 |
| Germany |
Powdered soft drink |
Bacterial count |
1 |
| Turkey |
Fruits juice for raw material |
Coliform bacteria |
1 |
| Norway |
Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption |
Coliform bacteria |
1 |
| Pakistan |
Hermetically packaged, Pressure and heat sterilized food product |
Possible microbes |
1 |
| Belgium |
Soft drink |
Coliform bacteria |
1 |
| Hong kong |
Frozen food (fish) |
Bacterial count |
1 |
| Malaysia |
Frozen food (other foods) |
Bacterial count |
1 |
| South Africa |
Powdered soft drink |
Coliform bacteria |
1 |
| Mauritius |
Frozen fresh fish and shellfish for raw consumption |
Coliform bacteria |
1 |
| Total |
207 |
* Gross number of cases violations
Table 8-2 – Violations by Country, Item and Violation details for residual agricultural chemicals (FY 2014)
Country of Production |
Item Category |
Violation Details |
Cases*1 |
| Standard Value |
Uniformity Standard |
| China |
Onion |
|
Thiamethoxam(26) |
49 |
| Short-neck clam |
|
Prometryn(6) |
| Lychee |
Diflubenzuron(2), 4-CPA |
|
| Taro |
Chlorpyrifos(3) |
|
| Hard clam |
|
Prometryn(2) |
| Oolong tea |
|
Indoxacarb(2) |
| Asparagus |
|
Ametryn |
| Green soybean |
|
Difenoconazole |
| Arrowhead |
|
Paclobutrazol |
| Shiso(perilla) |
|
Isoprocarb(MIPC) |
| Osmund |
|
Acetochlor |
| Immature pea |
|
Pyridaben |
| Allium Wakegi |
|
Difenoconazole |
| Ghana |
Cacao bean |
Cypermethrin(42),
Imidacloprid(2) |
Fenvalerate |
45 |
| South Korea |
Red hot pepper |
|
Difenoconazole(7) |
16 |
| Green hot pepper |
|
Difenoconazole(2),
Fluquinconazole(2) |
| Tomato |
|
Fluquinconazole(3) |
| Green pepper |
Tricyclazole,Hexaconazole |
|
| Thailand |
Feverweed |
Chlorpyrifos(3), Cypermethrin(2) |
|
13 |
| Red hot pepper |
|
Difenoconazole(2) |
| Durian |
|
Metalaxyl and mefenoxam(2) |
| Green soybean |
|
Triazophos |
| Okra |
|
Isoprothiolane |
| Holy basil |
Chlorpyrifos |
|
| Pandanus palm leaf |
2,4-D |
|
| Ecuador |
Cacao bean |
|
2,4-D (10) |
10 |
| India |
Red hot pepper |
|
Triazophos(6) |
9 |
| Cumin |
Profenofos(2) |
|
| Chickpea |
Glyphosate |
|
| Tanzania |
Sesame seed |
|
Imidacloprid(5) |
5 |
| New Zealand |
Green pesas |
|
Haloxyfop(4) |
5 |
| Carrot |
Methamidophos |
|
| Burkina Faso |
Sesame seed |
|
Imidacloprid(5) |
5 |
| Philippines |
Mango |
|
Phenthoate(PAP)(4) |
4 |
| Norway |
Whale meat |
Dieldrin(3) |
|
3 |
| Paraguay |
Sesame seed |
|
Carbaryl(NAC)(3) |
3 |
| Bangladesh |
Cumin |
Profenofos(3) |
|
3 |
| USA |
Cocoa powder |
|
2,4-D |
3 |
| Red hot pepper |
|
Triazophos |
| Blueberry |
|
Buprofezin |
| Vietnam |
Bell pepper |
|
Difenoconazole(3)*2 |
3 |
| Venezuela |
Cacao bean |
|
2,4-D (3) |
3 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Myanmar |
Croaker surimi |
|
Chlorpyrifos(2) |
3 |
| Sesame seed |
|
Imidacloprid |
| Argentina |
Chia seed |
2, 4-D,Pirimiphos methyl |
|
2 |
| Netherlands |
Cabbage |
|
Pencycuron(2) |
2 |
| Mexico |
Avocado |
Methamidophos |
|
2 |
| Immature kidney beans |
|
Flonicamid |
| Ethiopia |
Coffee bean |
Chlorpyrifos |
|
1 |
| Australia |
Rape seed |
|
Fenitrothion(MEP) |
1 |
| Guatemala |
Broccoli |
Profenofos |
|
1 |
| Cote D'ivoire |
Cacao bean |
|
2, 4-D |
1 |
| Colombia |
Coffee bean |
Chlorpyrifos |
|
1 |
| Hong Kong |
Oolong tea |
Fipronil |
|
1 |
| Honduras |
Coffee bean |
Chlorpyrifos |
|
1 |
| Total |
195 |
*1 Gross number of cases violations.
