

| INDEX | HOME |
| BACK | NEXT |
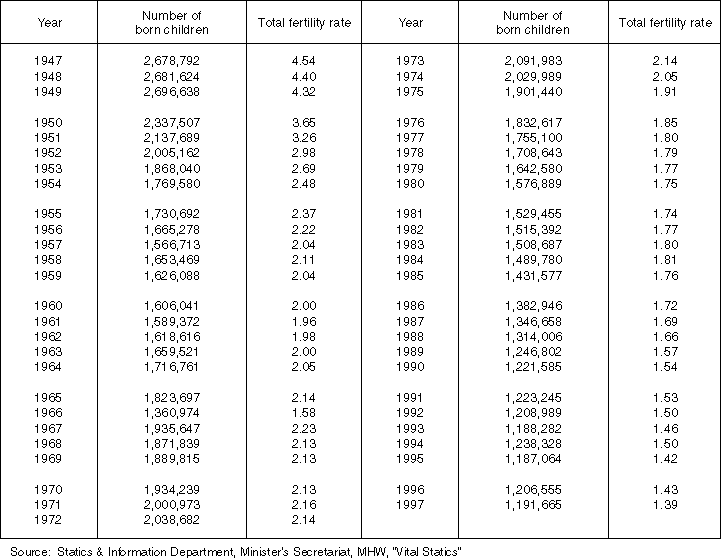
Detailed Data 1
Changes in the Number of Born Children and Total Fertility Rate
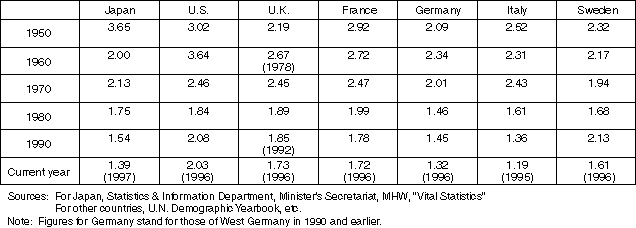
Detailed Data 2
Changes in Total Fertility Rates in Developed Countries
Detailed Data 3
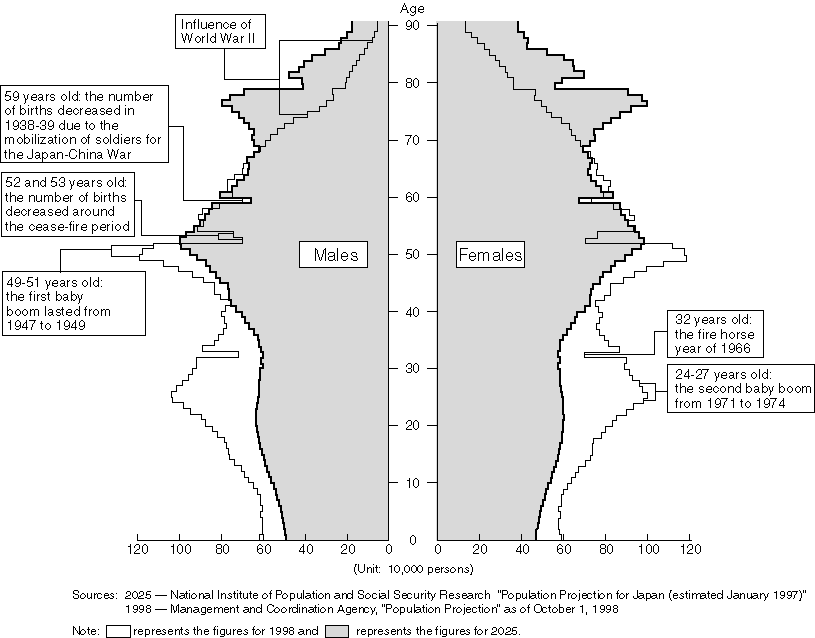
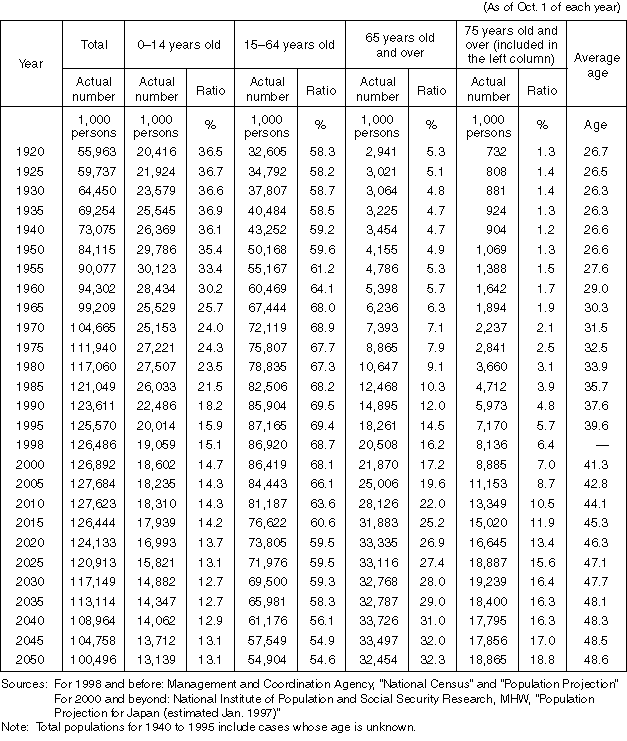
Changes and Future Projections for the Population in Different Age Groups
