Overview
An Overview of TB Preventive Measures

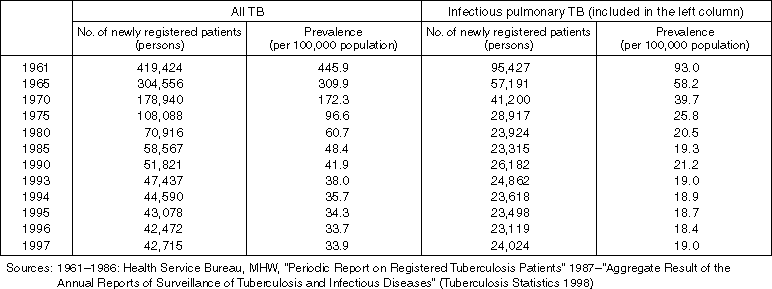
Detailed Data 1
Number of Newly Registered Patients and the Rate of Prevalence
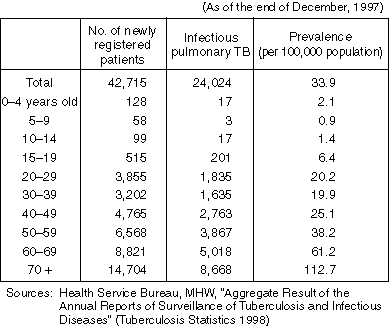
Detailed Data 2
Number of Newly Registered Patients and the Rate of Prevalence (per 100,000 Population) by Age Group
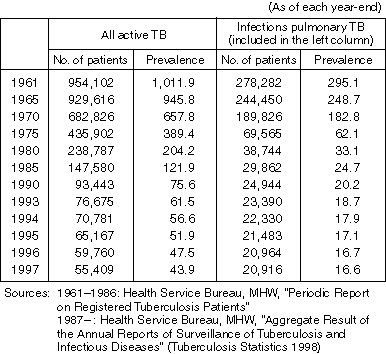
Detailed Data 3
Number of Registered Patients With Active TB and the Rate of Prevalence (per 100,000 Population)
Overview
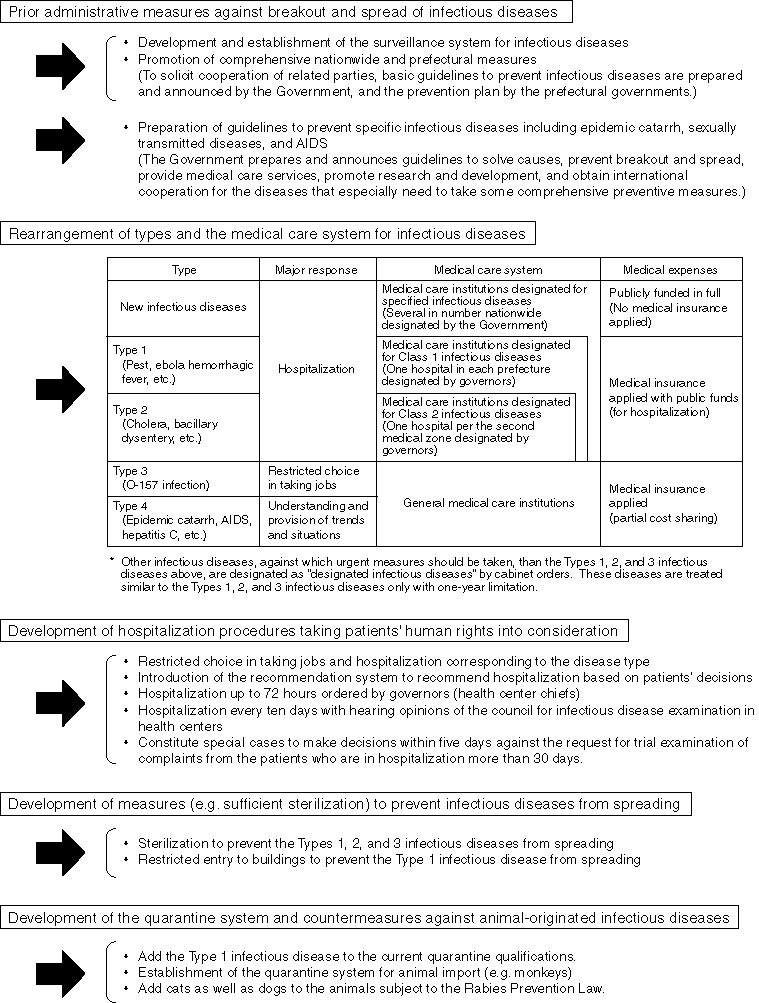
Summary of the Law Regarding Infectious Disease Prevention and Medical Care for the Patients
(Established on September 28, 1998, enforced on April 1, 1999)
Overview
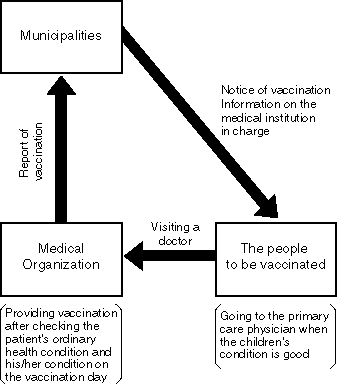
System of Vaccination (Individual Vaccination)
Detailed Information 1
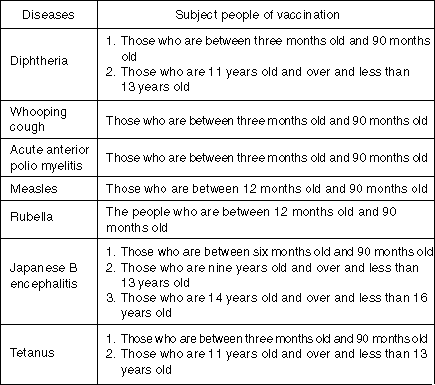
Subject Diseases and Subject People of Regular Vaccination
Detailed Information 2
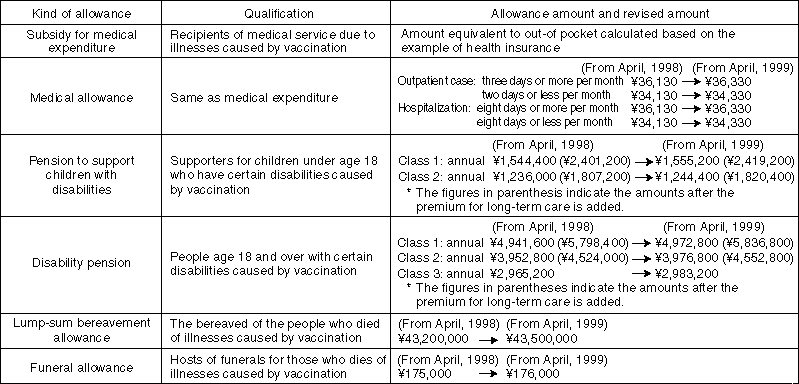
Kind and Amount of Relief Measures for Sufferers of Vaccination-Related Complications