*2 Violation in the reference value before the revision
Table 8-3 – Violations by Country, Item and Violation details for Hazardous and Toxic substances and pathogenic microorganisms (FY 2014)
Country/Region of Production |
Item Category |
Violation Details |
Cases* |
| USA |
Almond |
Aflatoxin (13) |
43 |
| Corn |
Aflatoxin (11) |
| Peanut |
Aflatoxin (9) |
| Pistachio nut |
Aflatoxin (4) |
| Walnut |
Aflatoxin (2) |
| Chocolate |
Aflatoxin |
| Health food |
Cyanide |
| Confectionery |
Aflatoxin |
| Nutmeg |
Aflatoxin |
| China |
Peanut |
Aflatoxin (19) |
28 |
| Arch shell |
Diarrhetic shellfish toxin (3) |
| Job's tears |
Aflatoxin (2) |
| Red pepper |
Aflatoxin (2) |
| Lotus seed |
Aflatoxin |
| Seasoning |
Aflatoxin |
| Italy |
Unheated meat product |
Listeria monocytogenes (15) |
26 |
| Pistachio nut paste |
Aflatoxin (5) |
| Natural cheese |
Listeria monocytogenes (3) |
| Red pepper |
Aflatoxin |
| Western confectionery |
Cyanide |
| Chestnut preparation |
Aflatoxin |
| Nigeria |
Sesame seed |
Aflatoxin (11) |
11 |
| India |
Red pepper |
Aflatoxin (3) |
6 |
| Peanut |
Aflatoxin (2) |
| Fenugreek |
Aflatoxin |
| Turkey |
Dried fig |
Aflatoxin (3) |
6 |
| Substitutes for tea |
Cyanide (2) |
| Nutmeg |
Aflatoxin |
| France |
Fruit preparation |
Radioactive substance |
5 |
| Apple juice |
Patulin |
| Unheated meat product |
Listeria monocytogenes |
| Chestnut preparation |
Aflatoxin |
| Pistachio nut |
Aflatoxin |
| Iran |
Pistachio nut |
Aflatoxin (3) |
4 |
| Dried fig |
Aflatoxin |
| Spain |
Unheated meat product |
Listeria monocytogenes (3) |
4 |
| Almond |
Aflatoxin |
| Brazil |
Cassava powder |
Cyanide (3) |
4 |
| Peanut |
Aflatoxin |
| Indonesia |
Peanut |
Aflatoxin (2) |
3 |
| Nutmeg |
Aflatoxin |
| Thailand |
Red pepper |
Aflatoxin (2) |
3 |
| Pistachio nut |
Aflatoxin |
| Singapore |
Confectionery |
Cyanide |
2 |
| Mixed nut |
Aflatoxin |
| Sri Lanka |
Beans preparation |
Aflatoxin |
2 |
| Mixed spice |
Aflatoxin |
| Philippines |
Processed cassava product |
Cyanide |
2 |
| Tuna (for raw consumption) |
Salmonella spp. |
| South Africa |
Peanut |
Aflatoxin (2) |
2 |
| Myanmar |
Peanut |
Aflatoxin |
2 |
| Butter bean |
Cyanide |
| Canada |
Flax seed |
Cyanide |
1 |
| Greece |
Pistachio nut |
Aflatoxin |
1 |
| Croatia |
Confectionery |
Aflatoxin |
1 |
| Switzerland |
Unheated meat product |
Listeria monocytogenes |
1 |
| Denmark |
Processed agricultural product |
Aflatoxin |
1 |
| Nepal |
Mixed spice |
Aflatoxin |
1 |
| Vietnam |
Yellow-edged lyretail (variola louti) |
Poisonous fish contamination |
1 |
| Paraguay |
Chia seed |
Aflatoxin |
1 |
| Belarus |
Mushroom |
Radioactive substance |
1 |
| Romania |
Apple juice |
Patulin |
1 |
| Total |
163 |
* Gross number of cases violations.
Table 8-4 – Violations by Country, Item and Violation Details for Additives (FY 2014)
Country of Production |
Item Category |
Violation Details |
Cases* |
| China |
Salted bamboo shoots |
Sulfur dioxide (2) |
15 |
| Health food |
Cyclamic acid, Sorbic acid |
| Vegetable preparation |
TBHQ, Cyclamic acid |
| Fruit preparation |
Sulfur dioxide |
| Fruit in syrup |
Cyclamic acid |
| Dry & seasoning food |
Sorbic acid |
| Seasoning |
Potassium sorbate |
| Rape seed oil |
TBHQ |
| Boiled mushroom |
Sulfur dioxide |
| Frozen shrimp |
Sulfur dioxide |
| Frozen food (Livestock Foods) |
Sorbic acid |
| Frozen food (other processed product) |
Polysorbate |
| Italy |
Fruit vinegar |
Sulfur dioxide (3) |
12 |
| Brandy |
Methanol (2) |
| Vinegar |
Azorubin, Sulfur dioxide |
| Chocolate |
Patent blueⅤ |
| Pickles (olive) |
Ferrous gluconate |
| Natural cheese |
Natamycin |
| Processed agricultural product |
Sorbic acid |
| Other processed food |
Patent blueⅤ |
| Germany |
Liqueur |
Patent blueⅤ(4), Quinoline Yellow |
11 |
| Mix powder for manufacture |
Iodized salt (3) |
| Candy |
Acid blue 3 sodium salt |
| Chocolate |
Iodized salt |
| Fruit brandy |
Methanol |
| Thailand |
Seasoning |
Benzoic acid (3) |
8 |
| Fruit preparation |
Sulfur dioxide |
| Dried vegetable |
Sulfur dioxide |
| Processed agricultural product |
Sulfur dioxide |
| Rice crackers |
TBHQ |
| Boiled vegetable in water |
Sulfur dioxide |
| France |
Chocolate |
Azorubin (3), Quinoline Yellow (2), Patent blueⅤ |
7 |
| Caviar |
Boric acid |
| USA |
Roasted caffeineless coffee bean |
Methylene choloride (2) |
6 |
| Salmon roe |
Nitrate (2) |
| Health food |
Methyl parahydroxybenzoate |
| Biscuits |
TBHQ |
| Malaysia |
Frozen food (other processed product) |
Benzoic acid (4) |
6 |
| Fruit juice drinks |
Sulfur dioxide |
| Shortenings |
TBHQ |
| South Korea |
Salted herring roe |
Polysorbate |
5 |
| Seasoning Pollack roe |
Nitrate |
| Processed fishes viscera |
Polysorbate |
| Salmon roe |
Nitrate |
| Soy bean paste with red pepper |
Sorbic acid |
| Brazil |
Cassava powder |
BHT (3) |
5 |
| Heat meat product |
Nitrate |
| Mix powder for manufacture |
TBHQ |
| Spain |
Candy |
Azorubin (2) |
4 |
| Olive oil |
Sorbic acid |
| Bakery products |
Patent blueⅤ |
| Myanmar |
Salted bamboo shoots |
Sulfur dioxide (2) |
4 |
| Frozen shrimp |
Sulfur dioxide (2) |
| Turkey |
Vegetable preparation |
Sulfur dioxide (3) |
3 |
| Vietnam |
Tapioka starch |
Sulfur dioxide |
3 |
| Boiled octopus |
Sulfur dioxide |
| Frozen food (aquatic animal) |
Sulfur dioxide |
| Belgium |
Candy |
Acid blue 3 sodium salt |
3 |
| Alcoholic beverages |
Azorubin |
| Chocolate |
Quinoline Yellow |
| Hong Kong |
Chinese confectionery |
TBHQ (2) |
3 |
| Dried ume |
Cyclamic acid |
| India |
Syrup |
Azorubin |
2 |
| Frozen food (cereals) |
TBHQ |
| Indonesia |
Chili sauce |
Benzoic acid |
2 |
| Biscuits |
TBHQ |
| Netherlands |
Biscuits |
Sorbic acid (2) |
2 |
| Canada |
Alcoholic beverages |
Sorbic acid |
2 |
| Frozen food (cereals) |
Propionic acid |
| Taiwan |
Karasumi |
Cyclamic acid |
2 |
| Syrup |
Acesulfame potassium |
| Peru |
Fried pulse |
TBHQ |
2 |
| Fruit preparation |
TBHQ |
| Israel |
Syrup |
Cyclamic acid |
1 |
United
Kingdom |
Processed agricultural product |
Amidated pectin |
1 |
| Ecuador |
Snack food |
TBHQ |
1 |
| Australia |
Health food |
Methyl parahydroxybenzoate |
1 |
| Austria |
Chocolate |
Patent blueⅤ |
1 |
| Greece |
Frozen shrimp |
Sulfur dioxide |
1 |
| Croatia |
Salt |
Potassium iodate |
1 |
| Tajikistan |
Dried apricot |
Sulfur dioxide |
1 |
| Panama |
Frozen tuna |
Carbon monoxide |
1 |
| Hungary |
Fruit brandy |
Methanol |
1 |
| Philippines |
Boiled octopus |
Sulfur dioxide |
1 |
| Finland |
Coffee beans |
Magnesium stearate |
1 |
| Total |
119 |
*Gross number of cases violations.
