(Appendix 1)
ContactOffice of Imported Food Safety, Inspection and Safety Division, Department of Food Safety, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau, Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (extension: 2474, 2497, 2498) |
Results of Monitoring and Guidance Based on the Imported Foods
Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY2008
August 2009
Department of Food Safety
Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
Results of Monitoring and Guidance Based on the Imported Foods
Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY2008
Introduction
The total number of foods, additives, equipment, containers and packages, and toys (hereinafter collectively referred to as “foods”) imported to Japan in FY2008 was about 1.76 million, with animported weight of about 31.55 million tons. According to the Food Balance Sheet for FY 2007 by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, the food self-sufficiency ratio in Japan (food self-sufficiency ratio based on the total caloric value supplied) was estimated at 40%, indicating that, on a calorie basis, approximately 60% of foods consumed in Japan are imported.
Regarding the monitoring and guidance conducted by the national government for the purpose of ensuring the safety of foods imported to Japan (hereinafter referred to as “imported foods”), the Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY2008 (hereinafter referred to as the “Plan”) was developed based on public comments and risk communications, and was conduced in line with the Guidelines for the Implementation of Monitoring and Guidance on Food Sanitation (Notification No. 301 of the Ministry of Labour, Health and Welfare, 2003) under Article 23, paragraph 1 of the Food Sanitation Act (Act No. 233 of 1947; hereinafter referred to as the “Act”), and was implemented based on the Plan after being publicized in an official gazette pursuant to paragraph 3 of the same Article.
The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) has recently collected and compiled the detailed results of inspections on imported foods, such as for monitoring and inspection orders that have been implemented based on the Plan, as well as the monitoring of and guidance for importers and the relevant results, which are published herein.
Reference: Website on safety of imported food
https://www.mhlw.go.jp/topics/vuvu/tp0130-1.html
Inquiry: Office of Imported Food Safety, Inspection and Safety Division, Department of Food Safety, Pharmaceutical and Food Safety Bureau

1. Overview of the Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY 2008
(1) What is the Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan?
The Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan is a plan for the implementation of monitoring and guidance conducted by the national government with respect to imported foods (Article 23 of the Act).
[Objective]
To ensure greater safety of imported foods by promoting the national government to conduct inspections at the time of importation and to conduct monitoring of and guidance for importers in an intensive, effective and efficient manner.
(2) Principles for Monitoring and Guidance on Imported Foods
Based on Article 4 of the Food Safety Basic Act (Act No.48 of 2003) (that is, food safety shall be ensured by taking appropriate measures at each stage of the domestic and overseas food supply process), the Plan is prepared in order that three stages of sanitation measures are taken, namely, in the exporting country, at the time of importation, and at the time of domestic distribution.
(3) Priority Items for Monitoring and Guidance
- Confirmation of whether violations of the Act exist at the time of import declaration
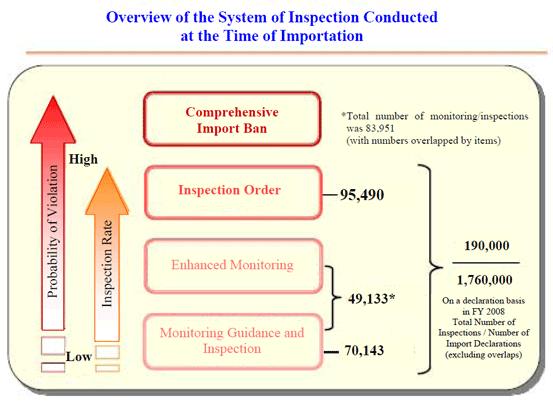
- Monitoring*1 (Plan for 2008: about 80,000 items across 126 food groups)
- Inspection orders*2 (as of March 31, 2009:16 items from all exporting countries and 190 items from 36 countries and 1 region)
- Regulations for comprehensive import bans*3
- Emergency responses based on overseas information, etc.
(4) Promotion of Sanitation Measures in Exporting Countries
- Requests to the governments of exporting countries for the establishment of sanitation control measures.
- Strengthening of control and monitoring systems for agricultural chemicals, etc., and the promotion of pre-export inspections, through on-site inspections and bilateral talks
(5) Guidance for Importers on Voluntary Sanitation Control
- Pre-import guidance (so-called “import consulting”)
- Guidance for voluntary inspections at initial importation and on a regular basis
- Instructions for record keeping
- Dissemination of knowledge on food sanitation to importers, etc.
*1: Systematic inspections based on statistical concepts that take into account the volume of imports and violation rates, etc., for different food types.
*2: With regard to items having a high probability of being in violation of the Act, inspections are ordered by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare at each and every importation. Items are not permitted to be imported or distributed unless they pass that inspection.
*3: Regulations by which the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare can prevent the sale or import of specified foods, without the need for inspections, in cases where it is deemed necessary from the perspective of preventing harm to public health.
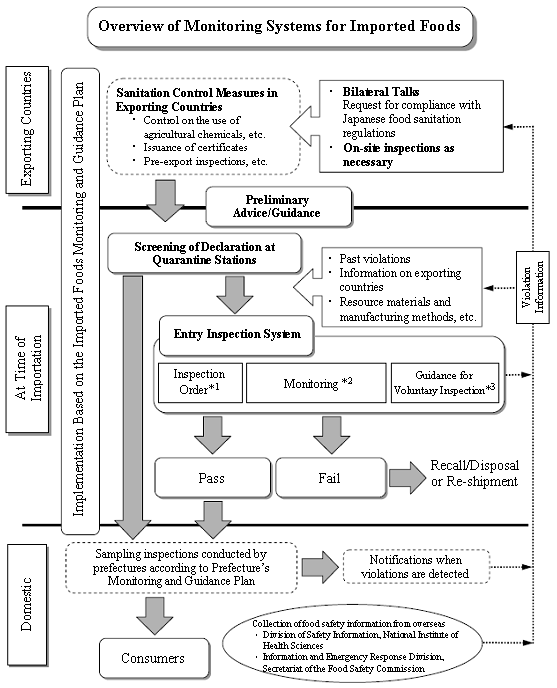
*1: With regard to items having a high probability of being in violation of the Act, inspections are ordered by the Minister of Health, Labour and Welfare at each and every importation. Items are not permitted to be imported or distributed unless they pass that inspection.
*2: Systematic inspections based on statistical concepts that take into account the volume of imports and violation rates, and hazard levels etc., for different types of food.
*3:Inspection and guidance conducted as part of the voluntary sanitation control of an importer at the time of first importation, etc. in order to confirm that the relevant imported foods conform to the Act.
2. Results of Monitoring and Guidance Based on the Imported Foods Monitoring and Guidance Plan for FY2008
With regard to ensuring the safety of imported foods, based on the fundamental concept that appropriate measures need to be implemented at each stage, from production, manufacturing and processing in exporting countries to post-importation sales in the domestic market, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare together with quarantine stations conducted monitoring and guidance at the time of importation of foods by implementing the following measures, and promoted sanitation measures in exporting countries through bilateral talks and dispatch of experts at times when food sanitation issues occurred. Furthermore, in an attempt to reinforce cooperation, such as at times when violations are detected, with prefectures that conduct monitoring and guidance at the stages of domestic distribution and sales subsequent to importation, appropriate measures were implemented so that importer recalls, etc. would be expedited. Inspections at the time of importation were also enhanced as necessary.
(1) Confirmation by Import Declaration Based on Article 27 of the Act

Examination of declarations using the
computer system
Using import declarations and other documents, submitted under Article 27 of the Act, examinations were conducted to check for compliance with the Act, including compliance with the specifications and standards for foods based on the provisions contained within Article 11, paragraph 1 and Article 18, paragraph 1 of the Act (hereinafter referred to as the “standards”). Inspections required at the time of importation were also conducted.
Looking at the declarations, inspections and violations for FY2008 (Table 1), the number of import declarations was about 1.76 million, and the weight of declared items, based on preliminary figures, was about 31.55 million tons. Inspections were carried out on about 190, 000 declarations (11.0%). Of these, 1, 150 were found to be in violation of the Act (total 1, 226 cases), and steps were taken for their re-shipment or disposal, etc. This is equivalent to 0.1% of the number of import declarations.
(2) Monitoring Based on Article 28 of the Act

Sampling at a container yard
The basis for monitoring is that the number of inspections should be such that violations can be detected with a certain level of statistical confidence across a diverse range of imported foods, etc. This is the basis for determining the number of inspections conducted and the types of substances tested by quarantine stations, with consideration given to actual import records and violation rates, etc. for each food group. In FY2008, 79,809 inspections were planned.
In light of the enforcement of the Positive List System, the number of food sanitation inspectors was increased from 334 to 341, and additional inspection equipment associated with residual agricultural chemicals was also installed. Furthermore, in view of the usage of agricultural chemicals overseas, tested substances increased from 500 to 510 for residual agricultural chemicals, from 130 to 140 for residual veterinary drugs, and about 4000 residual chemical tests were additionally conducted on processed foods.

Inspection of residual agricultural chemicals in
agricultural products (condensation)
Records of monitoring in FY2008 (Table 2) show that, in comparison to the 79, 809 planned inspections, 83, 951 inspections (actual count 49, 133) were actually conducted (implementation rate of the total number of cases: about 105%), and of these, recalls were made based on 221 (total 245 cases) violations of the Act.
Inspection rates were increased as needed in cases where violations of the Act were detected during the monitoring (Table 3). In addition, testing was enhanced in cases where multiple violations of the Act were detected for food products from a single country on grounds of residual agricultural chemicals or residual veterinary drugs: foods potentially having a high probability of being in violation of the Act became subject to inspection orders, whereby they would be inspected at each importation (Table 4); and foods in which substances such as aflatoxin or listeria monocytogenes were detected became immediately subject to inspection orders (Table 5).
(3) Inspection Orders Based on Article 26 of the Act

Analysis using High-speed liquid chromatograph
mass spectrometer
For the purpose of preventing harm to public health in terms of food sanitation, certain countries/regions, inspected foods and tested substances, etc. were specified for imported foods having a high probability of being in violation of the Act. Inspection orders were then implemented based on the provisions of Article 26 of the Act.
As of March 31, 2009, inspection orders had been applied to 16 products from all exporting countries and 190 products from 36 countries and 1 region. The record of inspection orders in FY2008 (Table 6) shows that 95, 490 (total 174, 610) inspection orders were conducted. Of these, re-shipment or disposal were undertaken based on 421 (total 432) violations of the Act.
(4) Violations
Records of violations categorized by Article (Table 7), including 49,133 (total 83,951) monitoring inspections and 95,490 (total 174,610) inspection orders, show that the most frequent violations were the 847 violations of Article 11 of the Act, which is related to such standards as microbiological criteria for food, standards on residual agricultural chemicals and standards for the use of additives (69.1%: ratio to the gross number of violations [1,226]). The next most frequent were the 256 (20.9%) violations of Article 6 of the Act, which is related to contamination with hazardous or toxic substances such as aflatoxin, followed by the 65 (5.3%) violations of Article 10 of the Act, which is related to the use of undesignated additives, the 43 (3.5%) violations of Article 18 pertaining to standards for the apparatus or containers and packaging, and the 8 (0.7%) violations of Article 62 (application mutatis mutandis) of the Act, which pertains to standards for toys.