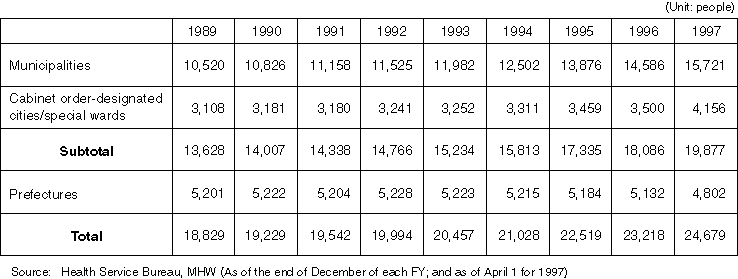
Detailed Data 1
Relief System for Sufferers of Vaccination-Related Complications
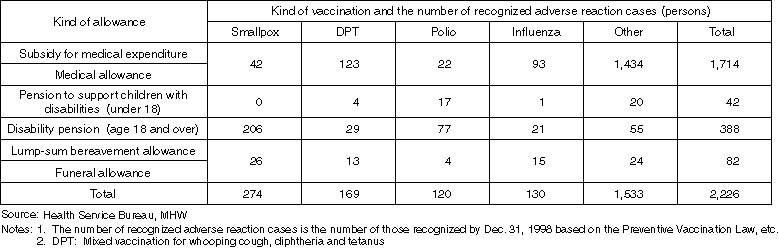
Overview
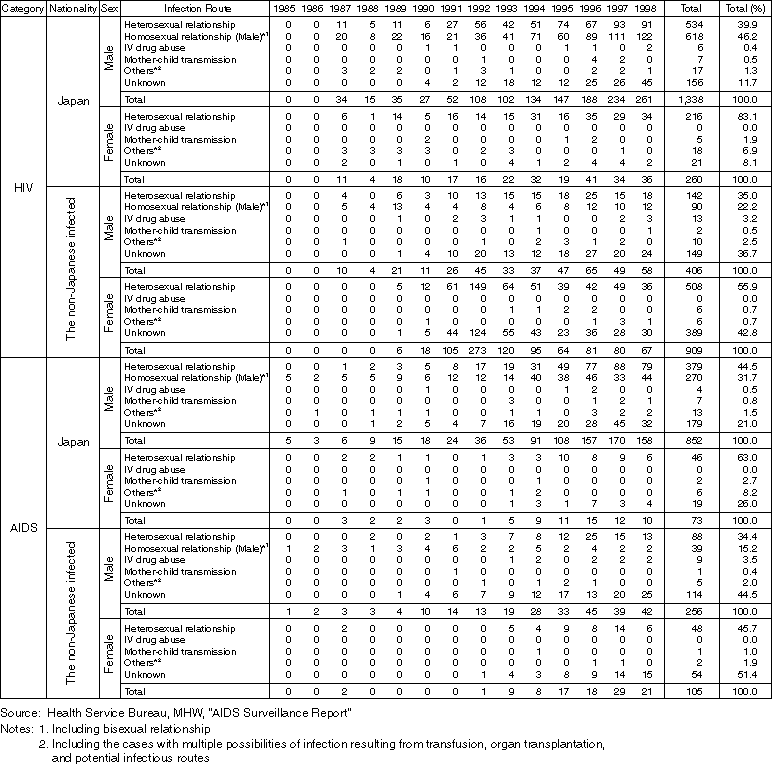
Detailed Data 1
Annual Changes in the Number of HIV Carriers and AIDS Patients by Nationality, Sex, and Infection Route
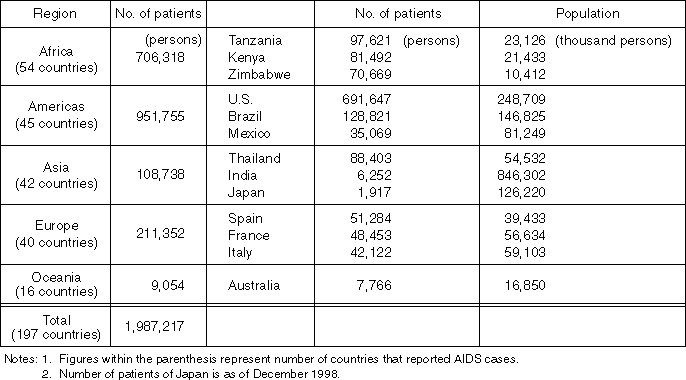
Detailed Data 2
AIDS Patients in the World (WHO Report on November 15, 1998)
Overview
Changes in National Health Promotion Measures
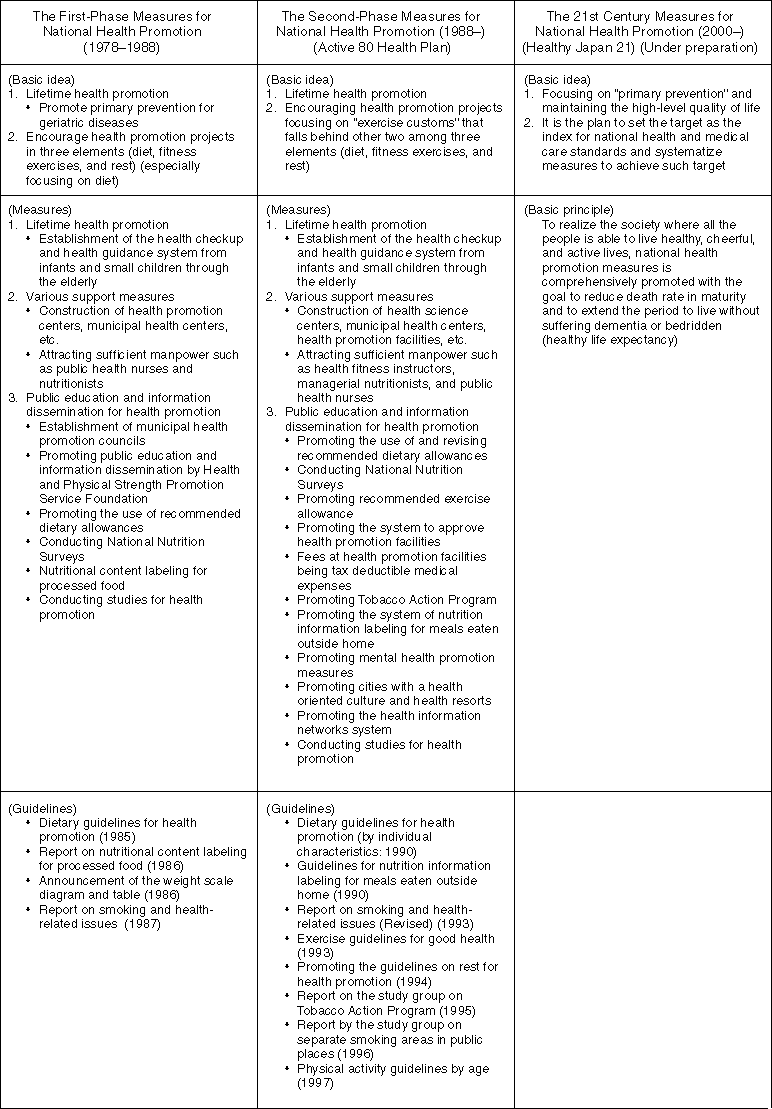
Detailed Information 1
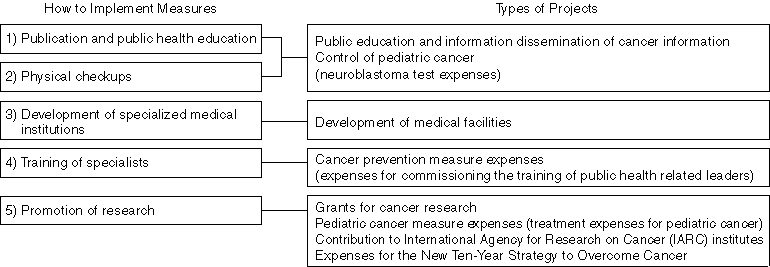
History of Japan's Cancer Control

Detailed Information 2
An Outline of the New Ten-Year Strategy to Overcome Cancer
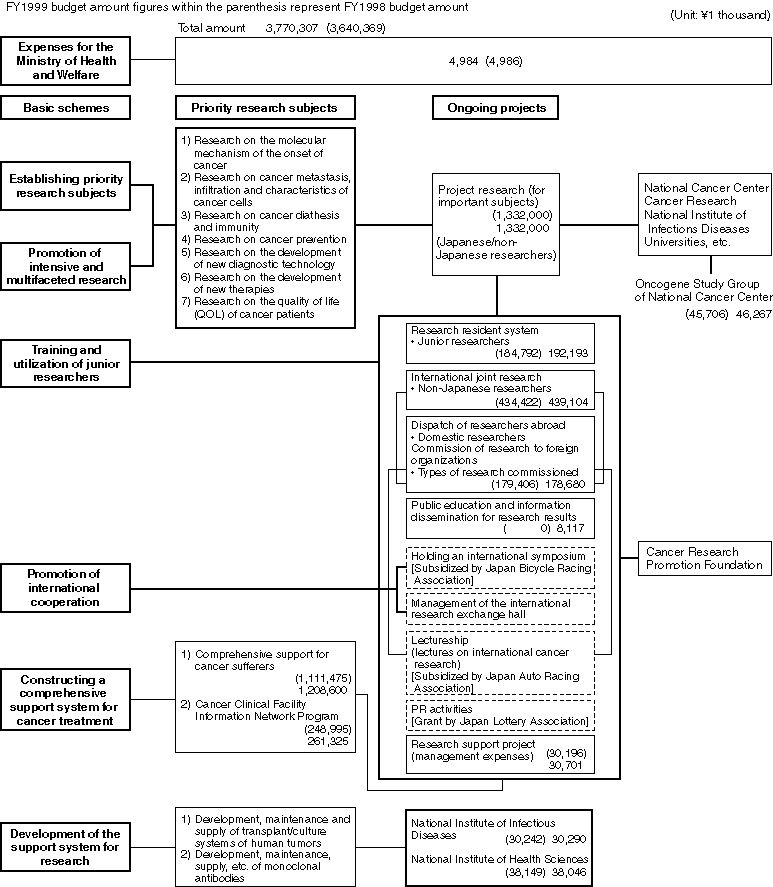
From the "Comprehensive Ten-Year Strategy for Cancer Control" to the "New Ten-Year Strategy to Overcome Cancer"