Table 8-5 – Violations by Country, Item for Decay, Deterioration, Nasty smell and Fungus Formation (FY 2014)
Country of Production |
Item Category |
Cases |
| USA |
Wheat(12) |
19 |
| Soybean(3) |
| Rice(2) |
| Kidney beans |
| Potato |
| Thailand |
Rice(18) |
18 |
| Colombia |
Coffee bean(10) |
10 |
| Brazil |
Soybean(4) |
7 |
| Coffee bean(3) |
| Ethiopia |
Coffee bean(6) |
6 |
| Honduras |
Coffee bean(6) |
6 |
| Vietnam |
Coffee bean(5) |
5 |
| Canada |
Soybean(3) |
4 |
| Rape seed |
| Australia |
Wheat |
2 |
| Rice |
| Tanzania |
Coffee bean(2) |
2 |
| Indonesia |
Coffee bean |
1 |
| Timor-Leste |
Coffee bean |
1 |
| France |
Wheat |
1 |
| Total |
82 |
Table 8-6 – Violations by Country and Material for Apparatus, Containers and Packaging (FY 2014)
Country/Region of Production |
Material type |
Violation Details |
Cases* |
| China |
Synthetic resin |
Evaporation residue (21), Coloring agent (3)
Potassium permanganate consumption (2), Lead (2) |
36 |
| Combination |
Evaporation residue (2)
Potassium permanganate consumption (2) |
| Porcelain |
Lead (2) |
| Porcelain enamel |
Lead |
| Paper |
Coloring agent |
| Malaysia |
Rubber |
Zinc (7) |
8 |
| Tin alloy ware |
Lead |
| Italy |
Rubber |
Zinc |
3 |
| Synthetic resin |
Caprolactam |
| Ceramic |
Lead |
| South Korea |
Synthetic resin |
Evaporation residue (2) |
3 |
| Rubber |
Zinc |
| Germany |
Rubber |
Zinc |
3 |
| Synthetic resin |
Caprolactam |
| Ceramic |
Lead |
| USA |
Combination |
Evaporation residue (2)
Potassium permanganate consumption |
3 |
| Hong Kong |
Synthetic resin |
Potassium permanganate consumption (2) |
3 |
| Combination |
Evaporation residue |
| Sweden |
Ceramic |
Cadmium (2) |
2 |
| Spain |
Synthetic resin |
Evaporation residue |
2 |
| Ceramic |
Lead |
| Thailand |
Combination |
Zinc |
2 |
| Porcelain enamel |
Cadmium |
| Taiwan |
Rubber |
Zinc (2) |
2 |
| Turkey |
Synthetic resin |
Evaporation residue |
1 |
| France |
Rubber |
Zinc |
1 |
| Vietnam |
Synthetic resin |
Lead |
1 |
| Total |
|
|
70 |
*Gross number of cases violations.
Table 8-7 – Violations by Country, Item and Violation details for Residual Veterinary Drugs (FY 2014)
Country of Production |
Item Category |
Violation details |
Cases*1 |
| Excess of standard values |
Do not contain |
Non-detectable |
| Vietnam |
Shrimp |
Oxytetracycline(4) |
Enrofloxacin (10), Sulfadiazine |
Furazolidone
(as AOZ) (4),
Chloramphenicol (2) |
26 |
| File fish |
|
|
Chloramphenicol (4) |
| Squid |
|
|
Chloramphenicol |
| India |
Shrimp |
|
|
Furazolidone
(as AOZ) (10) |
10 |
| China |
Octopus |
|
, |
Furazolidone
(as AOZ) (2) |
5 |
| Eel |
|
|
Malachite green |
| Shirimp |
|
Chlortetracycline |
|
| Soft-shelled turtle |
|
Enrofloxacin |
|
| France |
Guinea fowl meat |
Brotizolam |
|
|
1 |
| Total |
42 |
* Gross number of cases violations.
Table 8-8 – Violations by Country and Material for Toys (FY 2014)
Country of Production |
Material type |
Violation Details |
Cases* |
| China |
Combination |
Bisphthalate |
2 |
| Synthetic resin |
Bisphthalate |
| Total |
|
|
2 |
*Gross number of cases violations.