Detailed Data 4
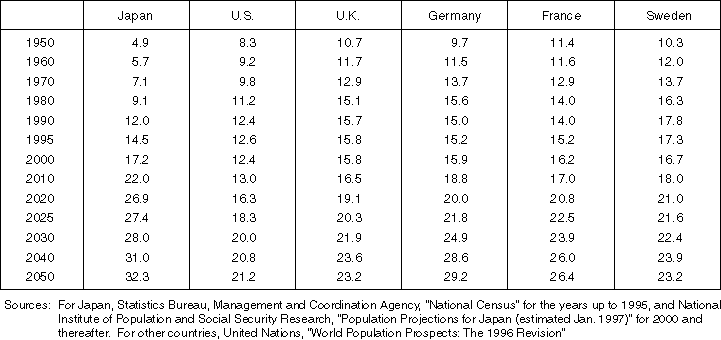
Ratio of the Population Age 65 and Older in Major Countries
Detailed Data 5
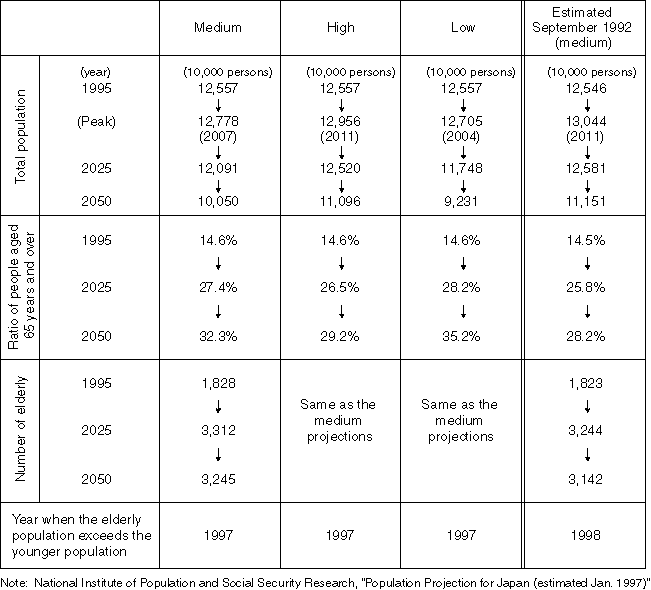
Summary of Population Projections for Japan (estimated January 1997)
Detailed Data 6
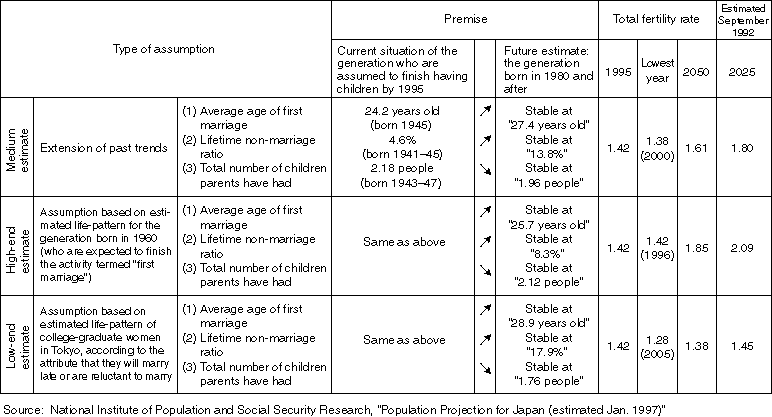
Premises for Birth Rate Estimates
Overview
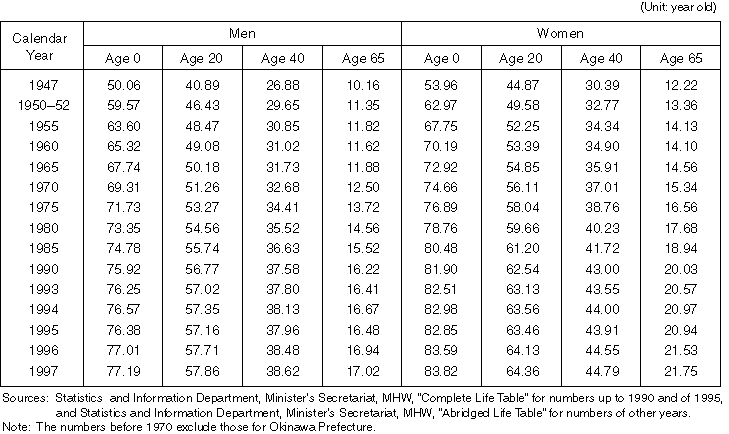
Detailed Data 1