After the "Comprehensive Ten-Year Strategy for Cancer Control" ended in fiscal 1993, the "New Ten-Year Strategy to Overcome Cancer" was implemented starting in fiscal 1994 (with the fiscal 1999 budget of \19,213 million.) as a joint project among the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Ministry of Education, and Science and Technology Agency. This new scheme places priority on further substantiation of basic studies of cancer pathology as well as its application to clinical research.
As well as expanding research support programs in such areas as manpower and research materials, the Ministry of Health and Welfare plans to promote the Cancer Information Network, which is a comprehensive support system for cancer diagnosis and treatment for the purpose of disseminating results of the research to clinics and hospitals nationwide. Through this program, the Ministry intends to correct the gaps in medical standards throughout Japan.
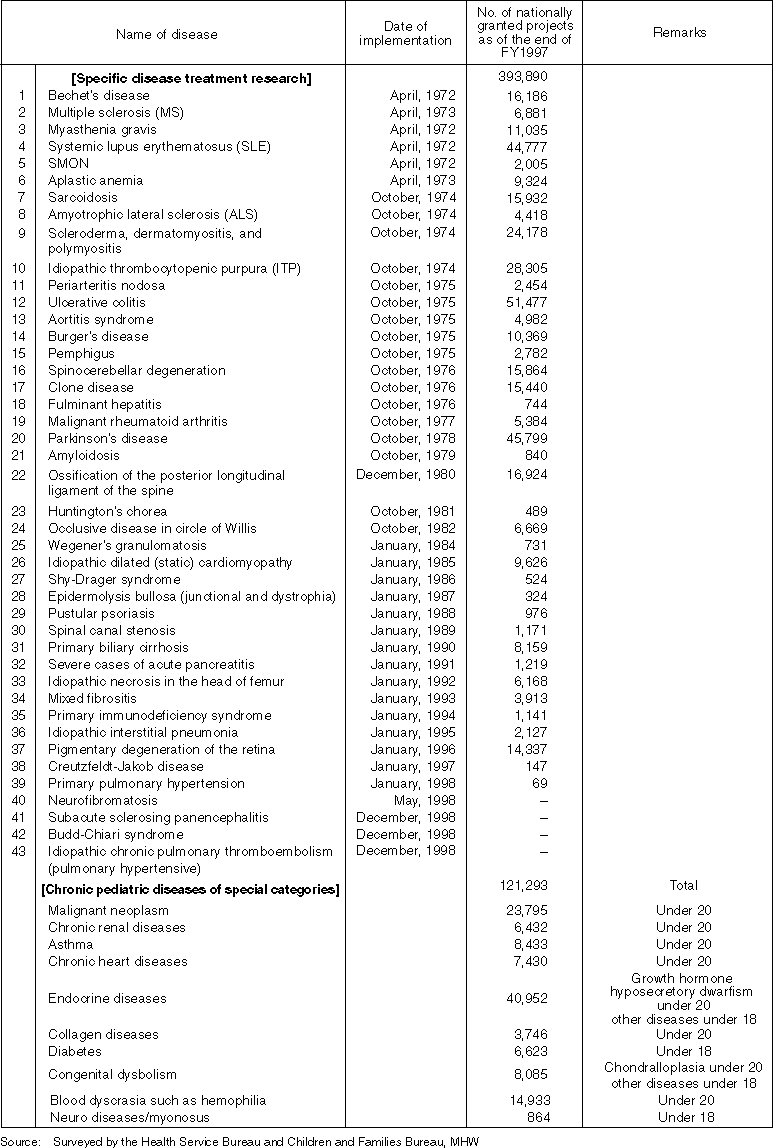
Various projects have been implemented based on the "Outline of the Measures against Intractable Diseases" instituted in 1972.