Table 9 – Major Examples of Enhanced Monitoring based on Overseas Information (FY 2014)
Month of Enhancement |
Subject country or area |
Subject Food and Details |
Background and Status |
| July |
Denmark |
Pork
(Possible contamination with diethylstilbestrol) |
Information was received stating that in Denmark contamination with diethylstilbestrol was found in the urine of pigs processed by DANISH CROWN (EST.71) and relevant pork was recalled. When an import notification was made for such recall products, steps were taken for reshipment. |
| July |
France |
Soft and semi-soft natural cheeses
(Possible contamination with enterohemorrhagic E. coli O26) |
Information was received stating that in France contamination with enterohemorrhagic E. coli O26 was found in soft and semi-soft natural cheeses and relevant cheeses were recalled. When an import notification was made for such recall products, steps were taken for reshipment. |
| September |
Taiwan |
Food products
(Possible contamination with waste oil) |
Information was received stating that in Taiwan cooking oils containing waste oil were sold as food product materials and relevant food products using such oils were recalled. When an import notification was made for food products from the relevant manufacturer, steps were taken to contact the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. |
| September |
France |
Soft and semi-soft natural cheeses
(Possible contamination with enterohemorrhagic E. coli O26) |
Information was received stating that in France contamination with enterohemorrhagic E. coli O26 was found in soft and semi-soft natural cheeses. When an import notification was made for such products, an order of inspection for enterohemorrhagic E. coli O26 was made. |
| December |
Switzerland
Germany |
Blended cereals
(Possible contamination with Datura seeds) |
Information was received stating that blended cereals manufactured in Switzerland and packed in Germany were contaminated with Datura seeds and relevant cereals were recalled. When an import notification was made for such recall products, steps were taken for reshipment. |
| February |
Australia |
Crocodile meat
(Possible contamination with metal piece) |
Information was received stating that in Australia contamination with metal was found in crocodile meat and relevant crocodile meat was recalled by the manufacturer. When an import notification was made for such recall meat, steps were taken for reshipment. |
Table 10 – Implementations of Major Bilateral Talks and On-Site Inspections (FY 2014)
Subject Item
(Inspection order item, etc.) |
Bilateral Talks |
Date of Site Survey, etc. |
India, cultured shrimp
(furazolidone) |
The consultation began in November 2012. Talks are continuing on control of furazolidone. |
- |
Poland, Beef
(BSE) |
Based on the Risk Assessment Report issued by FSCJ in April 2014, the consultation with Poland was carried out to lift import bans within the limits of the assessment.
On-site inspections were carried out to confirm the preparation state for enforcing a Japan export verification program. The import ban on Polish beef was lifted in August 2014. |
June 2014 |
China, Onion
(agricultural chemical residues) |
The consultation began in August 2014. Talks are continuing. |
- |
Spain, Meat products and unheated meat products
(Listeria monocytogenes) |
On-site inspections were carried out in October 2014, to verify the sanitation control systems for Listeria monocytogenes in Spain. In December 2014, the Spanish government issued a report on the sanitation control of manufacturers for Listeria monocytogenes, and inspection orders for meat products and unheated meat products from some manufacturers were cancelled. |
October 2014 |
Italy, Unheated meat products, natural cheeses and gorgonzola cheese
(Listeria monocytogenes) |
On-site inspections were carried out in October 2014, to verify the sanitation control systems for Listeria monocytogenes in Italy. In December 2014, the Italian government issued a report on the sanitation control of manufacturers for Listeria monocytogenes, and inspection orders for unheated meat products, natural cheeses and gorgonzola cheese from some manufacturers were cancelled. |
October 2014 |
USA, Beef
(BSE) |
In February 2013, import from designated facilities resumed, with observation of the new Japan export verification program as export conditions. Audits were carried out on facilities approved for export to Japan, to verify observation of the Japan export program. Talks are continuing. |
November 2014 |
Korea, Green hot pepper
(agricultural chemical residues) |
The consultation began in January 2015. Talks are continuing. |
- |
Thailand, Papaya
(genetic modified food) |
The consultation began in July 2013. Talks are continuing on the control of genetic modified foods. |
- |
Thailand, Asparagus, okra, banana, mango and mangosteen
(agricultural chemical residues) |
The consultation began in November 2013. The Thai government conducted investigation and adopted preventive measures pertaining to violations of agricultural chemical residues, and on-site inspections were carried out at registered businesses approved by the Thai government. Talks are continuing. |
February 2015 |
Canada, Beef
(BSE) |
In February 2013, import from designated facilities resumed, with observation of the new Japan export verification program as export conditions. Audits were carried out on facilities approved for export to Japan, to verify observation of the Japan export program. Talks are continuing. |
March 2015 |
Table 11 – Implementation of Exporting Country Pre-Inspections (FY 2014)
|
Argentina |
| Subject of inspection |
System investigation of foods exported to Japan in Argentina |
| Relevant law |
- Food standards (Ley No. 18.284 “Código Alimentario Argentino”)
- Law on general and specific food safety services
(Decreto 4238/68 “Reglamento de inspección de productos, subproductos y derivados de origen animal”)
- Law on export registration for cereals and their by-products
(RESOLUCIÓN EX IASCAV 44/94 “Registro de controladores y certificadores de granos y subproductos con destino a la exportación”), etc. |
| Summary |
Descriptions were given by a representative from the Argentine government on the food sanitation regulations in Argentina, and inspection and opinion exchange were carried out. Further, a seminar on import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan was held targeting Argentine government officials.
Additionally, on-site inspections were carried out at salmon processing facilities and beef slaughterhouse and processing facilities, for the conditions of control. |
| Chile |
| Subject of inspection |
System investigation of foods exported to Japan in Chile |
| Relevant law |
- Food Sanitation Law (Regulamento Sanitario de Los Alimentos DTO. No 977/96)
- Regulation on agricultural and farming services (ESTABLECE NORMAS SOBRE EL SERVICIO AGRICOLA Y GANADERO Ley 18755)
- Law for Fisheries and Aquaculture (Ley Pesca Acuicultura)
- Regulation on food labeling (Decreto Nº 12 respecto a la normativa gráfica para el etiquetado informativo en los alimentos), etc.
|
| Summary |
Descriptions were given by a representative from the Chilean government on the food sanitation regulations in Chile, and inspection and opinion exchange were carried out. Further, a seminar on import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan was held targeting government officials etc.
Additionally, on-site inspections were carried out at pig farms, slaughterhouses and salmon farms/processing facilities for the conditions of veterinary drug control . |
| Paraguay |
| Subject of inspection |
System investigation of foods exported to Japan in Paraguay |
| Relevant law |
- Sanitation Law (LEY N°836/80)
- Law on Establishing the National Plant and Seed Quality and Health Service (LEY N°2459/2004)
- Law on Establishing the National Animal Quality and Health Service (LEY N°2426/2004)
|
| Summary |
Descriptions were given by a representative from the Paraguayan government on the food sanitation regulations in Paraguay, and opinion exchange was carried out. Further, a seminar on import food monitoring systems and sanitation regulations in Japan was held targeting the Paraguayan government officials, food suppliers, etc.