In the category of violations categorized by type, violations related to residual agricultural chemicals (Table 8-1) were most common at 359 instances (29.3% ratio to the gross number of violations [1,226]). This was followed by the 260 (21.2%) violations related to standards for microbiological criteria for frozen food (Table 8-2), 181 (14.8%) violations related to hazardous or toxic substances (Table 8-3), 142 (11.6%) violations related to the use of undesignated additives and noncompliance with the standards for the use of additives (Table 8-4), and 115 (9.4%) violations related to residual veterinary drugs (Table 8-5).
A breakdown, by country, of violations related to residual agricultural chemicals (Table 8-1) shows that Ethiopia had 77 violations (21.4%: ratio to the gross number of violations related to residual agricultural chemicals [359]), followed by China with 61 violations (17.0%), and Canada with 34 violations (9.5%). The further breakdown, by item and violation type, shows that the most dominant violations for Ethiopia were γ-BHC (lindane), chlordane and heptachlor in coffee beans. For China, it was acephate and methamidofos in carrots; and for Canada, it was glyphosate in common beans.
A breakdown, by country, of violations related to microbiological criteria (Table 8-2)shows that Thailand had 57 violations (21.9%: ratio to the gross number of violations related to microbiological criteria [260]), followed by China with 50 violations (19.2%) and the Philippines with 30 violations (11.5%). The further breakdown by item and violation type shows that the most dominant violation for every country was the violation of microbiological criteria for frozen food (viable cell count, coliform bacteria, E.coli (colon bacilli)).
A breakdown, by country, of violations related to hazardous or toxic substances (Table 8-3) shows that the U.S. had 68 violations (37.6%: ratio to the gross number of violations related to mycotoxin [181]), followed by China with 19 violations (10.5%) and France with 17 violations (9.4%). The further breakdown, by item and violation type, shows that the most dominant violation for the U.S. was the contamination of corn with aflatoxin. For China, it was the contamination of peanuts with aflatoxin; and for France, it was the contamination of confectionery with cyanide compounds.
A breakdown, by country, of violations related to additives (Table 8-4) shows that China had 39 violations (27.5%: ratio to the gross number of violations related to additives [142]), followed by Taiwan with 19 violations (13.4%), and the U.S. 14 violations (9.9%). The further breakdown, by item and violation type, shows that the most dominant violations for China were milk and dairy products containing melamine. For Taiwan, it was the use of sodium aluminosilicate in powdered foods and for the U.S., it was the violation of the standards for residual nitrite in salmon roe.
A breakdown, by country, of violations related to residual veterinary drugs (Table 8-5)shows that China had 58 violations (50.4%: ratio to the gross number of violations related to residual veterinary drugs [115]), followed by Vietnam with 43 violations (37.4%), and Indonesia with 10 violations (8.7%). The further breakdown, by item and violation type, shows that the most dominant violation for China was AOZ and AMOZ in chicken products. For Vietnam it was chloramphenicol and AOZ in prawns; and for Indonesia, it was AOZ in prawns.
(5) Emergency Responses Based on Information from Overseas Regarding the Occurrence of Food Sanitation Issues

Inspection on residual agricultural
chemicals in processed food
(pulverization)
Organizations such as the National Institute of Health Sciences and the Food Safety Commission in the Cabinet Office collect information from overseas, such as on the occurrence of food poisonings and the recall of food products that are in violation of law. Based on this information, during FY2008, the system for monitoring items at the time of importation was enhanced and the domestic distribution was examined for such issues as Salmonella-contaminated chili peppers from Mexico, dioxin-contaminated pork from Chile, melamine-contaminated infant formula from China, and Salmonella-contaminated peanut products from the U.S. (Table 9).
In response to food poisoning cases caused by frozen dumplings from China in January 2008, tests for residual agricultural chemicals in processed foods were performed on a total of 3105 samples before the end of FY2008, and no violations were found.
(6) Promotion of Sanitation Measures in Exporting Countries
During FY2008, as a way of promoting sanitation measures in exporting countries, information on violations of food products subject to inspection orders and enhanced monitoring was provided to the governments of exporting countries, and, through bilateral discussions, etc., they were urged to probe the causes of violations and to implement measures to prevent recurrence.

On-site inspection at a
slaughterhouse in Italy
In instances when it was necessary to confirm sanitation measures at the production and processing stage in an exporting country for such cases as residual agricultural chemicals or bovine spongiform encephalopathy (hereinafter referred to as “BSE”), experts were dispatched to the relevant country and on-site inspections were conducted on the sanitation measures in that exporting country (Table 10).
With respect to U.S. beef, on-site inspections were held from August 17 to August 31, 2008, at 10 facilities exporting to Japan (including one facility which will start exporting to Japan) to verify compliance with the USDA Beef Export Program for Japan. Also, with respect to Canadian beef, on-site inspections were held from October 14 to October 25, 2008, at 5 facilities exporting to Japan to verify compliance with the Export Program for Japan.
(7) Regulations for Comprehensive Import Bans Based on Articles 8 and 17 of the Act
With regard to comprehensive import ban measures based on the Guidelines for the Prohibition of the Sale and Import of Specified Foods based on Article 8 Paragraph 1 and Article 17 Paragraph 1 of the Food Sanitation Act (Attachment to Notice No. 0906001 of the Department of Food Safety dated September 6, 2002), sanitation control by the each government was confirmed for common beans produced in Canada (glyphosate), constricted tagelus produced in Korea (endosulfan), carrots produced in Taiwan (acephate), carrots produced in China (acephate) and coffee beans produced in Ethiopia (γ-BHC, chlordane and heptachlor) (the violation rates for these items based on the 60 most recent inspection orders had temporarily exceeded 5%), and requests for improvement measures were repeated. As a result, in FY2008, there were no items for which this measure was exercised.
(8) Guidance for Importers on Voluntary Sanitation Control

Consultation for declaration
at the consultation desk
Based on the Plan, importers were instructed to confirm the safety of imported foods in advance by obtaining necessary information from the producers or manufacturers of the foods. Seminars were also held at individual quarantine stations to publicize that importers should consult with quarantine stations in advance with regard to foods being imported into Japan for the first time or those foods with a violation history. Furthermore, in light of cases of foods contaminated with toxic and harmful substances, the government has promoted the collection of information on hygiene measures that have been taken by the exporting countries to prevent the occurrence of incidents. Particularly with respect to processed foods, the government re-instructed importers to make necessary confirmation at every stage of the raw material, production/processing, storage and transportation processes in exporting countries in accordance with the Guidelines on Hygiene Control of Import Processed Foods, notified in June 2008.
Records of import consultations (Table 11) conducted at the Imported Food Consultation Offices, located in quarantine stations, show that 27,083 consultations by product were conducted in FY2008, of which 410 (total 499) cases were identified in advance as being in violation of the Act.

Seminars for importers at a quarantine station
The breakdown, by Article, of cases in violation of the Act (Table 12) shows that the most frequent violations were the 259 violations of Article 11 of the Act which is related to such standards as those for the use of additives (51.9%: ratio to the gross number of violations [499]). The next most frequent were the 224 violations of Article 10 of the Act, related to the use of undesignated additives (44.9%).
The breakdown by country (Table 13) shows that with 131 violations, the U.S. had the greatest number of violations (26.3%: ratio to the gross number of violations [499]), followed by Italy with 57 violations (11.4%), and China with 34 violations (6.8%).
Looking into the major cases of violation by item and details of the violations, we can see that examples of frequent cases of violation include the use of non-designated additives in health foods in the U.S., non-compliance with manufacturing standards for ice cream in Italy, and unauthorized use of sorbic acid in seasonings in China.

Consultations at Offices of Imported Food
Consultation
When cases were identified at these import consultations as being in violation of the Act, importers were instructed to take appropriate measures to comply with the Act, and to postpone importing until improvements were in place. Even if the effects of the improvements and the compliance of the foods with the Act could be confirmed on paper, importers were instructed to confirm, by testing as necessary, whether the foods satisfied the standards, etc., such as by importing samples.
(9) Disclosure of Information on Imported Foods Violating the Act, and Cooperation with Prefectures
In accordance with the provisions of Article 63 of the Act, for the purpose of clarifying the extent of hazards in terms of food sanitation, the names and addresses of importers who are in violation of law, as well as information on the imported foods were published on the Ministry website. In addition to disclosing the names of the violators, details of the improvement measures and the causes of the violations were also made public as soon as they were identified.
Furthermore, with regard to imported foods identified as being in violation of the Act as a result of the inspections at the time of importation, if any of them had already cleared customs, they were immediately recalled in cooperation with the relevant prefectures. Monitoring was enhanced as necessary for those violations detected in inspections conducted by prefectures at the time of domestic distribution (Table 14).
| Number of Import Declarations |
Imported Weight (thousand tons) |
Number of Inspections*1 |
Ratio*2 (%) |
Number of Violations |
Ratio*2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,759,123 | 31,551 | 193,917 (95,490)*3 |
11.0 | 1,150 (432)*3 |
0.1 (0.5)*3 |
| (FY2007 Actual) 1,797,086 |
32,261 | 198,542 | 11.0 | 1,150 | 0.1 |
*1 Total inspections conducted by administrative agencies, registered inspection agencies and foreign public organizations, subtracting duplicate inspections.
*2 Ratio to the number of import declarations.
*3 Figures related to inspection orders (repeated elsewhere)
| Food Group | Tested Substances*1 | Number of Planned Tests*2 |
Number of Actual Tests |
Number of Violations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Livestock Food Products Beef, pork, chicken, horsemeat, other poultry meat, etc. |
Antibiotics, etc | 2,213 | 2,160 | 1 |
| Agricultural chemicals | 1,678 | 1,908 | 1 | |
| Additives | - | 10 | 0 | |
| Compositional standards | 657 | 740 | 0 | |
| Removal of SRM | - | 4,249 | 0 | |
| Processed Livestock Food Products Natural cheese, meat products, ice cream, frozen food (meats), etc. |
Antibiotics, etc | 1,490 | 1,794 | 6 |
| Agricultural chemicals | 532 | 705 | 0 | |
| Additives | 1,128 | 1,558 | 0 | |
| Compositional standards | 1,820 | 1,867 | 7 | |
| Fishery Food Products Clams, fish, shellfish (shrimp, crabs), etc. |
Antibiotics, etc | 3,527 | 3,399 | 7 |
| Agricultural chemicals | 831 | 1,993 | 3 | |
| Additives | 235 | 387 | 1 | |
| Compositional standards | 895 | 1,165 | 0 | |
| Differentiation of fish species (Pufferfish genes) |
- | 2 | 0 | |
| Processed Fishery Food Products Processed fish products (filleted, dried, minced, etc.), frozen food (aquatic animals, fish), processed fish and shellfish egg products, etc. |
Antibiotics, etc | 3,286 | 3,861 | 2 |
| Agricultural chemicals | 1,729 | 2,655 | 0 | |
| Additives | 1,787 | 2,546 | 1 | |
| Compositional standards | 3,885 | 4,446 | 26 | |
| Differentiation of fish species (Pufferfish genes) |
- | 87 | 0 | |
| Agricultural Food Products Fruit and vegetables, wheat and barley, corn, beans, peanuts, nuts, seeds, etc. |
Antibiotics, etc | 741 | 1,153 | 1 |
| Agricultural chemicals | 18,367 | 17,419 | 127 | |
| Additives | 598 | 580 | 0 | |
| Compositional standards | 1,243 | 1,269 | 0 | |
| Mycotoxin | 2,210 | 2,744 | 3 | |
| GMOs | 1,254 | 1,273 | 1 | |
| Exposure to radiation | - | 6 | 0 | |
| Processed Agricultural Food Products Frozen food (processed vegetables), processed vegetables, processed fruits, spices, instant noodles, etc. |
Antibiotics, etc | - | 122 | 0 |
| Agricultural chemicals | 6,571 | 6,362 | 9 | |
| Additives | 4,204 | 4,604 | 4 | |
| Compositional standards | 2,119 | 2,139 | 15 | |
| Mycotoxin | 2,238 | 1,897 | 3 | |
| GMOs | 207 | 54 | 0 | |
| Exposure to radiation | 310 | 420 | 8 | |
| Other Foods Health foods, soups, seasonings, confectionery, edible oils and fats, frozen foods, etc. |
Antibiotics, etc | 299 | 104 | 0 |
| Agricultural chemicals | 238 | 455 | 0 | |
| Additives | 3,078 | 2,738 | 7 | |
| Compositional standards | 657 | 567 | 4 | |
| Mycotoxin | 598 | 609 | 0 | |
| GMOs | - | 35 | 0 | |
| Exposure to radiation | - | 7 | 0 | |
| Beverages Mineral water, soft drinks, alcoholic beverages, etc. |
Agricultural chemicals | 299 | 216 | 0 |
| Additives | 897 | 1,185 | 0 | |
| Compositional standards | 897 | 735 | 4 | |
| Mycotoxin | 299 | 173 | 2 | |
| Additives, equipment, containers and packaging, toys |
Compositional standards | 1,792 | 1,553 | 2 |
| Total (gross) 5,000 tests for enhanced monitoring are included in the total number of planned tests |
79,809 | 83,951 Implementation rate of about 105% |
245 | |
*1: Examples of tested substances
• Antibiotics, etc.: antibiotics, antimicrobial agents, hormone drugs, feed additives, etc.