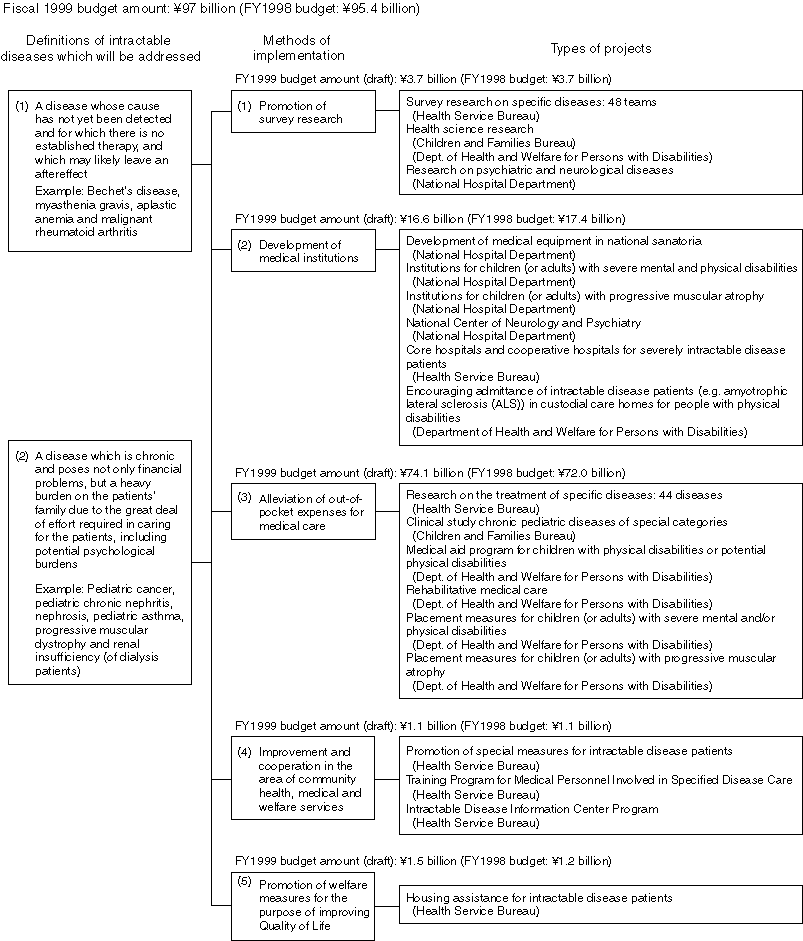
Detailed Data 1
Diseases Subject to Specific Disease Research
Overview
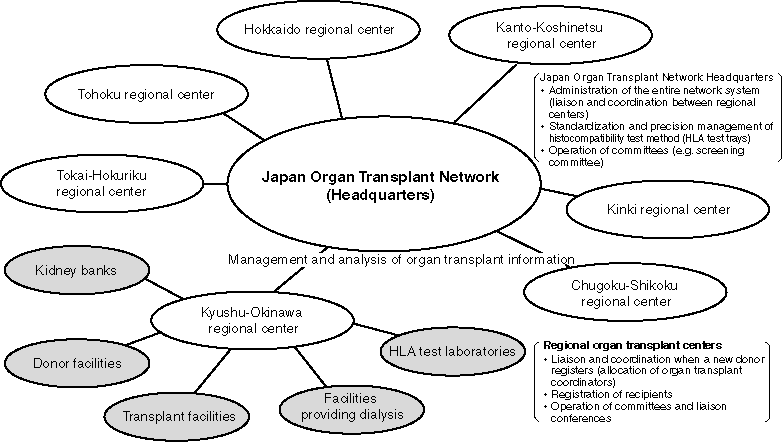
New Organ Transplant System
Organ Transplant Network System
The existing kidney transplant system was reviewed and beginning in fiscal 1995, a centralized, nationwide kidney transplant network was launched. This network subsequently expanded according to enforcement of the "Organ Transplant Law" (October 1997), which enabled multi-organ transplant. The headquarters of the network was established in a central location and seven regional kidney transplant centers were set up in different parts of Japan. Through these facilities, the Ministry of Health and Welfare seeks to improve the equity and appropriateness of the organ distribution by, for example, selecting patients to receive organ transplants based on universal standards. Main services are provided predominantly through the Japan Organ Transplant Network. Moreover, 44 kidney banks which have been established nationwide are promoting public education regarding kidney transplants.
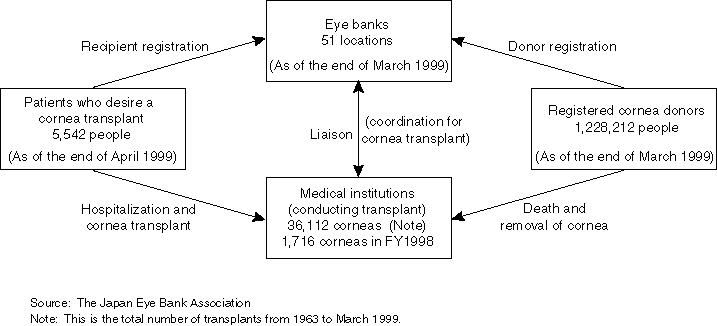
Cornea Transplant System
The Japan Eye Bank Association plays a central role in cornea transplants and 51 eye banks throughout the country promote public education on cornea transplants, register donors and mediate the transplants.