Additionally, on-site inspections were carried out for the conditions of agricultural chemical residues control of sesame seeds, pertaining to those exported to Japan. |
Table 12 – Outcomes of Import Consultations at Office on Imported Food Consultation by FY
| |
FY 2010 |
FY 2011 |
FY2012 |
FY2013 |
FY2014 |
| Import consultations implemented |
14,324 |
15,122 |
13,962 |
12,492 |
11,826 |
| Import consultations on item-by-item basis |
34,479 |
27,334 |
27,825 |
23,903 |
24,360 |
| Violations on item-by-item basis |
426 |
354 |
372 |
354 |
257 |
* Offices of Imported Food Consultation are set up in each quarantine station in Otaru, Sendai, Narita Airport, Tokyo, Yokohama, Niigata, Nagoya, Osaka, Kansai Airport, Kobe, Hiroshima, Fukuoka, and Naha.
* Figures include only advance consultations implemented prior to import in Office of Imported Food Consultation.
Table 13 – Number of Violations in Import Consultation by Provision (FY 2014)
| Provision |
Violations (cases) |
Proportion(%) |
Details of major violations |
Article 6
(Foods and additives prohibited to distribute, etc.) |
2 |
0.6 |
Use of lupin
Puffer fish (non-importable fish forms) |
Article 9
(Prohibition of distribution, etc. of diseased meat, etc.) |
8 |
2.2 |
Use of material sourced from beef arriving via countries with incidents of BSE (instruct to keep from importing) |
Article 10
(Limitation on distribution, etc. of additives, etc.) |
162 |
45.3 |
Use of L-Cysteine, TBHQ, α-ketoglutaric acid, Potassium aspartate, Azorubin, Sodium aluminium silicate,
Carboxymethylcellulose, Magnesium citrate, Citrulline, Pantothenic acid, Sodium molybdate, Iodized salt, Potassium iodate, Malic acid, Ferric phosphate, Chromium chloride, Zinc oxide, Potassium sodium tartrate, Manganese sulfate, Magnesium aspartate, etc. |
Article 11
(Standards and criteria for foods and additives) |
186 |
52.0 |
Non-compliance with manufacturing and stroage standard, Violation of usage standards for additives
・ Non-compliance with manufacturing standard: inadequate sterilization of soft drink, etc.
・ Use to inhibited foods: use of sodium benzoate in instant noodle, etc.
・ Use of excessive amounts: use of acesulfame potassium in jam, etc.
・ Residue of excessive amounts: residue of sulfur dioxide in soft drink, etc.
|
| Total |
358 (Gross)
257 (Actual) |
|
Table 14 – Cases of Import Consultations by County, Item and Violation details (FY 2014)
| Country of Production |
Item |
Violation details |
Cases※2 |
| USA |
Health food |
Potassium sorbate(8), α-Ketoglutaric acid(3), Potassium sodium tartrate(3), Potassium aspartate(3), Malic acid(3), Sodium benzoate(3), Magnesium aspartate(3), Citrulline(3), Choline bitartrate(2), Magnesium stearate(2), Magnesium citrate(2), Methylcobalamin(2), Sodium selenite, Chromium picolinate, Zinc citrate, Riboflavin-5'-phosphate, Manganese gluconate, Choline acid tartrate, Glutathione, Potassium bicarbonate, Calcium hydrogen citrate, Acetyl carnitine, Iodine, Croscarmellose sodium, Potassium iodide, Salidroside, Zinc gluconate, Magnesium lactate, Choline chloride, Manganese sulfate, L-cysteine, Talin, Nicoxatin, Biotin, Pantothenic acid, Aspartic acid, Selenomethionine |
117 |
| Cereals preparation |
Chromium chloride(3), Manganese sulfate(3), Zinc oxide(3), Potassium iodate(3), Sodium molybdate(3), Ferric phosphate(3) |
| Powdered soft drink |
Sodium aluminosilicate(6), Ethylene oxide |
| Confectionery |
TBHQ, Potassium sorbate, Potassium bromate, Calcium propionate, Sodium benzoate |
| Soft drink |
Potassium benzoate, Potassium sorbate, Retinol acetate, Sodium sorbate, Potassium sodium L-tartrate |
| Seasoning |
Potassium sorbate(4) |
| Meat products |
Non-conformity with manufacturing standard(2), Use of material sourced from beef in the countries with incidents of BSE |
| Chocolate |
TBHQ(3) |
| Sauce |
Cross linked sodium carboxy methyl cellulose, Sodium stearoyl lactylate |
| Wine |
Potassium sorbate(2) |
| Food additive (Argon, Manganese gluconate) |
Undesignated additives |
| Syrup |
Sodium benzoate |
| Frozen food (cereals) |
Calcium propionate |
| Filter aid |
Potassium sodium tartrate |
| Other food |
Fine silicon dioxide |
| Taiwan |
Jam |
Potassium sorbate(5), Acesulfame potassium(5) |
32 |
| Other food |
Sodium stearoyl lactylate(4), Sodium aluminium silicate(2), Carboxymethylcellulose, Potassium sorbate |
| Confectionery |
Potassium sorbate(6), Carmine |
| Soft drink |
Potassium sorbate(2), Non-conformity with manufacturing standard(2), Sodium benzoate |
| Fruits puree |
Sodium benzoate |
| Health food |
Polyethylene glycol |
| Italy |
Sauce |
Potassium sorbate(7) |
26 |
| Confectionery |
Zinc oxide, Sodium copper chlorophyllin, Manganese sulfate, Potassium iodide, Potassium sorbate, Sodium selenite |
| Sorbet |
Non-conformity with manufacturing standard(3) |
| Caffeineless coffee |
Ethyl acetate, Methylene chlorides, Dichloromethane |
| Health food |
Azorubine, Magnesium stearate |
| Brine pickled olives |
Ferrous gluconate |
| Chocolate |
Iron sesquioxide |
| Natural cheese |
Potassium sorbate |
| Wine |
Argon |
| Frozen food (Fishes) |
Sodium iodide |
| Spain |
Soft drink |
Pantothenic acid(2), Glucuronolactone(2), Potassium sorbate |
22 |
| Processed fishes |
Sodium benzoate, Copper chlorophyll, Black PN |
| Yogurt |