• Agricultural chemicals: organophosphorous, organochlorine, carbamates, pyrethroid, etc.
• Additives: sorbic acid, benzoic acid, sulfur dioxide, coloring agents, polysorbate, cyclamic acid, TBHQ, antimold agents, etc.
• Compositional standards, etc.: Items stipulated in the compositional standards (bacteria count, coliform bacteria, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, etc.), pathogenic microorganisms (enterohemorrhagic E. coli O157, listeria monocytogenes, etc.), shellfish poisons (diarrhetic shellfish poison, paralytic shellfish poison), fungicide for disposable wooden chopsticks, etc.
• Mycotoxin: aflatoxin, deoxynivalenol, patulin, etc.
• Genetically modified foods: genetically modified foods, etc. that have not been assessed for safety.
* 2: The numbers of planned tests are estimated numbers, categorized by tested substances such as antibiotics and agricultural chemicals.
| Country/Region | Monitored Food | Tested Substances |
|---|---|---|
| China | Cultured shrimps | Sulfadiazine |
| Eel | Dicofol | |
| Royal Jelly | Nitrofurans | |
| Kidney beans | DDT | |
| Komatsuna (Brassica rapa var. peruviridis) | Pyridalyl, pyrimethanil, buprofezine | |
| Perilla (perilla frutescens var. crispa) | Isoprocarb | |
| Carrots | Ethoprophos | |
| Green onions (including wakegi green onion) | Fluazifop | |
| Green peppers | Difenoconazole | |
| Swiss chard | Atrazine | |
| Spinach | Clothianidin | |
| Matsutake mushrooms | Chlorpyrifos, difenoconazole | |
| Sesame seeds | Acetochlor | |
| Thailand | Cultured soft-shelled turtles | Enrofloxacin |
| Soft-shelled turtles | Furaltadone | |
| Kan-Jong (Limnocharis flava) | EPN | |
| Holy basil | Flusilazole | |
| Coconut trunk | Paclobutrazol | |
| Asiasarum root | EPN | |
| Ginger | Oxytetracycline | |
| Pandanus palm | Difenoconazole | |
| Mangoes | Tetraconazole | |
| Lemongrass | EPN | |
| Vietnam | Fishery food products | Shigella |
| Cultured shrimps | Sulfamethoxazole | |
| Immature beans | Difenoconazole, flusilazole | |
| Italy | Fennel | Chlorpyrifos-methyl |
| Leek | Famoxadone | |
| Apple juice and raw material juice | Patulin | |
| Brazil | Coffee beans | Pyraclostrobin, flutriafol |
| Chicken | Ethoxyquin | |
| India | Prawns | Pendimethalin |
| Fermented tea | Quinalphos | |
| Australia | Barley | Amitraz, fipronil |
| Apple juice and raw material juice | Patulin | |
| Spain | Wild strawberries | Bupirimate |
| Hazelnuts | MCPA | |
| France | Cherries | Monocrotophos |
| Blackcurrants | Bupirimate | |
| Venezuela | Cacao beans | Chlorpyrifos |
| Sesame seeds | Chlorpyrifos |
| Country/Region | Monitored Food | Tested Substances |
|---|---|---|
| Myanmar | Galvanso beans | Cypermethrin |
| Coffee beans | DDT | |
| Yemen | Coffee beans | γ-BHC, chlordane, heptachlor |
| Argentine | Tomatoes | Haloxyfop |
| Indonesia | Coffee beans | Isoprocarb |
| Ethiopia | Coffee beans | Piperonyl butoxide |
| Ghana | Cacao beans | Profenofos |
| Korea | Green chili peppers | Flusilazole |
| Arch shells for raw consumption *3 | Vibrio parahaemolyticus*3 | |
| Tairagigai (Atrina pectinata) for raw consumption | Vibrio parahaemolyticus*3 | |
| Philippines | Sea urchins for raw consumption | Vibrio parahaemolyticus*4 |
| Gambia | Sesame seeds | γ-BHC |
| Guatemala | Sesame seeds | Methamidofos |
| Sudan | Sesame seeds | Diazinon, carbaryl |
| Taiwan | Groupers | Malachite green |
| Tilapia for raw consumption | Vibrio parahaemolyticus*4 | |
| Chile | Blueberries | Indoxacarb |
| Bangladesh | Red chili peppers | Triazophos |
| U.S. | Potato | Dazomet, metam, methyl isothiocyanate |
| Pelu | Quinoas | Methamidofos |
| Belgium | Red currants | Trifloxystrobin, flusilazole |
| Malaysia | Cultured shrimps | Sulfadiazine |
| Mozambique | Sesame seeds | DDT |
| Laos | Kale | Fipronil |
| All exporting countries (excluding India) |
Sickle senna seeds | Aflatoxin |
| All exporting countries (excluding India and Indonesia) |
Turmeric | Aflatoxin |
| All exporting countries (excluding Nigeria) |
Sesame seeds | Aflatoxin |
| All exporting countries (excluding U.S. and Italy) |
Processed almond products | Aflatoxin |
*1 During FY2008, inspections were usually conducted on half (30%) of all import declarations for items that are subject to enhanced monitoring following a detected violation. However, if there were no reoccurrences of similar violations during the year following the enhanced monitoring, the items reverted back to the usual monitoring system.
*2 Not including items included in Table 4.
*3 As a reinforcement of inspections during the summer period, all (100%) import declarations were inspected (Jun-Oct 2008).
*4 As a reinforcement of inspections during the summer period, 50% of import declarations were inspected (Jun-Oct 2008).
| Country/Region | Monitored Food | Tested Substances |
|---|---|---|
| China | Chicken | Furazolidone, furaltadone |
| Weather loaches | Endosulfan | |
| Milk and dairy products | Melamine | |
| Cultured shrimps | Sulfamethoxazole | |
| Carrots | Acephate | |
| Wakegi green onion | Pyrimethanil | |
| Sesame seeds | 2,4-D, dicofol | |
| Ethiopia | Coffee beans | γ-BHC, DDT, chlordane, heptachlor |
| Canada | Kidney beans | Glyphosate |
| Korea | Green chili peppers | Tebuconazole*1 |
| Thailand | Green asparagus | EPN |
| Taiwan | Carrots | Methamidofos |
| Paraguay | Sesame seeds | Imidacloprid |
| Philippines | Okra | Fluazifop, methamidofos |
| Brazil | Wheat | Methamidofos |
| France | Blackcurrants | Flusilazole |
| U.S. | Celery | Boscalid |
| Venezuela | Cacao beans | 2,4-D |
*1 The inspection order was lifted as of June 30, 2009.
| Country/Region | Shifted Item | Tested Substances |
|---|---|---|
| Italy | Processed almond products | Aflatoxin |
| India | Sickle senna seeds | Aflatoxin |
| Turmeric | Aflatoxin | |
| Canada | Lobsters | Paralytic shellfish poison |
| Thailand | Mangosteens | Imazalil*1 |
| Nigeria | Sesame seeds | Aflatoxin |
| Taiwan | Carrots | Acephate*2 |
| U.S. | Soft and semi-soft natural cheese (limited to manufacturers) |
Listeria |
| Corn (including cornflour, excluding sweet corn) |
Aflatoxin | |
| Vietnam | Fishery food products (limited to manufacturers) |
Shigella |
| Bolivia | Sesame seeds | Aflatoxin |
| All exporting countries | Ammonium hydrogen carbonate, including foods containing ammonium hydrogen carbonate (limited to manufacturers) |
Melamine |
*1 Item shifted to inspection order after more than one violation was identified on the same day
*2 Item shifted to inspection order after violations were identified within a few days of each other (April 25 and May 2)
| Country/Region | Main Foods Subject to Inspection Orders |
Main Tested Substances | Number of Inspections | Number of Violations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All exporting countries (16 items) |
Peanuts, nuts, chili peppers, etc. | Aflatoxin | 9,078 | 64 |
| Beans containing cyanide, cassava |
Cyanide compounds | 462 | 11 | |
| Salmon roe | Nitrite | 327 | 10 | |
| China (45 items) |
Chicken, prawns, eel, honey, etc. | Nitrofurans, Tetracycline antibiotic, malachite green, etc. |
50,205 | 38 |
| Fruit and vegetables, beans, fish (shiitake mushrooms, green onions, weather loaches, etc.) |
Fenpropathrin, tebufenozide, methamidofos, pyrimethanil, etc. |
28,518 | 33 | |
| Milk, dairy products, and processed foods containing those as an ingredient |
Melamine | 5,228 | 11 | |
| Clams | Diarrhetic shellfish poison, paralytic shellfish poison |
5,833 | 8 | |
| Processed eel products | Viable cell count, coliform bacteria |
607 | 0 | |
| All processed foods | Cyclamic acid | 912 | 0 | |
| Thailand (26 items) |
Fruit and vegetables (okra, mangoes, bananas, etc.) |
EPN, chlorpyrifos, cypermethrin, etc. |
3,108 | 2 |
| Cultured shrimps | Oxolinic acid | 2,196 | 0 | |
| Basil seeds | Aflatoxin | 3 | 0 | |
| Korea (20 items) |
Constricted tagelus, freshwater clams |
Endosulfan | 193 | 10 |
| Vegetables (paprikas, chili peppers, perilla (perilla frutescens var. japonica), etc.) |
Ethoprophos, chlorpyrifos, bifenthrin , etc. |
636 | 6 | |
| Clams | Paralytic shellfish poison, diarrhetic shellfish poison |
902 | 1 | |
| Arch shells for raw consumption | Vibrio parahaemolyticus | 2 | 0 | |
| Taiwan (15 items) |
Vegetables, fruit, tea (oolong tea, chinese chives, mangoes, etc.) |
Bromopropylate, chlorpyrifos, cyfluthrin, etc. |
795 | 19 |
| Eel, royal jelly, soft-shelled turtle | Chloramphenicol, nitrofurans, etc. |
5,266 | 0 | |
| Processed foods, etc. | Cyclamic acid, carbon monoxide |
64 | 0 | |
| U.S. (13 items) |
Corn, almonds, etc. | Aflatoxin | 2,628 | 49 |
| Vegetables, cereals (parsley, celery, etc.) |
Chlorpyrifos, boscalid, etc. | 356 | 2 | |
| Vietnam (8 items) |
Prawns, squid, cultured eel | Chloramphenicol, nitrofurans, etc. |
28,338 | 42 |
| Spinach | Indoxacarb | 151 | 1 | |
| Sesame seeds, etc. | Aflatoxin | 42 | 0 | |
| Fishery food products | Shigella | 29 | 0 | |
| Processed foods, etc | Cyclamin acid | 89 | 0 | |
| Ethiopia (1 item) |
Coffee beans | γ-BHC, DDT, chlordane, etc. |
372 | 31 |
| Other (30 countries, 63 items) | 28,270 | 94 | ||
| Total | 174,610 | 432 | ||
*”Number of inspections” is the gross number of inspections by tested substance.