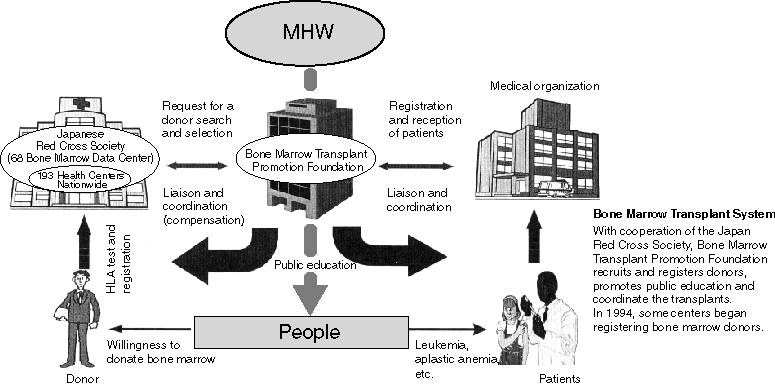
Bone Marrow Transplant System Chart
Detailed Data 1
Changes in the Number of Dialysis Patients, Registered Patients Desiring Kidney Transplant and Administered Transplants
(1) Before establishment of Japan Organ Transplant Network
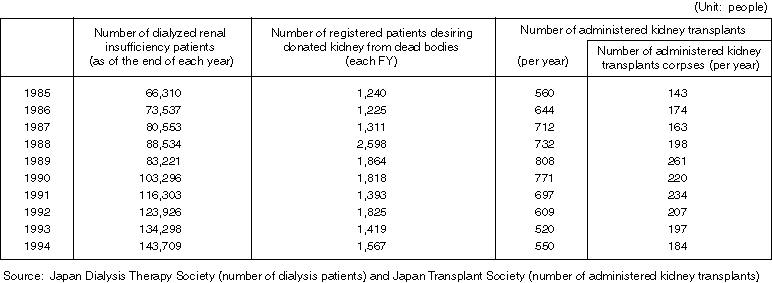
(2) After establishment of Japan Organ Transplant Network
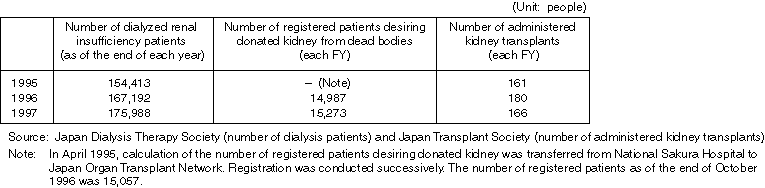
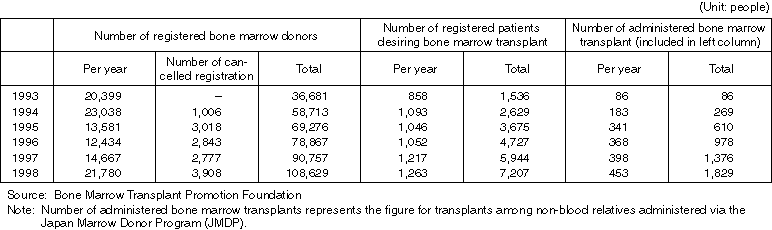
Detailed Data 2
Changes in the Number of Registered Bone Marrow Donors, Registered Patients Desiring Bone Marrow Transplant, and Administered Transplants
Overview
History of the 8020 (Eighty-Twenty) Campaign

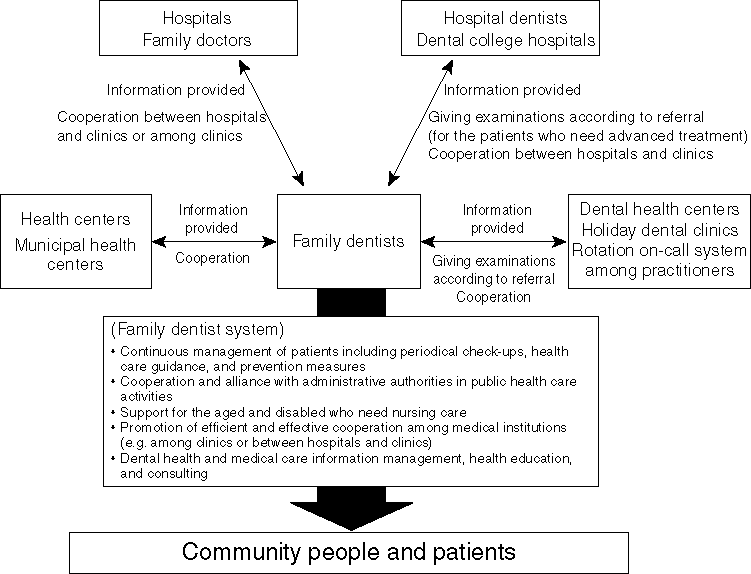
The 8020 Campaign and Family Dentist System
An opinion at a Study Group on the future dental health and medical care claimed, from the viewpoint of promotion of the 8020 Campaign, to make use of the family dentist system, promote the measures for teeth decay prevention, periodontal diseases, and prosthetic procedures for lost teeth. From 1997, as a part of dental health promotion programs, the policy to support the family dentist system was implemented to disseminate and establish the said system.
Overview
The Status Quo of National Hospitals and Sanatoria
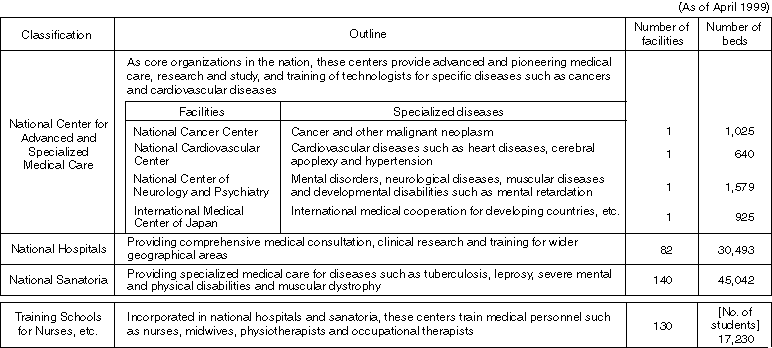
Detailed Data 1
Management of National Hospitals and Sanatoria
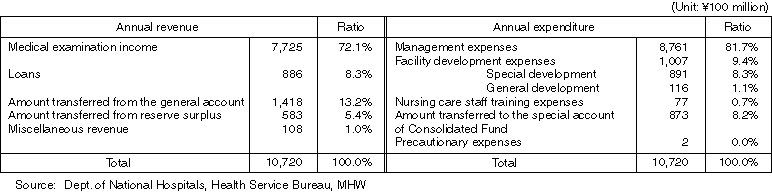
Balance of the national hospital special account (FY1999 original budget)
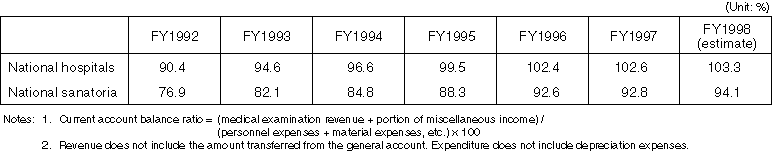
Changes in current account balance ratio of national hospitals and sanatoria
- Current account balance ratio has been steadily improving since FY1992.