Annual Changes in Mortality Rate Classified by Major Causes of Death (per population of 100 thousand)
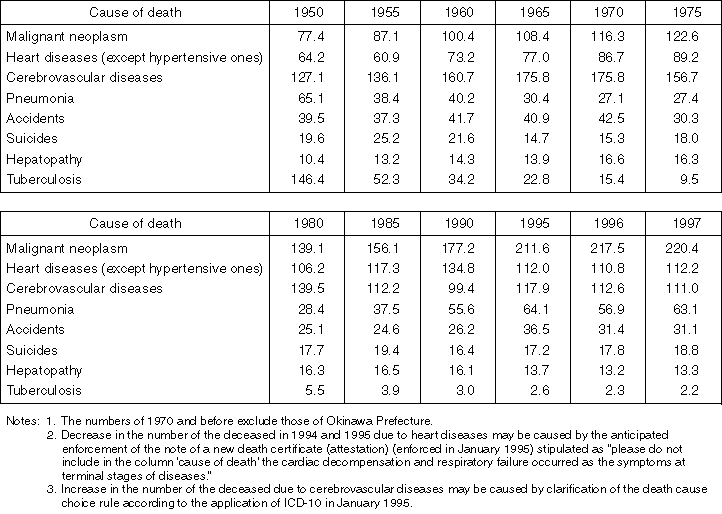
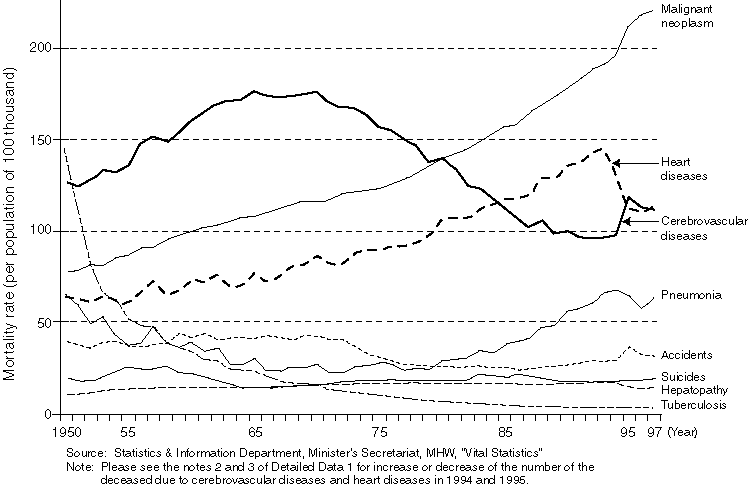
Detailed Data 2
Annual Changes in Mortality Rate Classified by Major Causes of Death
Overview
Annual Changes in the Number of Households and Average Number of Household Members
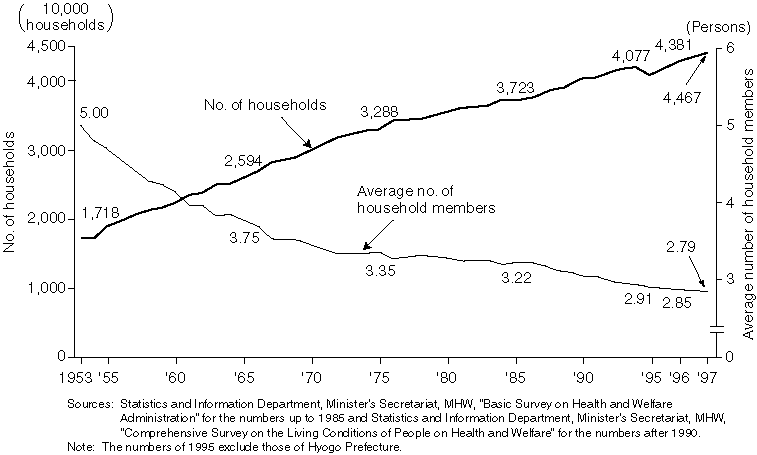
Detailed Data 1