| Violated Article | Number of Violations | Ratio (%) | Main Violations |
|---|---|---|---|
Article 6
(Food and additives banned from sale) |
256 | 20.9 | Contamination of peanuts, adlay, corn, chili peppers, cacao beans, sesame seeds and almonds, etc. with aflatoxin; contamination with toxic fish; detection of diarrhetic and paralytic shellfish poisons; detection of cyanide compounds; detection of Listeria monocytogenes and unheated meat products; decay, deterioration, and fungus formation due to accidents during the transport of rice, wheat, etc. |
Article 9 (Restriction on the sale, etc. of diseased meat, etc.) |
7 | 0.6 | Failure to attach sanitary certificate. |
Article 10 (Restriction on the sale, etc. of additives, etc.) |
65 | 5.3 | Use of undesignated additives, including melamine, cyclamic acid, azorubine, TBHQ, sodium alumininosilicate, Patent Blue V, Brilliant Black BN, Rhodamine B, methylene chloride, carbon monoxide, etc. |
Article 11 (Standards for foods or additives) |
847 | 69.1 | Violation of compositional standards for vegetables and frozen vegetables (violation of standards for residual agricultural chemicals); violation of compositional standards for seafood and processed seafood products (violation of standards for residual drugs for animal use and violation of standards for residual agricultural chemicals); violation of compositional standards for other processed foods (coliform bacteria positive, etc.); violation of standards for the use of additives (sorbic acid, benzoic acid, sulfur dioxide, etc.); violation of standards for the ingredients of additives |
Article 18 (Standards for equipmentand containers/packaging) |
43 | 3.5 | Violation of specifications for equipment and containers/packaging. Violation of material-specific specifications for raw materials. |
Article 62 (Mutatis mutandisapplication to toys, etc.) |
8 | 0.7 | Violation of specifications for toys or their raw materials |
| Total | 1,226 (gross) *1 1,150 (real) *2 |
||
*1: Gross number of violations by tested substance.
*2: Number of notifications for which inspection was carried out.
| Country of Production (Number of violations Total) |
Item Type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New/Conventional Standard |
Uniform Standard | |||
| Ethiopia (77) |
Coffee beans | γ-BHC (lindane) (53) | DDT (2), chlordane (5), piperonyl butoxide (1), heptachlor (16) |
77 |
| China (61) |
Carrots | Methamidofos (5), ethoprophos (1) |
Acephate (10) | 16 |
| Sesame seeds | Dicofol (3), 2, 4-D (2) | Acetochlor (1) | 6 | |
| Cloud ear mushrooms | Chlorpyrifos (4) | Bifenthrin (2) | 6 | |
| Green peppers | Difenoconazole (1), pyrimethanil (3) |
4 | ||
| Large peanuts | BHC | 4 | ||
| Komatsuna (Brassica rapa var. peruviridis) |
Pyridalyl (1), pyrimethanil (1), buprofezine (1) |
3 | ||
| Green tea | Triazophos | 3 | ||
| Ginger | BHC | 2 | ||
| Weather loaches | Endosulfan | 2 | ||
| Green onions | Fluazifop (1) | Tebufenozide (1) | 2 | |
| Matsutake mushrooms | Chlorpyrifos (1) | Difenoconazole (1) | 2 | |
| Wakegi green onion | Pyrimethanil | 2 | ||
| Shiitake mushrooms | Fenpropathrin | 2 | ||
| Kidney beans | DDT | 1 | ||
| Eel | Dicofol | 1 | ||
| Perilla (perilla frutescens var. crispa) |
Isoprocarb | 1 | ||
| Swiss chard | Atrazine | 1 | ||
| Immature beans | Fenpropathrin | 1 | ||
| Small peanuts | Daminozide | 1 | ||
| Oolong tea | Triazophos | 1 | ||
| Canada (34) |
Kidney beans | Glyphosate | 34 | |
| Ecuador (31) |
Cacao beans | Cypermethrin (1) | 2, 4-D (30) | 31 |
| Ghana (31) |
Cacao beans | Pirimiphos-methyl (13), endosulfan (6), chlorpyrifos (7), |
Fenvalerate (4), profenofos (1) | 31 |
| Taiwan(14) | Carrots | Methamidofos (4) | Acephate (16) | 20 |
| Semi-fermented tea | Bromopropylate | 4 | ||
| Korea (19) |
Constricted tagelus | Endosulfan | 10 | |
| Green chili peppers | Tebuconazole (4), flusilazole (1) | 5 | ||
| Grape tomato | Fluquinconazole | 3 | ||
| Perilla (perilla frutescens var. japonica) |
Bifenthrin | 1 | ||
| Philippines | Okra | Fluazifop (11), methamidofos (1) | 12 | |
| Mangoes | Chlorpyrifos(1), cypermethrin(1) |
2 | ||
| Thailand (14) |
Asparagus | EPN | 2 | |
| Mangoes | Pirimiphos-methyl | Tetraconazole | 2 | |
| Holy basil | Flusilazole | 1 | ||
| Ginger | Oxytetracycline | 1 | ||
| Country of Production (Number of violations Total) |
Item Type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New/Conventional Standard |
Uniform Standard | |||
| Thailand (14) |
Mangosteens | Imazalil | 2 | |
| Coconut trunk | Paclobutrazol | 1 | ||
| Kan-Jong | EPN | 1 | ||
| Pandanus palm | Difenoconazole | 1 | ||
| Lemongrass | EPN | 1 | ||
| Chili peppers | Triazophos | 1 | ||
| Okura | EPN | 1 | ||
| U.S. (11) |
Celery | Boscalid | 6 | |
| Oranges | Pendimethalin | 1 | ||
| Blueberries | Oryzalin | 1 | ||
| Broccoli | Flonicamid | 1 | ||
| Lemons | Pendimethalin | 1 | ||
| Parsley | Chlorpyripos | 1 | ||
| India | Chili peppers | Triazophos | 4 | |
| Fermented tea | Hexaconazole (1), quinalphos (1) |
2 | ||
| Prawns | Pendimethalin | 1 | ||
| France | Blackcurrants | Bupirimate (1), flusilazole (2) | 3 | |
| Cherries | Monocrotophos | 2 | ||
| Turnip roots | Difenoconazole | 1 | ||
| Spain | Hazelnuts | MCPA | 3 | |
| Wild strawberries | Bupirimate | 1 | ||
| Brazil | Coffee beans | Pyraclostrobin (1), flutriafol (1) | 2 | |
| Chicken | Ethoxyquin | 1 | ||
| Wheat | Methamidofos | 1 | ||
| Venezuela | Cacao beans | Chlorpyrifos (1) | 2, 4-D (1) | 2 |
| Sesame seeds | Chlorpyrifos | 1 | ||
| Belgium | Red currants | Trifloxystrobin (1), flusilazole (1) | 2 | |
| Leek | Haloxyfop | 1 | ||
| Yemen | Coffee beans | γ--BHC (lindane) (1) | Chlordane (1), heptachlor (1) | 3 |
| Myanmar | Coffee beans | DDT | 1 | |
| Galvanso beans | Cypermethrin | 1 | ||
| Vietnam | Spinach | Indoxacarb | 1 | |
| Immature field peas | Flusilazole | 1 | ||
| Paraguay | Sesame seeds | Imidacloprid | 2 | |
| Italy | Fennel | Chlorpyrifos-methyl | 1 | |
| Leek | Famoxadone | 1 | ||
| Indonesia | Coffee beans | Isoprocarb | 1 | |
| Mozambique | Sesame seeds | DDT | 1 | |
| Chile | Blueberries | Indoxacarb | 1 | |
| Peru | Quinoas | Methamidofos | 1 | |
| Guatemala | Sesame seeds | Methamidofos | 1 | |
| Total | 359 | |||
* “Number of cases” is the gross number of violations.