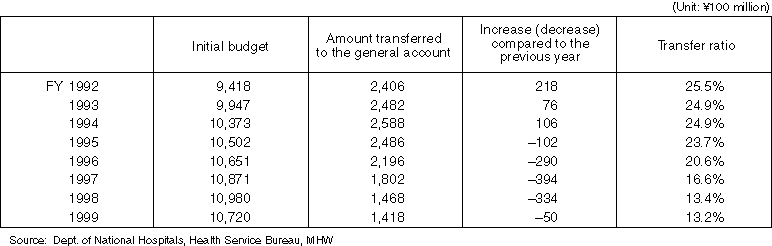
Changes in the amount transferred from the national hospital general account to the special account
- The amount and ratio is drastically decreasing.
Overview
Review of Reorganization of National Hospitals and Sanatoria
| 1. Clarification of the range of policy-based medical services |
Clarify the range of policy-based medical services to specify medical services based on governmental policies to be wholly borne by the government.
(1) Area
<Policy-based medical services>
Cancer, cardiovascular diseases, mental diseases, neuromuscular diseases, medical program for healthy children, renal diseases, severe mental and physical disabilities, bone and motor system diseases, respiratory diseases, immunopathy, endocrine and metabolic diseases, sensorial diseases, blood and hematopoietic organ diseases, hepatic diseases, AIDS, geriatric disease medical care, medical care for disasters, international medical cooperation, and international infectious diseases
(2) Description
At implementation of policy-based medical services, medical care service system is developed integrating other functions such as clinical research, educational training , and information transmission with medical consultation.
| 2. Additional organizations to be reorganized |
As a result, twelve cases (including three model cases transferring the function of treatment for severe mental and physical disabilities to other corporations) are added to institutions subject to reorganization.
| 3. Authorization for medical care institutions and establishment of the policy-based medical service network |
Categorize functions of institutions into National Centers, basic medical care institutions, and specialized medical care institutions, disclose medical functions for each institution, then establish the nationwide policy-based medical service network, for which National Centers and National Centers for Advanced and Specialized Medical Care take the lead for medical consultation, clinical research, educational training, and information transmission according to the plan, for the purpose of improving advanced and specialized functions of national hospitals and sanatoria and achieving their roles more appropriately and effectively.