Use of material sourced from beef in the countries with incidents of BSE(3) |
| Processed aquatic animals |
Potassium ascorbate(2) |
| Sparkling wine |
Iron sesquioxide, Sorbic acid |
| Chocolate |
Patent blue V, Azorubine |
| Food additive |
Enzymatically decomposed sunflower lecithin(2) |
| Meat products |
Monosodium citrate |
| Natural cheese |
Polyvinyl acetate |
| Frozen food (cereals) |
L-cysteine |
| France |
Frozen food (cereals) |
Sodium iodide(4), L-cysteine, L-cysteine monohydrochloride, Potassium sorbate |
17 |
| Soft drink |
Non-conformity with manufacturing standard(6) |
| Liqueur |
Nitrous oxide(3) |
| Seasoning |
Potassium sorbate |
| Thailand |
Cashewnut |
Sodium iodide(3), Sodium aluminum silicate |
16 |
| Mixed nuts |
Sodium iodide(2), Sodium aluminum silicate |
| Confectionery |
Sodium iodide, Acesulfame potassium |
| Fruits Preparing |
Carboxymethylcellulose(2) |
| Soft drink |
Potassium sorbate |
| Seasoning |
Sodium benzoate |
| SorbetIce confectionery |
Sodium copper chlorophyllin |
| Macadamia nut |
Sodium iodide |
| Frozen food |
Sodium iodide |
| China |
Wakame |
Food yellow no.4, Food blue no.1, Chlorine dioxide |
16 |
| Cereals preparation |
Calcium propionate, Potassium propionate |
| Suger |
Sodium benzoate, Potassium sorbate |
| Confectionery |
Potassium propionate |
| Health food |
Ethyl acetate |
| Sauce |
Food yellow no.2 |
| Soy bean |
Hydrogen cyanide |
| Pepper preparation |
Potassium sorbate |
| Agricultural processed foods |
Carboxymethylcellulose |
| Fugu (puffy fish) |
Non-importable fish forms |
| Western confectionery |
Potassium sorbate |
| Frozen food (cereals) |
Calcium propionate |
| Canada |
Soft drink |
Potassium sorbate(4), Zinc chelate, Magnesium citrate |
11 |
| Powdered soft drink |
Potassium iodide, Chromium ascorbate, Potassium bicarbonate, Zinc ascorbate, Manganese gluconate |
| South Korea |
Health food |
Zinc oxide(2), HPMCP, Polyvinyl alcohol |
11 |
| Seasoning |
Potassium sorbate(2), Carboxymethylcellulose |
| Cereals preparation |
Zinc oxide, Ferrous fumarate |
| Frozen food (cereals) |
Non-conformity with storage standard |
| Food additive |
Sodium silicate |
| Netherlands |
Confectionery |
Magnesium stearate(6) |
8 |
| Fruits in syrup |
Sodium benzoate(2) |
| New Zealand |
Sorbet |
Non-conformity with manufacturing standard(4) |
8 |
| Fruit wine |
Potassium sorbate(2) |
| Flaxseed oil |
Argon |
| Frozen food (cereals) |
L-cysteine |
| Czech |
Powdered soft drink |
Magnesium citrate(3), Riboflavin 5'-phosphate |
7 |
| Health food |
Propionic acid, Potassium sorbate |
| Collagen casing |
Use of material sourced from beef in the countries with incidents of BSE |
| Brazil |
Soft drink |
Potassium sorbate(2), Glucuronolactone |
7 |
| Fruits preparing |
Carboxymethylcellulose |
| Health food |
Polyethylene glycol |
| Powdered soft drink |
Carboxymethylcellulose |
| Other food |
Acesulfame potassium |
| Myanmar |
Instant noodle |
Potassium sorbate(3), Sodium benzoate(3),
Carboxymethylcellulose |
7 |
| Vietnam |
Soft drink |
Non-conformity with manufacturing standard(4) |
6 |
| Sauce |
Potassium sorbate |
| Western confectionery |
Sodium propionate |
| Indonesia |
Health food |
L-glutathione(2), Iodine |
5 |
| Seasoning |
Sodium benzoate(2) |
| Denmark |
Other food |
Sodium benzoate(2), Potassium sorbate(2) |
5 |
| Sauce |
L-cysteine |
| Malaysia |
Prepared fruits |
Iron sesquioxide, Potassium sorbate |
5 |
| Soft drink |
Potassium sorbate |
| Frozen food (cereals) |
L-cystein, BHA |
| Costa Rica |
Soft drink |
Non-conformity with manufacturing standard(4) |
4 |
| Belgium |
Soft drink |
Sulfer dioxide(3) |
4 |
| Alcoholic beverage |
Sodium benzoate |
| United Kingdom |
Shrimp |
4-hexylresorcin |
3 |
| Seasoning |
Benzoic acid |
| Suger |
Potassium sorbate |
| Zambia |
Seasoning |
Sodium benzoate(2), Potassium sorbate |
3 |
| Turkey |
Confectionery |
Use of material sourced from beef in the countries with incidents of BSE(3) |
3 |
| Hungary |
Meat products |
Non-conformity with storage standard(2), calcium disodium ethylendiaminetetraacetate |
3 |
| Colombia |
Confectionery |
Sodium benzoate, Potassium sorbate |
2 |
| Germany |
Health food |
Vitamin K1 |
2 |
| Food additive preparation |
Magnesium hydrogencarbonate |
| Finland |
Jam |
Sodium benzoate(2) |
2 |
| India |
Confectionery |
Propionic acid |
1 |
| Australia |
Pulses |
Lupine beans |
1 |
| Kenya |
Confectionery |
Azorubine |
1 |
| Singapore |
Substitute tea |
Irradiation |
1 |
| St. Lucia |
Sauce |
Sodium benzoate |
1 |
| Undetermined |
Placenta powder |
Potassium sorbate |
1 |
| Total |
358 |
* Gross number of cases violations.
Table 15 – Imported Food Violations Detected IN Domestic Monitoring (FY 2014)
| Country of Production |
Item |
Violation Details |
Cases* |
| South Korea |
Cultured olive flounder |
Kudoa septempunctata (4) |
4 |
| China |
Snap pea |
Diniconazole |
4 |
| Rice noodle |
Unauthorised genetically modified rice (63Bt) |
| Frozen food(squid) |
E.coli |
| Frozen shinoda maki |
Bacterial count |
| USA |
Biscuit |
TBHQ |
3 |
| Dried peach |
Sulfur dioxide |
| Celery |
Bifentherin |
| Spain |
Liqueur |
Patent blue V |
2 |
| Frozen food(onion) |
Bacterial count |
| India |
Frozen food(green pea) |
E.coli |
1 |
| Greece |
Honey |
Coumafos |
1 |
| Total |
15 |
*Gross number of cases violations.