| Country of Production (Number of violations Total) |
Item Type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thailand (57) |
Frozen food (prawns) | Viable cell count (11), coliform bacteria (3) | 14 |
| Frozen food (livestock) | Viable cell count (5), coliform bacteria (7), E. coli (1) | 13 | |
| Frozen food (fish) | Viable cell count (3), coliform bacteria (6), E. coli (1) | 10 | |
| Frozen food (squid) | Viable cell count (4), coliform bacteria (3) | 7 | |
| Frozen food (fruit) | Viable cell count (2), coliform bacteria (3) | 5 | |
| Frozen food (aquatic animals) |
Viable cell count (1), coliform bacteria (2) | 3 | |
| Fish paste products | Coliform bacteria | 2 | |
| Meat products | E. coli | 1 | |
| Frozen food (other) | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| Frozen food (vegetables) | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| China (50) |
Frozen food (other) | Viable cell count (3), coliform bacteria (5), E. coli (1) | 9 |
| Frozen food (vegetables) | Coliform bacteria (5), E. coli (4) | 9 | |
| Frozen food (fish) | Viable cell count (3), coliform bacteria (4) | 7 | |
| Meat products | Staphylococcus aureus (1), coliform bacteria (3), E. coli (2) | 6 | |
| Frozen food (shellfish) | Viable cell count (2), coliform bacteria (3) | 5 | |
| Frozen food (aquatic animals) |
Viable cell count (4), E. coli (1) | 5 | |
| Food packed in containers and sterilized by pressurization and heating |
Microorganisms with potential to grow | 3 | |
| Frozen food (squid) | Viable cell count (1), coliform bacteria (1) | 2 | |
| Frozen food (livestock food products) |
Viable cell count (1), E. coli (1) | 2 | |
| Frozen food (prawns) | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| Frozen food (agricultural food products) |
Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| Philippines (30) |
Frozen food (aquatic animals) |
Viable cell count | 9 |
| Frozen food (squid) | Viable cell count (4), coliform bacteria (4) | 8 | |
| Frozen food (fruit) | Viable cell count (2), coliform bacteria (1), E. coli (1) |
4 | |
| Frozen food (sea urchins) | Viable cell count (2), Most probable number
(MPN) of vibrio parahaemolyticus (1) |
3 | |
| Frozen food (fish) | Viable cell count (1), coliform bacteria (2) | 3 | |
| Boiled octopus | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| Frozen food (shellfish) | Viable cell count | 1 | |
| Frozen food (vegetables) | Viable cell count | 1 |
| Country of Production (Number of violations Total) |
Item Type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Korea (29) |
Frozen food (vegetables) | Viable cell count (7), coliform bacteria (4) | 11 |
| Boiled crab | Viable cell count (2), coliform bacteria (2) | 4 | |
| Frozen food (squid) | Viable cell count (3), coliform bacteria (1) | 4 | |
| Frozen food (shellfish) | Viable cell count (2), Most probable number (MPN) of vibrio parahaemolyticus (2) |
4 | |
| Frozen food (aquatic animals) | Viable cell count (1), coliform bacteria (2), E. coli (1) |
4 | |
| Frozen food (other) | Viable cell count | 2 | |
| Vietnam (23) |
Frozen food (fish) | Viable cell count (1), coliform bacteria (4), E. coli (3) |
8 |
| Fish paste products | Coliform bacteria | 3 | |
| Frozen food (squid) | Viable cell count (2), coliform bacteria (1) | 3 | |
| Frozen food (prawns) | Coliform bacteria (2), E. coli (1) | 3 | |
| Frozen food (octopus) | Viable cell count (1), coliform bacteria (1) | 2 | |
| Frozen food (vegetables) | Coliform bacteria (1), E. coli (1) | 2 | |
| Boiled octopus | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| Frozen food (other) | Viable cell count | 1 | |
| Taiwan (11) |
Frozen food (other) | Viable cell count (3), coliform bacteria (1) | 4 |
| Ice | Coliform bacteria | 2 | |
| Meat products | E. coli | 1 | |
| Food packed in containers and sterilized by pressurization and heating |
Microorganisms with potential to grow | 1 | |
| Frozen food (fruit) | Viable cell count | 1 | |
| Frozen food (fish) | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| Frozen food (vegetables) | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| U.S. (10) |
Powdered beverages | Viable cell count (3), coliform bacteria (3) | 6 |
| Frozen food (vegetables) | Coliform bacteria | 3 | |
| Frozen food (fruit) | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| Indonesia | Boiled octopus | Viable cell count (1), coliform bacteria (2), | 3 |
| Frozen food (fish) | Coliform bacteria | 2 | |
| Frozen food (prawns) | E. coli | 1 | |
| Frozen food (shellfish) | Viable cell count | 1 | |
| Frozen food (aquatic animals) | Viable cell count | 1 | |
| Chile | Frozen food (fish) | Viable cell count (2), coliform bacteria (5) | 7 |
| Norway | Frozen food (fish) | Viable cell count (5), coliform bacteria (1) | 6 |
| India | Frozen food (other) | Viable cell count (2), coliform bacteria (1), E. coli (1) |
4 |
| Powdered beverages | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| Italy | Meat products | Staphylococcus aureus | 2 |
| Frozen food (other) | Viable cell count (1), coliform bacteria (1) | 2 | |
| Netherlands | Frozen food (other) | Viable cell count (1), coliform bacteria (2) | 3 |
| Sweden | Frozen food (other) | Coliform bacteria | 2 |
| Frozen food (vegetables) | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| Canada | Frozen food (desserts) | Coliform bacteria | 1 |
| Frozen food (fish) | Viable cell count | 1 | |
| Boiled crab | Coliform bacteria | 1 |
| Country of Production (Number of violations Total) |
Item Type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peru | Frozen food (vegetables) | Viable cell count (1), E. coli (1) | 2 |
| France | Frozen food (other) | Viable cell count | 1 |
| Butter | Coliform bacteria | 1 | |
| Russia | Boiled crab | Coliform bacteria | 1 |
| Pakistan | Frozen food (fish and shellfish) | Viable cell count | 1 |
| Denmark | Butter | Coliform bacteria | 1 |
| Costa Rica | Frozen food (fruit) | Viable cell count | 1 |
| Malaysia | Frozen food (other) | Viable cell count | 1 |
| Australia | Butter | Coliform bacteria | 1 |
| Sri Lanka | Powdered beverages | Viable cell count | 1 |
| Total | 260 | ||
* “Number of cases” is the gross number of violations.
| Country of Production (Number of violations Total) |
Item Type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. (68) |
Corn | Aflatoxin | 50 |
| Peanuts | Aflatoxin | 8 | |
| Almonds | Aflatoxin | 6 | |
| Pistachio nuts | Aflatoxin | 2 | |
| Brazil nuts | Aflatoxin | 1 | |
| Dried figs | Aflatoxin | 1 | |
| China (19) |
Peanuts | Aflatoxin | 9 |
| Frozen food (shellfish) | Diarrhetic shellfish poison | 4 | |
| Ark shell | Paralytic shellfish poison (3), diarrhetic shellfish poison (1), | 4 | |
| Adlay | Aflatoxin | 2 | |
| France (17) |
Other (frozen desserts) | Cyanide compounds | 17 |
| India (14) |
Sickle senna seeds | Aflatoxin | 5 |
| Chili peppers | Aflatoxin | 3 | |
| Nutmeg | Aflatoxin | 3 | |
| Peanuts | Aflatoxin | 1 | |
| Curry powder | Aflatoxin | 1 | |
| Turmeric | Aflatoxin | 1 | |
| Thailand (13) |
Adlay | Aflatoxin | 10 |
| Cassava | Cyanide compounds | 2 | |
| Chili peppers | Aflatoxin | 1 | |
| Italy (13) |
Confectionery | Aflatoxin (1), cyanide compounds (6) | 7 |
| Pistachio nuts | Aflatoxin | 2 | |
| Dried figs | Aflatoxin | 2 | |
| Apple juice | Patulin | 1 | |
| Lima beans | Cyanide compounds | 1 | |
| Brazil | Powdered seasonings | Cyanide compounds | 4 |
| Cassava | Cyanide compounds | 1 | |
| Canada | Lobster | Paralytic shellfish poison | 3 |
| Crawfish | Paralytic shellfish poison | 1 | |
| Indonesia | Nutmeg | Aflatoxin | 3 |
| Cassava | Cyanide compounds | 1 | |
| South Africa | Peanuts | Aflatoxin | 3 |
| Australia | Apple juice | Patulin | 2 |
| Peanuts | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Country of Production (Number of violations Total) |
Item Type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iran | Pistachio nuts | Aflatoxin | 2 |
| Peru | Snack food | Cyanide compounds | 1 |
| Other (peanut products) | Aflatoxin | 1 | |
| Myanmar | Butter beans | Cyanide compounds | 1 |
| Chili peppers | Aflatoxin | 1 | |
| Venezuela | Cacao beans | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Paraguay | Peanuts | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Philippines | Cassava | Cyanide compounds | 1 |
| Turkey | Hazelnuts | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Bolivia | Sesame seeds | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Bangladesh | Peanut products | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Korea | Freshwater clams | Paralytic shellfish poison | 1 |
| Vietnam | Adlay | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Nigeria | Sesame seeds | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Sri Lanka | Chili peppers | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Argentine | Peanuts | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Jamaica | Curry powder | Aflatoxin | 1 |
| Total | 181 | ||
* “Number of cases” is the gross number of violations.
| Country of Production (Number of violations Total) |
Item Type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| China (39) |
Foods containing milk and dairy products |
Melamine | 13 |
| Processed vegetables | Polysorbate (1), sulfur dioxide (6) | 7 | |
| Processed fishery food products |
Sorbic acid (1), sulfur dioxide (4) | 5 | |
| Pickles | Cyclamic acid (1), sorbic acid (1), undesignated coloring agent (2) |
4 | |
| Frozen food (other) | TBHQ | 4 | |
| Health foods | p-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Esters (1), ethyl p-hydroxybenzoate (1), cyclamic acid (1) |
3 | |
| Herring roe | Hydrogen peroxide | 1 | |
| Processed fruit products | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Other (Daimyo Oak leaf) | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Taiwan (19) |
Other (powdered food) | Sodium aluminosilicate | 5 |
| Processed bean products | Sorbic acid (1), sulfur dioxide (1) | 2 | |
| Dried vegetables | Sulfur dioxide | 2 | |
| Syrup | Cyclamic acid | 1 | |
| Fishery food products | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Processed nut and seed products |
Cyclamic acid | 1 | |
| Prepared cereals | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Retort pouch foods | Iodized salt | 1 | |
| Frozen food (fishery food products) |
Cyclamic acid | 1 | |
| Beverages | Potassium sorbate | 1 | |
| Soybean oil | TBHQ | 1 | |
| Pickles | Cyclamic acid | 1 | |
| Seasonings | Rhodamine B | 1 | |
| U.S. (14) |
Salted salmon roe | Nitrite | 4 |
| Processed fishery food products (boiled clam) |
Disodium ethylenediaminotetraacetate | 2 | |
| Syrup | Sorbic acid | 1 | |
| Processed bean products | Disodium ethylenediaminotetraacetate | 1 | |
| Milk and dairy products | Sorbic acid | 1 | |
| Margarine | TBHQ | 1 | |
| Frozen food (agricultural food products) |
Sorbic acid | 1 | |
| Meat products | Sodium aluminosilicate | 1 | |
| Fruit vinegars | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Other | Sodium aluminosilicate | 1 |
| Country of Production (Number of violations Total) |
Item Type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thailand(12) | Seasonings | Benzoic acid | 2 |
| Fish paste products | Benzoic acid (1), trimethylamine (1) | 2 | |
| Rice | Rhodamine B | 2 | |
| Rice flour | Sulfur dioxide | 2 | |
| Cookies | TBHQ | 1 | |
| Prepared vegetables | TBHQ | 1 | |
| Prepared cereals | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Boiled vegetables | Benzoic acid | 1 | |
| Italy | Fruit vinegars | Sulfur dioxide | 3 |
| Instant coffee | Methylene chloride | 1 | |
| Bakery products | Iodized salt | 1 | |
| Processed fruit products | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Confectionery | Patent Blue V | 1 | |
| Chocolate | Sorbic acid | 1 | |
| Spain | Health foods | Isopropanol (1), butyl acetate (1) | 2 |
| Processed fruit products | Sorbic acid (2) | 2 | |
| Pickles | Ferrous gluconate (1), sulfur dioxide (1) | 2 | |
| Prepared vegetables | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Spices | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Vietnam | Frozen food (fishery food products) | Cyclamic acid (1), sulfur dioxide (1) | 2 |
| Coffee products | Cyclamic acid | 1 | |
| Processed fishery products | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Beer | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Brazil | Vegetable oil and fat | TBHQ | 3 |
| Corn flour | TBHQ | 1 | |
| Processed propolis | Polyethylene glycol | 1 | |
| Denmark | Salted salmon roe | Nitrite | 3 |
| Jam | Sorbic acid | 1 | |
| Malaysia | Confectionery | Polysorbate (1), melamine (2) | 3 |
| Netherlands | Liqueur | Patent Blue V (1), azorubine (1), Brilliant Black BN (1) |
3 |
| Philippines | Processed tuna products | Carbon monoxide | 2 |
| Fruit puree | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Canada | Salted salmon roe | Nitrite | 3 |
| France | Chocolate | Azorubine | 3 |
| Country of Production (Number of violations Total) |
Item Type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Madagascar | Processed fishery products | Sulfur dioxide | 2 |
| Bangladesh | Pickles | Benzoic acid (1), sulfur dioxide (1) | 2 |
| Hong Kong | Seasonings | TBHQ | 1 |
| Processed fishery products | Hydrogen peroxide | 1 | |
| Turkey | Dried fruit | Sulfur dioxide | 1 |
| Jamaica | Seasonings | Sorbic acid | 1 |
| Argentina | Soybean oil | TBHQ | 1 |
| Korea | Health foods | Polysorbate | 1 |
| Bolivia | Chocolate | TBHQ | 1 |
| United Arab Emirates |
Candy | Azorubine | 1 |
| India | Processed vegetables | Benzoic acid | 1 |
| Total | 142 | ||
* “Number of cases” is the gross number of violations.