Detailed Information 1
Progress in Reorganization
General Plan
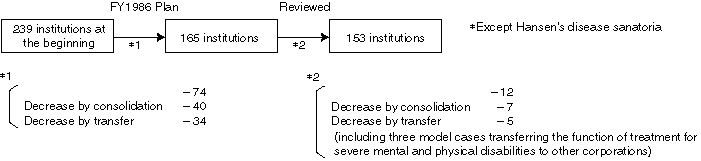
Past Results
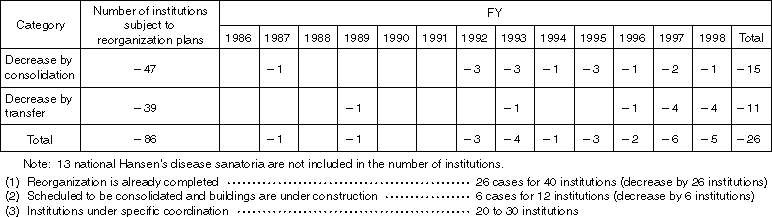
Overview
Changes in the Number of Medical Care Institutions (hospitals and clinics)
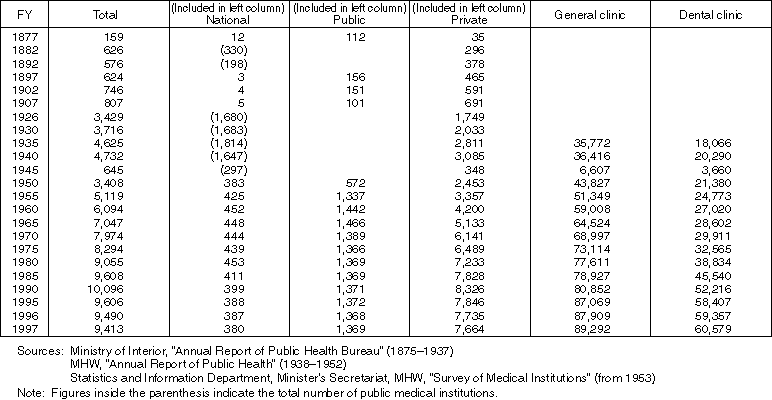
Detailed Data 1
The Number of Hospitals by the Establisher and by the Number of Beds
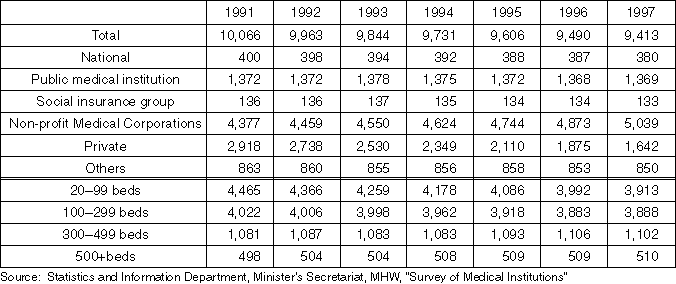
Detailed Data 2
The Number of Hospitals by Hospital Type
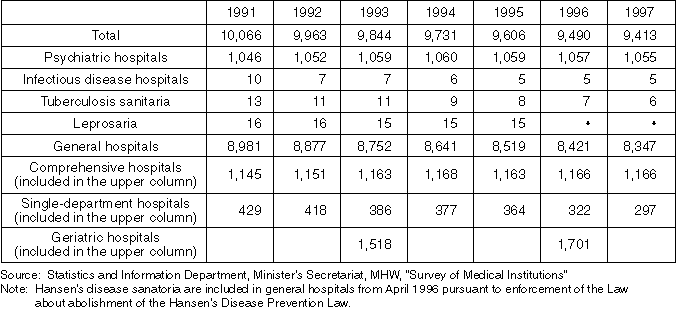
Detailed Data 3
Bed Utilization Rate by Bed Type
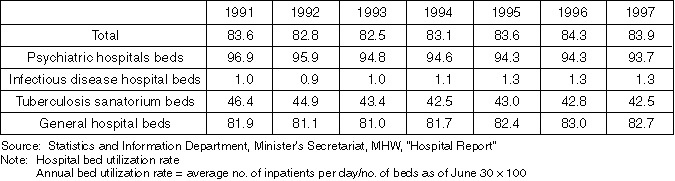
Detailed Data 4
The Number of Beds by Bed Type and Number of Beds per Hospital
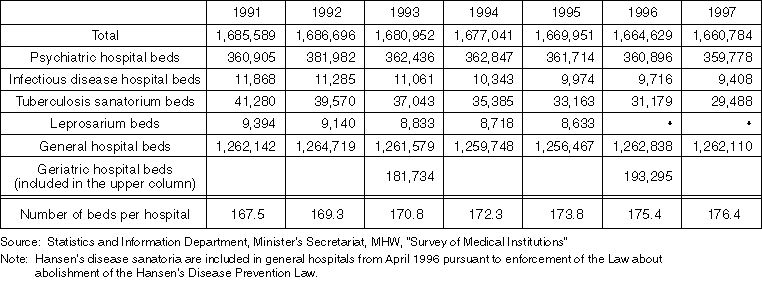
Detailed Data 5
Average Length of Stay by Bed Type
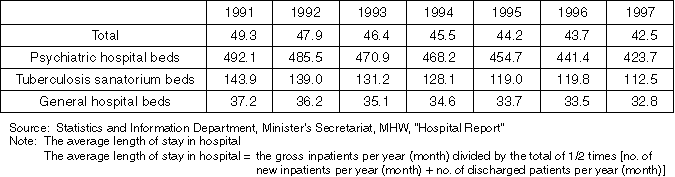
Overview
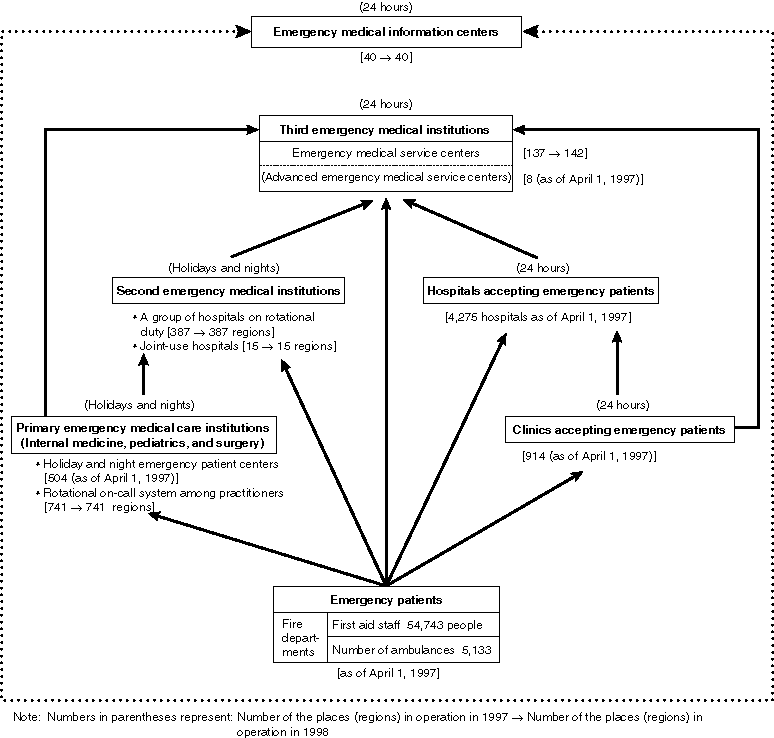
Overview
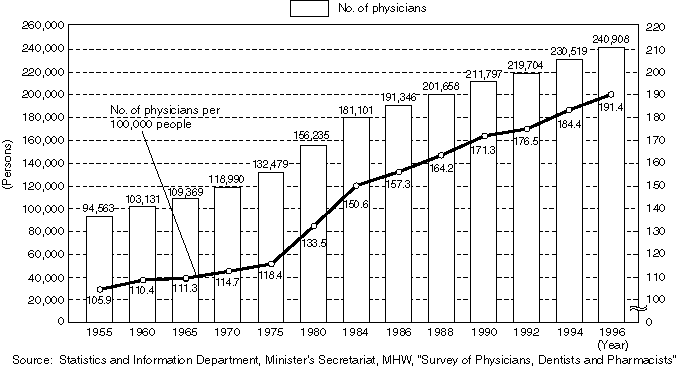
Changes in the Number of Physicians
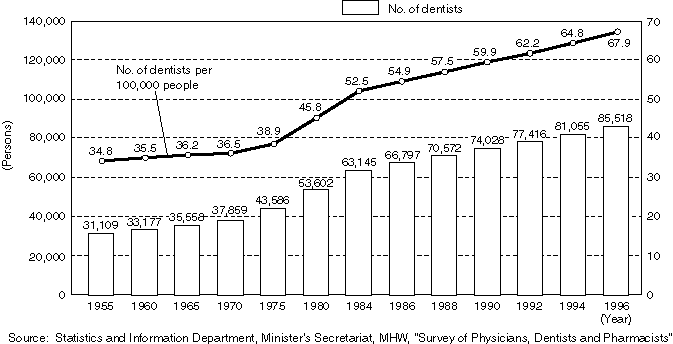
The number of physicians and dentists are increasing every year, numbering 240,908 and 85,518 respectively in 1996.
In 1986 a committee of experts submitted an opinion suggesting that new entry into medical and dental practice should be reduced by 10% and 20% respectively by around 1995. Since then, student capacity has been reduced by 7.7% for medical departments/schools and by 19.7% for dental departments/schools.
Observing physicians by age, those in their 30s are overall the highest in number. Among self-employed practitioners, however, those in their 60s scored the highest in number, which indicates an aging trend among practitioners.
Detailed Data 1
Changes in the Number of Physicians
Detailed Data 2
Changes in the Number of Dentists
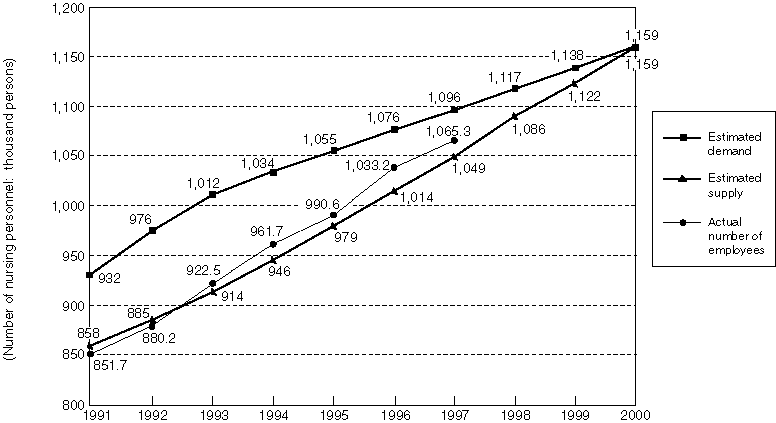
Projection of Supply and Demand for Nursing Personnel
The "Projection of Supply and Demand for Nursing Personnel" prepared in December of 1991 estimated that supply and demand would balance if the number of workers increases to approximately 1.16 million by year 2000.