(Reference) Description of Key Terms
| Term |
Description |
| Zinc chelate |
Undesignated addtive |
| Nitrous oxide |
Additive (Pressurizing agent) |
| Acid blue 3 sodium salt |
Undesignated additive |
| Nitrite |
Additive (color fixative agent) |
| Zinc ascorbate |
Undesignated additive |
| Potassium ascorbate |
Undesignated additive |
| Chromium ascorbate |
Undesignated additive |
| Aspartic acid |
Additive (Flavor enhancer) |
| Potassium aspartate |
Undesignated additive |
| Magnesium aspartate |
Undesignated additive |
| Acesulfame potassium |
Additive (sweetener) |
| Acethyl carnitine |
Undesignated additive |
| Acetochlor |
Agricultural chemical (anilide herbicide) |
| Acephate |
Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Sodium selenite |
Undesignated additive |
| Azorubine |
Undesignated additive |
| Aflatoxin |
Mycotoxin produced by the fungus Aspergillus, etc. |
| Amidated pectin |
Undesignated additive |
| Ametryn |
Agricultural chemical (triazine herbicide) |
| Argon |
Undesignated additive |
| Argon gas |
Undesignated additive |
| Sodium aluminosilicate |
Undesignated additive |
| Benzoic acid |
Additive (preservative) |
| Potassium benzoate |
Undesignated additive |
| Sodium benzoate |
Additive (preservative) |
| Carbon monoxide |
Undesignated additive |
| Isoprocarb |
Agricultural chemical (insecticide) |
| Isoprothiolane |
Agricultural chemical (fungicide) |
| Genetic modification |
Technology such as fragmentation of bacterial genes, followed by arrangement of the gene sequences or introducing the arranged genes into other organism’s genes. |
| Imidacloprid |
Agricultural chemicals (Neonicotinoid insecticide) |
| Indoxacarb |
Agricultural chemical (insecticide) |
| Ethylene oxide |
Undesignated additive |
| Calcium Disodium Ethylenediaminetetraacetate |
Additive (Antioxidizing agent) |
| Chromiun chloride |
Undesignated additive |
| Choline chloride |
Undesignated additive |
| Methylene chloride |
Undesignated additive |
| Endosulfan |
Agricultural chemical (organochlorine insecticide) |
| Enrofloxacin |
Veterinary drug (new quinolone synthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Ofloxacin |
Veterinary drug (synthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Cross linked sodium carboxy methyl cellulose |
Undesignated additive |
| Carbaryl |
Agricultural chemical (carbamate insecticide) |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose |
Undesignated additive |
| Calmin |
Undesignated additive |
| Quinoline yellow |
Undesignated additive |
| Zinc citrate |
Undesignated additive |
| Monosodium citrate |
Undesignated additive |
| Magnesium citrate |
Undesignated additive |
| Coumaphos |
Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Glyphosate |
Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous herbicide) |
| Glucuronolactone |
Undesignated additive |
| Zinc gluconate |
Additive (enhancer) |
| Ferrous gluconate |
Additive (color stabilizer) |
| Manganese gluconate |
Undesignated additive |
| Glutathione |
Undesignated additive |
| Croscarmellose sodium |
Undesignated additive |
| Clostridial bacteria |
Pathogenic microorganism (a bacterium that normally lives in soils, as well as in intestines of human and animals. ex: Clostridium perfringens, Clostridium botulinum)) |
| Chloramphenicol |
Veterinary drug (chloramphenicol antibiotical agent) |
| Chlorpyriphos |
Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Potassium aluminium silicate |
Undesignated additive |
| Sodium silicate |
Undesignated additive |
| Diarrhetic shellfish toxin |
Shellfish toxin (mainly refers to toxins produced by a harmful plankton accumulated in clams, toxic clams cause diarrhetic poisoning) |
| Enzymatically decomposed sunflower lecithin |
Undesignated additive |
| Cyclamic acid |
Undesignated additive |
| Salidroside |
Undesignated additive |
| Ethyl acetate |
Additive (manufacturing agent) |
| Retinol acetate |
Undesignated additive |
| Polyvinyl acetate |
Additive (gumbase) |
| Salmonella spp. |
Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium that is ubiquitous in the intestines of animals as well as in nature, such as rivers, sewage and lakes. It contaminates meat, mostly poultry and eggs, and causes acute abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever and vomiting.) |
| Zinc oxide |
Undesignated additive |
| Choline acid tartrate |
Undesignated additive |
| Cyanide |
Harmful or poisonous compound (cyanide-related compounds (e.g., cyanogenic glycoside) ) found in vegetables such as some varieties of beans. |
| Hydrogen cyanide |
Undesignated additive |
| Diethylstilbestrol |
Veterinary drug (hormonal agent) |
| Dichloromethane |
Undesignated additive |
| Dicofol |
Agricultural chemicals (organochloric insecticide) |
| Citrulline |
Undesignated additive |
| Diniconazole |
Agricultural chemical (triazole fungicide) |
| Difenoconazole |
Agricultural chemical (triazole fungicide) |
| Diflubenzuron |
Agricultural chemical (urea insecticide) |
| Cypermethrin |
Agricultural chemical (pyrethroid insecticide) |
| Choline bitartrate |
Undesignated additive |
| Potassium bromate |
Additive (flour treatment agents) |
| Potassium sodium tartrate |
Undesignated additive |
| Food Yellow No.2 |
Undesignated additive |
| Food Yellow No.4 (Tartrazine) |
Additive (coloring agent) |
| Food Blue No.1 (Brilliant Blue FCF) |
Additive (coloring agent) |
| Magnesium stearate |
Additive (enhancer) |
| Sodium stearoyl lactylate |
Additive (emulsifier) |
| Sulfadiazine |
Veterinary drug (fungicide) |
| Sulfadimidine |
Veterinary drug (synthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Sulfamethoxazole |
synthetic antibacterial agent (sulfa agent) |
| Selenomethionine |
Undesignated additive |
| Sorbic acid |
Additive (preservative) |
| Potassium sorbate |
Additive (preservative) |
| Sodium sorbate |
Undesignated additive |
| Talin |
Undesignated additive |
| Potassium bicarbonate |
Undesignated additive |