| Country of production (Number of violation Total) |
Item type | Violation | Number of cases* |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New/conventional standard |
Uniform standard | |||
| China (58) |
Meat products (chicken) |
Furazolidone (as AOZ) (7), furaltadone (as AMOZ) (13) |
20 | |
| Prawns | Oxytetracycline (1), tetracycline (1) |
Sulfamethoxazole (9), sulfadiazine (1) |
12 | |
| Frozen food (Chiken products) |
Furazolidone (as AOZ) (4), furaltadone (as AMOZ) (5) |
9 | ||
| Clam | Chloramphenicol | 5 | ||
| Eel | Leucomalachite green (1), enrofloxacin (3) |
4 | ||
| Processed royal jelly | Chloramphenicol (1), furazolidone (as AOZ) (1) |
2 | ||
| Prepared chiken | Furazolidone (as AOZ) | 1 | ||
| Food packed in containers and sterilized by pressurization and heating (chicken) |
Furazolidone (as AOZ) | 1 | ||
| Frozen food (pork products) |
Clenbuterol | 1 | ||
| Salmon | Oxytetracycline | 1 | ||
| Mackerel | Leucomalachite green | 1 | ||
| Processed pollen | Tetracycline | 1 | ||
| Vietnam (43) |
Frozen food (prawns) |
Chloramphenicol (6), furazolidone (as AOZ) (14) |
20 | |
| Prawns | Chloramphenicol (11), furazolidone (as AOZ) (3), sulfamethoxazole (1) |
15 | ||
| Squid | Chloramphenicol | 4 | ||
| Dried unseasoned products (squid) |
Chloramphenicol | 2 | ||
| Dried unseasoned products (prawns) |
Chloramphenicol | 1 | ||
| Frozen food (squid) | Chloramphenicol | 1 | ||
| Indonesia (10) |
Frozen food (prawns) | Nitrofurantoin (as AHD) (1), furazolidone (as AOZ) (5) |
6 | |
| Prawns | Nitrofurantoin (as AHD) (1), furazolidone (as AOZ) (3) |
4 | ||
| Thailand | Soft-shelled turtles | Furaltadone (1), enrofloxacin (1) |
2 | |
| Taiwan | Groupers | Leucomalachite green | 1 | |
| Malaysia | Prawns | Sulfadiazine | 1 | |
| Total | 115 | |||
* “Number of cases” is the gross number of violations.
| Month of reinforcement |
Country | Food and contents | Background and monitoring status |
|---|---|---|---|
| April 2008 | U.S. | Cereal (possibly contaminated with Salmonella) |
In response to information regarding product recall in the U.S., an instruction was issued for the reshipment of the product in question. |
| April 2008 | Italy | Natural cheese (possibly contaminated with Listeria) |
Measures were taken to return shipments for each import notification of such products, based on information that Italian-produced cheese was found to be contaminated with Listeria monocytogenes in Germany. Voluntary inspections measures were taken for cheese produced by the manufacturer in question. |
| April 2008 | Australia | Baby food (possibly containing foreign matters) |
In response to information regarding product recall in Australia, an instruction was issued for the reshipment of the product in question. |
| June 2008 | U.S. | Melon (possibly contaminated with Salmonella) |
Measures were taken to return shipments for each import notification of such a product based on information regarding product recall in the U.S. |
| June 2008 | U.S. | Cookies (risk of irradiation) |
In response to information regarding product recall in the UK, measures have been prepared to return the product in question if an import notification is submitted. |
| July 2008 | New Zealand | Beef (possibly contaminated with endosulfan) |
Voluntary inspections measures were taken for each import notification of such a product in response to a report from Korea that beef from New Zealand was found to be tainted with endosulfan. |
| July 2008 | New Zealand | Oysters (possibly contaminated with norovirus) |
Based on information regarding the recall of contaminated edible oysters that caused norovirus outbreaks in New Zealand, measures have been prepared to return the product in question if an import notification is submitted. |
| July 2008 | Philippines | Fish and shellfish, etc. (possibly contaminated with endosulfan) |
Based on information regarding the possible contamination with endosulfan that leaked into the sea after a ferry sunk off the coast of Sibuyan Island in the Philippines, measures have been taken to reship the fish and shellfish caught in the sea area in question. |
| July 2008 | Canada/U.S. | Lobster (possibly contaminated with paralytic shellfish poison) |
Voluntary inspections measures were taken for each import notification of lobster from the waters of the Atlantic Ocean from Canada to the U.S. based on a warning issued in the U.S. to avoid eating lobster tomalley because of potential contamination with paralytic shellfish poison. |
| Month of reinforcement |
Country | Food and contents | Background and monitoring status |
|---|---|---|---|
| August 2008 | Mexico | Chili peppers (possibly contaminated with Salmonella) |
In response to a report that Mexican-grown raw peppers had been linked to a salmonella outbreak in the U.S., guidelines were issued for each import notification of such products, outlining the use of raw peppers only for heat processed foods. |
| August 2008 | Chile | Pork (possibly contaminated with dioxins) |
Based on a report from Korea that Chilean pork was found to be tainted with dioxins, measures were taken to ban imports of pork produced at the related farms, and to monitor pork produced at other farms for dioxins. |
| September 2008 | France | Natural cheese (possibly contaminated with Listeria) |
Based on a report that listeria had been found in soft natural cheese in France and that the cheese had been exported to Japan, an order was issued to inspect the producer in question. |
| September 2008 | China | Baby formula (possibly containing melamine) |
Orders were put in place to suspend import notifications of milk and dairy products based on a report from China regarding the occurrence of kidney stones in infants as a result of ingesting baby formula. In response to China's disclosure of the identity of the producers involved, an order was issued to importers of processed foods made from milk and dairy products to make sure that no melamine is present in the ingredients, and processed foods made from milk and dairy products were made subject to inspection. |
| October 2008 | China | Ice goby and sweetfish (possibly contaminated with formaldehyde) |
In response to information that a substantial amount of formaldehyde had been detected in ice goby sold in China, measures have been put in place for voluntary inspections when import notifications of ice goby and sweetfish are submitted. |
| December 2008 | Ireland | Pork (possibly contaminated with dioxins) |
In response to information that dioxins were found in pork in Ireland, a reshipment instruction of the product in question has been issued. |
| January 2009 | U.S. | Peanut products (possibly contaminated with Salmonella) |
In response to information that the outbreak of salmonellosis in U.S. was associated with peanut products, measures have been prepared to return the product in question if an import notification is submitted. |
| Item (Item Subject to Inspection Order, etc.) |
Bilateral Discussion | Time of On-site Inspection |
|---|---|---|
| Beef produced in the U.S. (BSE) |
Talks began in December 2003. In December 2005, exporting from specific facilities resumed, on the condition of compliance with an export program. In January 2006, as a result of veal produced in the U.S. being confirmed to contain spinal column, import procedures were suspended for all beef produced in the U.S. Import procedures resumed in July 2006. For the purpose of verifying compliance with the export program, on-site inspections were conducted at the authorized facilities focused on export to Japan. Talks are still underway. | August 2008 |
| Perilla and chili peppers produced in Korea (residual agricultural chemical) |
Consultations started in April 2008. Implemented on-site inspections on registered producers and farms. Removed inspection orders on imported foods. | September 2008 |
| Beef produced in Canada (BSE) |
Talks began in May 2003. For the purpose of verifying compliance with the export standards, on-site inspections were conducted at the Canadian government-authorized facilities focused on export to Japan. Talks are still underway. | October 2008 |
| Asparagus produced in the Philippines (Difenoconazole) |
Consultations started in May 2007. Implemented on-site inspections on registered producers and farms. Removed inspection orders on imported foods. | November 2008 |
| Okra produced in the Philippines (Tebufenozide, fluazifop, methamidophos) |
Consultations started in February 2008. Implemented on-site inspections on registered producers and farms. Removed inspection orders on imported foods. | November 2008 |
| Green asparagus produced in Thailand (EPN) |
Consultations started in July 2008. Implemented on-site inspections on registered producers and farms. Removed inspection orders on imported foods. | February 2009 |
| Bananas produced in Thailand (Cypermethrin) |
Consultations started in October 2008. Implemented on-site inspections on registered producers and farms. Removed inspection orders on imported foods. | February 2009 |
| Pork produced in Chile (Dioxin) |
Consultations started in July 2008. Implemented on-site inspections with an aim to verify the dioxin program. | February-March 2009 |
| Edamame (green soybeans), perilla and lychee produced in China (Residual agricultural chemicals) |
Implemented on-site inspections on registered producers and farms. Removed inspection orders on imported foods. | March 2009 |
| Honey produced in China (animal drugs) |
Implemented on-site inspections. Removed inspection orders. | March 2009 |
| Chicken produced in China (animal drugs) |
Consultations started in June 2008. Implemented on-site inspections on chicken farms and processing facilities. Consultations under way. | March 2009 |
| Foods produced in China (overall food sanitation) |
The MHLW requested that China prevent export of foods violating Chinese law and ensure compliance with the Food Sanitation Act of Japan. | March 2009 |
| Coffee beans produced in Ethiopia (Residual agricultural chemicals) |
Consultations started in May 2008. Implemented on-site inspections on registered producers and farms. Consultations under way. | March-April 2009 |
| 2004 | 2005 | FY2006 | FY2007 | FY2008 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Import consultations | 5,506 | 9,210 | 9,786 | 10,633 | 11,601 |
| Number of import consultations by item | 11,023 | 18,408 | 18,224 | 22,038 | 27,083 |
| Number of violations by item | 468 | 691 | 679 | 401 | 410 |
* Offices of Imported Food Consultation are located in quarantine stations in Otaru, Sendai, Narita Airport, Tokyo, Yokohama, Niigata, Nagoya, Osaka, Kansai Airport, Kobe, Hiroshima, Fukuoka, and Naha.
* Since FY2005, figures have been aggregated by fiscal year.