Based on the "Law to Promote Securing of Nursing Personnel" enacted in 1992 and subsequent basic guidelines based on that law, comprehensive efforts have been made to secure manpower, focusing on preventing unemployment, improving working conditions, promoting employment and strengthening training capacity.
Detailed Data 3
Projection of Estimated Supply and Demand for Nursing Personnel
(estimated in December of 1991)
Detailed Data 1
Regional Status of Standards Achievement
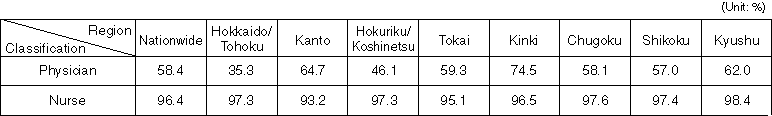
Detailed Data 2
Nationwide Status of Standards Achievement
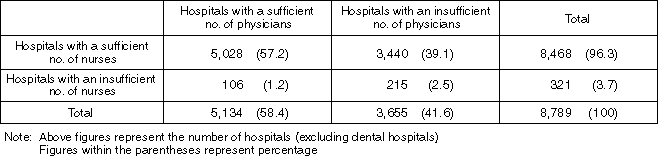
Overview
1. To meet the increasingly diversified needs of people, including the need for more advanced technology, the medical care was institutionalized pursuant to revision of the Medical Service Law as of December 1985, in order to promote the establishment of a systematic medical service delivery system in each region by utilizing medical resources effectively. This change also assured a mutual linkage and cooperation among the medical care institutions. Medical care plans are prepared by prefectural governments.
2. According to revision of the Medical Service Law as of December 1997, the medical care plan system was improved (enforced as of April 1998) with stipulating provisions about 1) objectives to improve hospitals supporting community medical services and medical rehabilitation-oriented beds, 2) shared functions and cooperation among medical service-related facilities, per the second medical care zone, for the purpose of necessary medical care services within daily living areas, and systematize community medical services.
3. Medical care plans are to be reviewed at least every five years. Prefectural governments review medical care plans, if necessary.
Detailed Data 1
The Number of Necessary Beds and Existing Beds by Prefecture
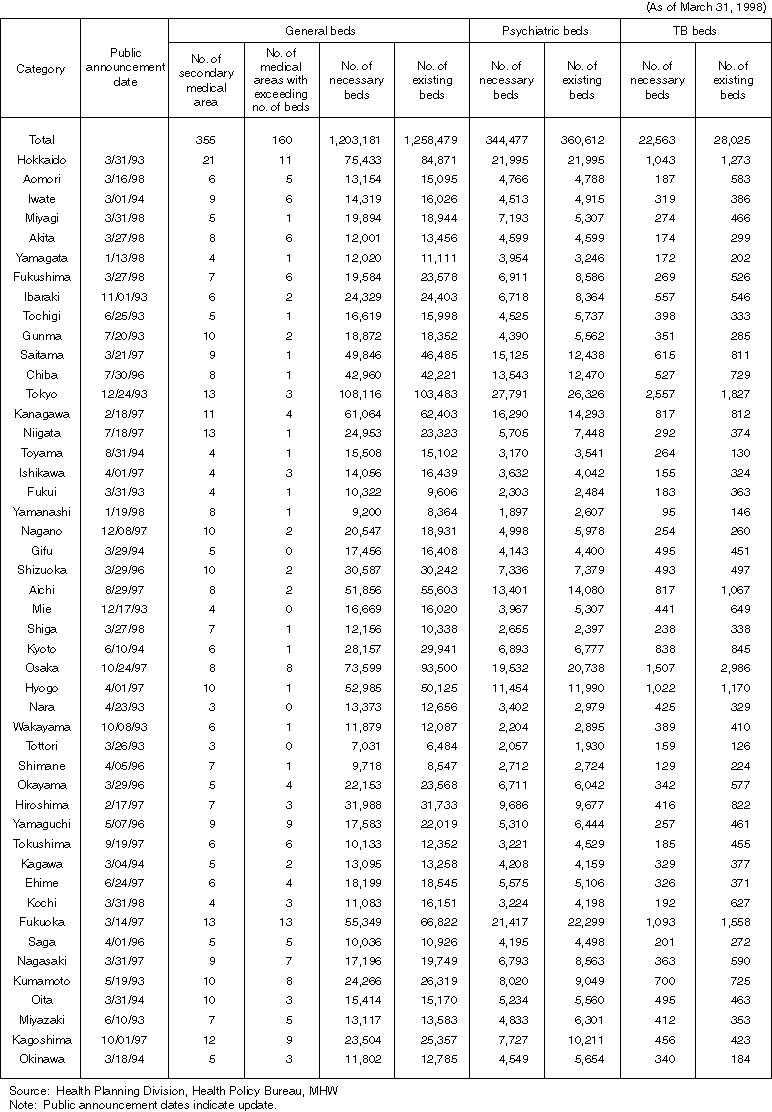
Overview
The purpose of health centers is to improve public health in their regions. Health centers are established by prefectures, cabinet order-designated cities or special wards (663 centers in total as of April 1 1998: 490 by prefectures, 137 by cabinet order-designate cities and 36 by special wards.) Following the full enforcement of the Community Health Law in April 1997, the service area definition was reviewed (expanded.) Furthermore, as key professional and technical facilities for regional health care measures covering a wide area, the services of health centers were enhanced in terms of the collection and organization of information, research and study, and planning and coordination.
Municipal health centers are the key facilities for regional health care measures at the municipal level. They offer local residents popular and frequently-used health care services, including health services for the elderly and for mothers and children (3,160 municipalities have established health centers or similar facilities.)
Detailed Data 1
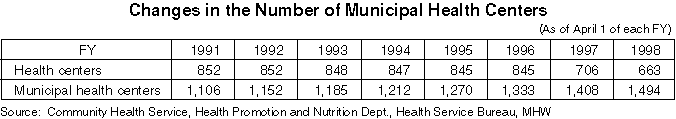
Medical Personnel at Health Centers
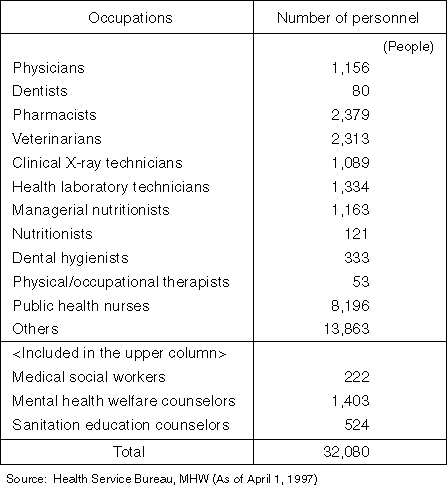
Detailed Data 2
Changes in the Number of Public Health Nurses