| Magnesium bicarbonate |
Undesignated additive |
| Thiamethoxam |
Agricultural chemicals (Neonicotinoid insecticide) |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus |
Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium living in seawater (estuaries, coastal areas, etc.) that commonly contaminates fish and shellfish, and causes abdominal pain, watery diarrhea, fever and vomiting.) |
| Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli ( E.coli ) O26, O157 etc. |
Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium that normally lives in the intestines of animals. It contaminates foods and drinking water by way of faces and urine, and causes acute abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea together with large amounts of blood after early cold-like symptoms.) |
| Dieldrin |
Agricultural chemical (organochlorine insecticide) |
| Tetracyclines antibiotics |
Generic name of the antibiotics having a constant spectrum. i.e., oxytetracycline, chlortetracycline and tetracycline etc. |
| Sodium copper chlorophyllin |
Additive (coloring agent) |
| Copper chlorophyll |
Additive (coloring agent) |
| Triadimenol |
Agricultural chemical (phenoxy fungicide) |
| Triazophos |
Agricultural chemical (phenoxy insecticide) |
| Tricyclazole |
Agricultural chemical (benzothiazole herbicide) |
| Natamycin |
Additive (preservative) |
| Nicoxatin |
Undesignated additive |
| Sulfur dioxide |
Additive (antioxidant agents) |
| Chlorine dioxide |
Additive (flour treatment agents) |
| Magnesium lactate |
Undesignated additive |
| Paclobutrazol |
Agricultural chemical (triazole growth regulator) |
| Patulin |
Mycotoxin (produced by the fungi such as Penicillium and Aspergillus) |
| Patent blue V |
Undesignated additive |
| Methyl p-hydroxybenzoate |
Undesignated additive |
| Haloxyfop |
Agricultural chemical (herbicide) |
| Pantothenic acid |
Undesignated additive |
| Biotin |
Additive (nutrition enhancer) |
| Chromium picolinate |
Undesignated additive |
| Vitamin K1 |
Undesignated additive |
| Calcium hydrogen citrate |
Undesignated additive |
| HPMCP (Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate) |
Undesignated additive |
| Bifenthrin |
Agricultural chemical (insecticide) |
| Pyridaben |
Agricultural chemical (insecticide) |
| Pirimiphos methyl |
Agricultural chemical (insecticide) |
| Silicon dioxide (fine) |
Additive (manufacturing agent) |
| Fipronil |
Agricultural chemical (heterocyclic synergist) |
| Fenitrothion |
Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Phenthoate |
Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Fenvalerate |
Agricultural chemical (pyrethroid insecticide) |
| Bisphthalate |
Plasticizer |
| Buprofezin |
Agricultural chemical (thiadiazine insecticide) |
| Ferrous fumarate |
Undesignated additive |
| Furazolidone |
Veterinary drug (nitrofuran synthetic antibacterial agent) ; generates AOZ when metabolized |
| Black PN |
Undesignated additive |
| Fluquinconazole |
Agricultural chemical (fungicide) |
| Flusilazole |
Agricultural chemical (triazole fungicide) |
| Brotizolam |
Veterinary Drug |
| Flonicamid |
Agricultural chemical (pyridinecarboxyamide insecticide) |
| Propionic acid |
Additive (preservative) |
| Calcium propionate |
Additive (preservative) |
| Potassium propionate |
Additive (preservative) |
| Sodium propionate |
Additive (preservative) |
| Propiconazole |
Agricultural chemical (fungicide) |
| Profenophos |
Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Prometryn |
Agricultural chemical (triazine herbicide) |
| Hexaconazole |
Agricultural chemical (triazole fungicide) |
| Pencycuron |
Agricultural chemical (urea fungicide) |
| Boric acid |
Undesignated additive |
| Polyethylene glycol |
Undesignated additive |
| Polysorbate |
Additive (emulsifier) |
| Polyvinyl alcohol |
Undesignated additive |
| Paralytic shellfish poison |
Shellfish poison (mainly refers to toxins produced by a harmful plankton accumulated in clams, toxic clams cause paralytic poisoning) |
| Malachite green |
Veterinary drug (triphenylmethane synthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Methanol |
Undesignated additive |
| Methamidophos |
Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Metalaxyl |
Agricultural chemical (anilide fungicide) |
| Methylcobalamin |
Undesignated additive |
| Mefenoxam |
Agricultural chemical (anilide fungicide) |
| Sodium molybdate |
Undesignated additive |
| Potassium iodide |
Undesignated additive |
| Iodine |
Undesignated additive |
| Iodized salt |
Undesignated additive |
| Potassium iodide |
Undesignated additive |
| Listeria monocytogenes |
Pathogenic microorganism (A normal flora in the natural environment that contaminates daily products and processed meat products, and causes influenza-like symptoms including tiredness and fever) |
| Manganese sulfate |
Undesignated additive |
| Riboflavin-5’-phosphate |
Undesignated additive |
| Maric acid |
Undesignated additive |
| Ferric phosphate |
Undesignated additive |
| 2,4-D |
Agricultural chemical (phenoxy acid herbicide) |
| 4-Chlorophenoxyacetic acid |
Agricultural chemical (plant growth regulator) |
| 4-hexylresorcin |
Undesignated additive |
| Iron sesquioxide |
Additive (coloring agent) |
| BHA (butylated hydroxyanisole) |
Additive (antioxidant agent) |
| BHT (butylhydroxytoluene) |
Additive (antioxidant agent) |
| BSE (bovin spongiform encephalopathy) |
An indolent malignant central neurological disease in cattle that causes a spongy degeneration in the brain tissues and symptoms including astasia. |
| EPN |
Agricultural chemical (organophosphorous insecticide) |
| Kudoa septempunctata |
Kind of parasite that causes food poisoning. (Myxosporidia) |
| L-glutathione |
Undesignated additive |
| L-cysteine |
Undesignated additive |
| L-cysteine hydrochloride |
Additive (enhancer) |
| Potasium sodium L-tartate |
Undesignated additive |
| TBHQ |
Undesignated additive |
| α-ketoglutaric acid |
Undesignated additive |