* The figures record only those consultations conducted at Offices of Imported Food Consultation prior to importation.
| Article | Number of Violations |
Ratio (%) |
Description of Major Violations |
|---|---|---|---|
Article 6
(Food and additives banned from sale) |
3 | 0.6 | Detection of cyanide compounds and epinephelus fuscoguttatus (non-importable fish species and forms), use of lupine beans |
Article 9
(Restriction on the sale, etc., of diseased meat, etc.) |
4 | 0.8 | Foods containing bovine-derived materials from a BSE-affected country (voluntary import restraint) |
Article 10
(Restriction on the sale, etc., of additives, etc.) |
224 | 44.9 | Use of iodized salt, Quinoline Yellow, rhodamine B, azorubine, Brilliant Black BN, Patent Blue V, TBHQ, cyclamic acid, sodium stearoyl lactylate, etc. |
Article 11
(Standards for foods or additives) |
259 | 51.9 | Noncompliance with manufacturing or processing standards Violation of standards for the use of additives
|
Article 18
(Standards for equipmentand containers/packaging) |
1 | 0.2 | Violation of specifications for equipment and containers/packaging. Violation of material-specific specifications for raw materials. |
Article 62
(Mutatis mutandisapplication to toys, etc.) |
8 | 1.6 | Violation of specifications for toys or their raw materials |
| Total | 499 (gross) 410 (real) |
||
| Country of Production |
Item | Description of Violations | Number of Cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. (131) |
Health foods | Citrulline maleate (1), sodium lauryl sulfate (1), L-cysteine hydrochloride (1), calcium citrate (2), tocopherol succinate (1), betaine hydrochloride (1), diacetone (1), sucralose (1), talc (2), chromium nicotinate (1), pantothenic acid (1), pantethine (1), calcium pyruvate (1), magnesium peroxide (1), selenomethionine (3), zinc citrate (3), calcium ascorbate (5), magnesium ascorbate (5), manganese hydrogen phosphate (1), lysine hydrochloride (1), croscarmellose sodium (2), hydroxymethyl cellulose (1), polyethylene glycol (1), colostrum (1), methanol (1), ethyl acetate (1), sodium chondroitin sulfate (1), copper chlorophyll (3), silicon dioxide (1), chromium chloride (1), zinc oxide (1), potassium acetate (1), copper sulfate (1) | 50 |
| Processed cereal products |
Potassium sorbate (16), calcium propionate (5), propionic acid (11), sodium sorbate (1), polyethylene glycol (1), L-cysteine (5) | 39 | |
| Soft drinks | Potassium sorbate (2), sodium propionate (1), benzoic acid (1), selenomethionine (2), vanadium citrate (2), magnesium citrate (1), manganese citrate (1), zinc citrate (1), copper citrate (1), chromium polynicotinate (2), sodium molybdate (1), potassium iodide (1), noncompliance with manufacturing standards (2) | 18 | |
| Confectionery | Sorbic acid (3), polysorbate (1), β-apo-8'-carotenal (3), sodium stearoyl lactylate (6), general noncompliance of additives with manufacturing standards (1) | 14 | |
| Powdered beverages | Propylene glycol (1), methyl chloride (1), ethyl acetate (1) | 3 | |
| Other foods | Saccharin | 1 | |
| Mineral water | Noncompliance with raw water standards | 1 | |
| Fruit wine | Argon | 1 | |
| Theobromine | Deviation from existing additive listing standards in terms of origin, method and composition | 1 | |
| Sugar | Polysorbate | 1 | |
| Processed bean products |
Use of lima beans | 1 | |
| Frozen foods | Sodium stearoyl lactylate | 1 | |
| Italy (57) |
Ice cream | Noncompliance with manufacturing standards | 29 |
| Meat products | Noncompliance with manufacturing standards | 9 | |
| Confectionery | Calcium ascorbate (1), sorbic acid (3), potassium sorbate (1), Patent Blue V (2), sunflower lecithin (1) | 8 | |
| Health foods | Ferrous fumarate (1) p-toluenesulfonic acid (1), zinc sulfate (1) | 3 | |
| Seasonings | Processed beef products from a BSE-affected country (1), potassium acetate (1), sodium acetate (1) | 3 | |
| Processed vegetables | Sulfur dioxide | 3 | |
| Processed fruit | Sodium copper chlorophyllin | 1 | |
| Soft drinks | Silicon resin | 1 |
| Country of Production |
Item | Description of Violations | Number of Cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| China (34) |
Seasonings | TBHQ (1), potassium sorbate (3), sorbic acid (7) | 11 |
| Toys | Bis phthalate | 7 | |
| Processed agricultural products |
Sorbic acid (1) | 5 | |
| Confectionery | TBHQ (2), sodium benzoate (2) | 4 | |
| Processed vegetables |
Potassium sorbate (1), copper chlorophyll (2), sulfur dioxide (1) | 4 | |
| Processed fish and shellfish products |
Potassium sorbate | 1 | |
| Equipment | Noncompliance with compositional standards | 1 | |
| Additives | Noncompliance with compositional standards | 1 | |
| Brazil | Confectionery | Sorbic acid (2), propionic acid (3), TBHQ (2), sodium aluminophosphate (2), potassium chlorate (1) | 10 |
| Seasonings | Sodium saccharin (1), benzoic acid (1), sodium aluminosilicate (1), sodium cyclamate (1), potassium iodide (1) | 5 | |
| Alcoholic beverages | Potassium sorbate | 2 | |
| Processed fruit products |
Liquid paraffin | 1 | |
| Processed fish products |
TBHQ | 1 | |
| Health foods | Propylene glycol | 1 | |
| Processed vegetables |
Liquid paraffin | 1 | |
| France | Confectionery | Amidated pectin (1), carmine (2), Brilliant Black BN (2), sodium stearoyl lactylate (6), azorubine (1) | 12 |
| Meat products | Bovine-derived gelatine from a BSE-affected country (2), noncompliance with manufacturing standards (1) | 3 | |
| Fruit wine | Metatartaric acid | 2 | |
| Soft drinks | Potassium sorbate | 1 | |
| Seasonings | Copper chlorophyll | 1 | |
| Canada | Health foods | Tocopherol succinate (5), potassium iodide (5), zinc acetate (5), undesignated additive (1) | 16 |
| Processed agricultural products |
Magnesium stearate (1), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (1) | 2 | |
| Korea | Health foods | DL-α- tocopherol acetate (1), tocopherol acetate (1), calcium monohydrogen phosphate (1), ferrous fumarate (2), zinc oxide (4) | 9 |
| Confectionery | TBHQ (1), polysorbate (2) | 3 | |
| Seasonings | Potassium sorbate (1), biotin (2) | 3 | |
| Processed fish and shellfish products |
Potassium sorbate | 1 | |
| Processed fish products |
Trimethylamine | 1 | |
| Soft drinks | Noncompliance with manufacturing standards | 1 |
| Country of Production |
Item | Description of Violations | Number of Cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belgium | Confectionery | Sorbic acid (1), use of lupine beans (1), azorubine (5), Quinoline Yellow (2), Patent Blue (2), undesignated additive (unidentified water-soluble orange pigment) (1), copper chlorophyll (1) | 13 |
| Soft drinks | Noncompliance with manufacturing standards (sterilization) (2), sulfur dioxide (2) | 4 | |
| Singapore | Instant coffee | Sodium aluminosilicate (6), magnesium silicate (5), sodium stearoyl lactylate (5) | 16 |
| Powdered beverages | Sodium aluminosilicate | 1 | |
| Philippines | Confectionery | Iodized salt | 6 |
| Processed nut and seed products | Iodized salt | 3 | |
| Seasonings | Iodized salt | 3 | |
| Processed fish products | Iodized salt | 2 | |
| Processed fruits | Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Powdered beverages | Selenium | 1 | |
| Taiwan | Soft drinks | Potassium sorbate | 6 |
| Frozen foods | Potassium iodate | 3 | |
| Processed nut and seed products | Inosine monophosphate (1), guanosine monophosphate (1) | 2 | |
| Kimchi | Silicon dioxide | 1 | |
| Processed fish and shellfish products | Polysorbate | 1 | |
| Health foods | Streptomycin | 1 | |
| Processed cereal products | Sodium stearoyl lactylate | 1 | |
| India | Health foods | Magnesium stearate (3), sodium propyl parahydroxybenzoate (3), sodium methyl parahydroxybenzoate (3) | 9 |
| Processed vegetables | Sodium benzoate | 3 | |
| Instant noodles | Iodized salt | 2 | |
| Thailand | Seasonings | Potassium sorbate (1), sorbic acid (5), TBHQ (1) | 7 |
| Processed fish and shellfish products | Saccharin | 3 | |
| Food packed in containers and sterilized by pressurization and heating | L-cysteine | 1 | |
| Confectionery | TBHQ | 1 | |
| Black tea | Food Yellow No.5 | 1 | |
| Processed vegetables | Sodium benzoate | 1 |
| Country of Production |
Item | Description of Violations | Number of Cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | Health foods | Glucosamine sulfate (1), magnesium ascorbate (1), mineral chelate (1), sodium lauryl sulfate (1), colostrum (1) | 5 |
| Soft drinks | Potassium sorbate (4), copper chlorophyll (1) | 5 | |
Processed cereal products |
TBHQ | 1 | |
| Confectionery | Azorubine | 1 | |
| Seasonings | Use of azorubine | 1 | |
| Sri Lanka | Processed |
Sodium benzoate | 6 |
| Seasonings | Sodium benzoate | 5 | |
| Health foods | Glucosamine sulfate | 1 | |
| Soft drinks | Noncompliance with manufacturing standards (sterilization) | 1 | |
| Malaysia | Seasonings | Sorbic acid (3), benzoic acid (3) | 6 |
| Other foods | Sodium aluminosilicate (1), sodium stearoyl lactylate (1) | 2 | |
| Powdered beverages |
Sulfur dioxide | 1 | |
| Mineral water | Noncompliance with raw water standards | 1 | |
| Peru | Confectionery | Potassium sorbate | 5 |
| Processed nut and seed products |
Calcium hydroxide | 2 | |
| Spain | Confectionery | Quinoline Yellow (1), Patent Blue (1), Black PN (1) | 3 |
| Natural cheese | Iron sesquioxide | 1 | |
| Processed nut and seed products |
Cyanide content | 1 | |
| Soft drinks | Noncompliance with manufacturing standards | 1 | |
| New Zealand | Confectionery | Potassium sorbate | 2 |
| Health foods | Iron sesquioxide (1), iron oxide (1) | 2 | |
| Honey | Chloramphenicol | 1 | |
| Soft drinks | Noncompliance with manufacturing standards (sterilization) | 1 | |
| Indonesia | Seasonings | Potassium sorbate (3), Sodium benzoate (1) | 4 |
| Processed fruit products |
Sodium benzoate | 1 | |
| Vietnam | Processed fish and shellfish products |
Sorbic acid (1), benzoic acid (1) | 2 |
| Confectionery | Isovaleric aldehyde | 1 | |
| Fresh fish | Epinephelus fuscoguttatus | 1 | |
| UK | Other foods | Sodium benzoate | 2 |
| Health foods | Bovine-derived processed goods from a BSE-affected country | 1 | |
| Soft drinks | Noncompliance with manufacturing standards | 1 | |
| Bulgaria | Processed vegetables |
Sodium benzoate (1), iodized salt (2), potassium benzoate (1) | 4 |
| Russia | Processed fruit products |
Sodium benzoate | 3 |
| Soft drinks | Potassium sorbate | 1 |
| Country of Production |
Item | Description of Violations | Number of Cases* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Turkey | Confectionery | Azorubine (2), trisodium pyrophosphate (1) | 3 |
| Processed fish and shellfish products |
Undesignated use of coloring agent | 1 | |
| Germany | Confectionery | Magnesium stearate | 2 |
| Soft drinks | DMDC (1), Sulfur dioxide (1) | 2 | |
| Australia | Olive oil | Isopropane | 3 |
| Mexico | Health foods | Magnesium stearate | 1 |
| Seasonings | Sodium nitrite (1), sodium benzoate (1) | 2 | |
| Estonia | Alcoholic beverages | Potassium sorbate | 3 |
| Romania | Processed nut and seed products |
Iodized salt | 2 |
| Chile | Alcoholic beverages | Ester gum | 2 |
| Switzerland | Toys | Coloring agent elution | 1 |
| Seasonings | Iodine | 1 | |
| Poland | Confectionery | Azorubine | 1 |
| Iran | Soft drinks | Noncompliance with manufacturing standards (sterilization) | 1 |
| Argentina | Confectionery | TBHQ | 1 |
| Vietnam | Sugar | Carboxymethylcellulose | 1 |
| Palau | Soft drinks | Noncompliance with manufacturing standards | 1 |
| Saudi Arabia | Confectionery | Sunflower lecithin | 1 |
| Egypt | Processed agricultural products |
Liquid paraffin | 1 |
| Austria | Soft drinks | Gluconolactone | 1 |
| Myanmar | Powdered beverages |
Sodium stearoyl lactylate | 1 |
| Total | 499 | ||
* “Number of cases” refers to the number of violation equivalents for each item.
| Country of Production | Item | Violation | Number of Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| China (3) | Dried gourd shavings | Sulfur dioxide | 1 |
| Pickles | Saccharin | 1 | |
| Toys | Bis phthalate | 1 | |
| India (2) | Prawns | Sulfur dioxide | 1 |
| Curry paste | TBHQ | 1 | |
| Myanmar (2) | Butter beans | Cyanide compounds | 2 |
| Taiwan | Seasonings | Benzoic acid | 1 |
| Peru | Maca powder | Irradiation | 1 |
| Malaysia | Prawns | Sulfadiazine | 1 |
| Total | 10 | ||
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Nitrite | Additive (color fixative) |
| Acetochlor | Pesticide (anilide herbicide) |
| Acephate | Pesticide (organophosphorus insecticide) |
| Azorubin | Undesignated additive |
| Atrazine | Pesticide (triazine herbicide) |
| Aflatoxin | Mycotoxin (produced by fungi such as Aspergillus) |
| Amitraz | Pesticide (amizine insecticide) |
| Alachlor | Pesticide (triazine herbicide) |
| Sodium aluminosilicate | Undesignated additive |
| Benzoic acid | Additive (preservative) |
| Carbon monoxide | Undesignated additive |
| Genetic modification | Technology such as fragmentation of bacterial genes, arrangement of the gene sequences or introducing the arranged genes into other organism's genes |
| Isoprocarb | Pesticide (carbamate insecticide) |
| Isopropanol | Additive (flavoring agent) |
| Imazalil | Additive (antifungal agent) |
| Imidacloprid | Pesticide (chloronicotinyl insecticide) |
| Indoxacarb | Pesticide (oxadiazine insecticide) |
| Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, disodium salt |
Additive (antioxidant) |
| Ethoxyquin | Feed additive (heterocyclic growth regulator) |
| Ethoprophos | Pesticide (organophosphorus insecticide) |
| Methylene chloride | Undesignated additive |
| Endosulfan | Pesticide (organochlorine insecticide) |
| Enrofloxacin | Animal drug (synthetic antimicrobial (new quinolone)) |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium that normally lives inside humans and animals and produces an enterotoxin, a type of heat-stable toxin that causes vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.) |
| Oxytetracycline | Animal drug (tetracycline antibiotic) |
| Oxolinic acid | Animal drug (Synthetic antimicrobial (quinolone)) |
| Oryzalin | Pesticide (dinitroaniline herbicide) |
| Hydrogen peroxide | Additive (bleaching agent) |
| Carbaryl | Pesticide (carbamate insecticide) |
| Quinalphos | Pesticide (organophosphorus insecticide) |
| Quinoline Yellow | Undesignated additive |
| Glyphosate | Pesticide (organophosphorus herbicide) |
| Ferrous gluconate | Additive (color stabilizing agent) |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Clenbuterol | Animal drug (uterine relaxant) |
| Clothianidin | Pesticide (neonicotinoide insecticide) |
| Chloramphenicol | Animal drug (chloramphenicol antibiotic) |
| Chlordane | Pesticide (organochlorine insecticide) |
| Chlorpyrifos | Pesticide (organophosphate insecticide) |
| Chlorpyrifos-methyl | Pesticide (organophosphate insecticide) |
| Magnesium silicate | Undesignated additive |
| Diarrhetic shellfish poison | Shellfish toxin (Clams accumulate biotoxins produced by plankton to excessive level, which causes poisoning) |
| Cyclamic acid | Undesignated additive |
| Butyl acetate | Additive (flavoring agent) |
| Saccharin | Additive (sweetening agent) |
| Salmonella | Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium that is ubiquitous in the intestines of animals as well as in nature, such as rivers, sewage and lakes. It contaminates meat, mostly poultry and eggs, and causes acute abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever and vomiting) |
| Iron sesquioxide | Additive (coloring agent) |
| Cyanide compounds | Toxic and harmful substances (cyanide-related compounds, such as cyanogenic glycoside, found in plants such as some varieties of beans) |
| Dicofol | Pesticide (organochlorine insecticide) |
| Difenoconazole | Pesticide (triazole fungicide) |
| Cyfluthrin | Pesticide (pyrethroid insecticide) |
| Cypermethrin | Pesticide (pyrethroid insecticide) |
| Magnesium stearate | Additive (reinforcing agent) |
| Streptomycin | Animal drug (aminoglycoside antibiotic ) |
| Sulfadiazine | Synthetic nitrofuran antimicrobial (sulfonamide) |
| Sulfamethoxazole | Synthetic nitrofuran antimicrobial (sulfonamide) |
| Shigella | Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium that normally lives in the intestines of humans and animals and causes gastroenteritis.) |
| Sorbic acid | Additive (preservative) |
| Diazinon | Pesticide (organophosphorus insecticide) |
| Dioxins | Generic name for the group of three substances: polychlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (PCDD), polychlorodibenzofuran (PCDF), and coplanar PCB |
| Dazomet | Pesticide (carbamate insecticide) |
| Daminozide | Pesticide (acid amide plant growth regulator) |
| Thiabendazole | Pesticide/animal drug (benzimidazole fungicide) |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium in seawater (at the river mouth, coastal areas, etc.) that commonly contaminates fish and shellfish, and causes abdominal pain, watery diarrhea, fever and vomiting.) |
| Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
Pathogenic microorganism (A bacterium that normally lives in the intestines of animals. It contaminates foods and drinking water by way of feces and urine, and causes acute abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea together with large amounts of fresh blood after early cold-like symptoms.) |
| Deoxynivalenol | Mycotoxin (produced by fungi such as Fusarium) |
| Tetraconazole | Pesticide (triazole fungicide) |
| Tetracycline | Animal drug (tetracycline antibiotic) |
| Tebuconazole | Pesticide (triazole fungicide) |
| Tebufenozide | Pesticide (benzoyl hydrazide insecticide) |
| Triazophos | Pesticide (organophosphate insecticide) |
| Trifloxystrobin | Pesticide (strobilurin fungicide) |
| Trimethylamine | Undesignated additive |
| Sulfur dioxide | Additive (antioxidant) |
| Nitrofurantoin | Animal drug (synthetic nitrofuran antimicrobial); generates AHD when metabolized |
| Nitrofurans | Generic name for nitrofuran synthetic antibacterial agent, an animal drug |
| Norovirus | Pathogenic virus (a type of virus that causes acute gastroenteritis and can be the causal agent of food poisoning from shellfish such as oysters) |
| Paclobutrazol | Pesticide (triazole plant growth regulator) |
| Patulin | Mycotoxin (produced by fungi such as Penicillium or Aspergillus) |
| Patent Blue V | Undesignated additive |
| Para-hydroxybenzoic acid esters | Additive (preservative) |
| Haloxyfop | Pesticide (organochlorine herbicide) |
| Bifenthrin | Pesticide (pyrethroid insecticide) |
| Piperonyl butoxide | Pesticide/animal drug (heterocyclic synergists) |
| Pyraclostrobin | Pesticide (strobilurin fungicide) |
| Pyridalyl | Pesticide (pyridyl ether insecticide) |
| Pirimiphos-methyl | Pesticide (organophosphate insecticide) |
| Pyrimethanil | Pesticide (pyrimidine fungicide) |
| Famoxadone | Pesticide (heterocyclic fungicide) |
| Fipronil | Pesticide (heterocyclic insecticide) |
| Fenvalerate | Pesticide (pyrethroid insecticide) |
| Fenpropathrin | Pesticide (pyrethroid insecticide) |
| Bis phthalate (DEHP) | Plasticizing agent (substance added to synthetic resin, making it pliable) |
| Bupirimate | Pesticide (pyrimidine fungicide) |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Buprofezine | Pesticide (heterocyclic insecticide) |
| Furazolidone | Animal drug (nitrofuran synthetic antibacterial agent); generates AOZ when metabolized |
| Furaltadone | Animal drug (nitrofuran synthetic antibacterial agent); generates AMOZ when metabolized |
| Brilliant Black BN | Undesignated additive |
| Fluazifop | Pesticide (phenoxy acid herbicide) |
| Fluquinconazole | Pesticide (triazole fungicide) |
| Flutriafol | Pesticide (azole fungicide) |
| Flusilazole | Pesticide (heterocyclic fungicide) |
| Flonicamid | Pesticide (Pyridine carboxamide insecticide) |
| Profenofos | Pesticide (organophosphorus insecticide) |
| Bromopropylate | Pesticide (acaricide) |
| Hexaconazole | Pesticide (triazole fungicide) |
| Heptachlor | Pesticide (organochlorine insecticide) |
| Pendimethalin | Pesticide (dinitroaniline herbicide) |
| Boscalid | Pesticide (anilide fungicide) |
| Polyethylene glycol | Undesignated additive |
| Polysorbate | Additive (emulsifying agent) |
| Formaldehyde | Undesignated additive |
| Paralytic shellfish poison | Shellfish poison (paralytic poison mainly caused by clams which accumulate poison produced by harmful plankton and which then become toxic) |
| Malachite green | Animal drug (triphenylmethane symthetic antibacterial agent) |
| Methamidofos | Pesticide (organophosphate insecticide) |
| Metam | Pesticide (carbamate insecticide) |
| Methyl isothiocyanate | Pesticide (carbamate insecticide) |
| Melamine | A chemical substance used as a primary raw material of melamine resin |
| Monocrotophos | Pesticide (organophosphate insecticide) |
| Iodized salt | Undesignated additive |
| Listeria | Pathogenic microorganism (A bacteria that is ubiquitous in the natural environment. It commonly contaminates dairy products and processed meat products, and causes flu-like symptoms with fatigue and fever.) |
| Rhodamine B | Undesignated additive |
| γ-BHC (lindane) | Pesticide (organochlorine insecticide) |
| AHD | Metabolite of nitrofurantoin, synthetic nitrofuran antimicrobial |
| AMOZ | Metabolite of furaltadone, synthetic nitrofuran antimicrobial |
| AOZ | Metabolite of furazolidone, synthetic nitrofuran antimicrobial |
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| BHC | Pesticide (organochlorine insecticide) |
| BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy) |
A delayed and malignant disease of the central nervous system, which causes the brain tissue of cows to become sponge-like, and which presents such symptoms as ananastasia |
| DDT | Pesticide (organochlorine insecticide) |
| EPN | Pesticide (organophosphorus insecticide) |
| MCPA | Pesticide (phenoxy herbicide) |
| SRM | Parts of a cow (the head [excluding tongue and cheek meat], the spinal cord, vertebral column, and ileum [up to a 2-m region from its connection with the cecum]) indicating the accumulation of an abnormal prion protein that is a possible causative agent of BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy). |
| TBHQ | Undesignated additive |
| 2,4-D | Pesticide (phenoxy acid herbicide) |