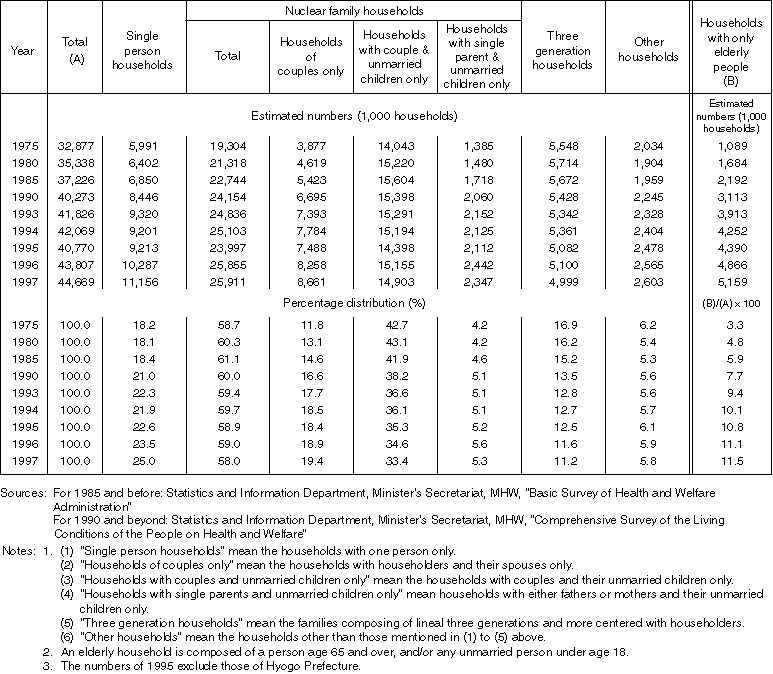
Changes in the Number of Households by Type
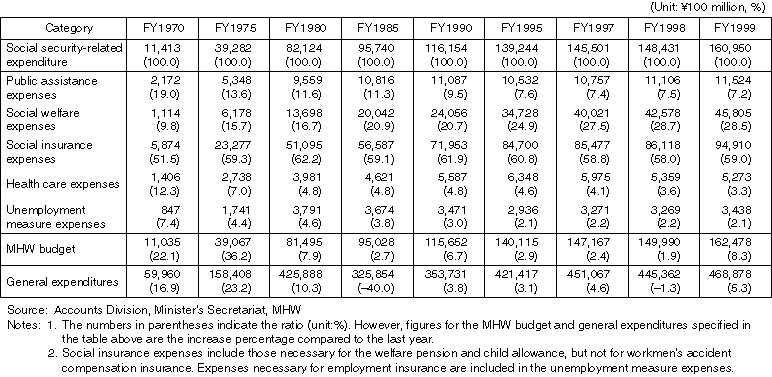
Overview
Changes in Social Security-Related Expenditure in the Governmental Budget
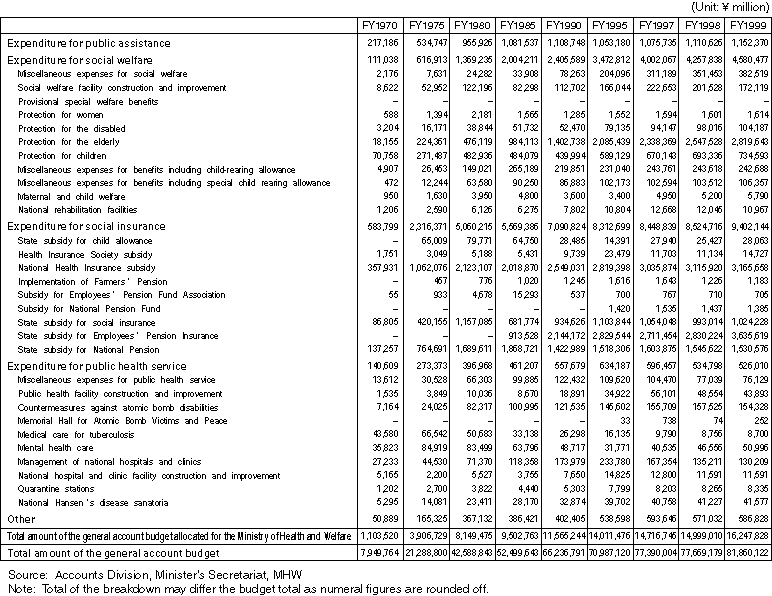
Detailed Data 1
Changes in the General Account Expenditure Budget Classified by Expense Item Allocated for the Ministry of Health and Welfare
Overview
Summary of Concepts
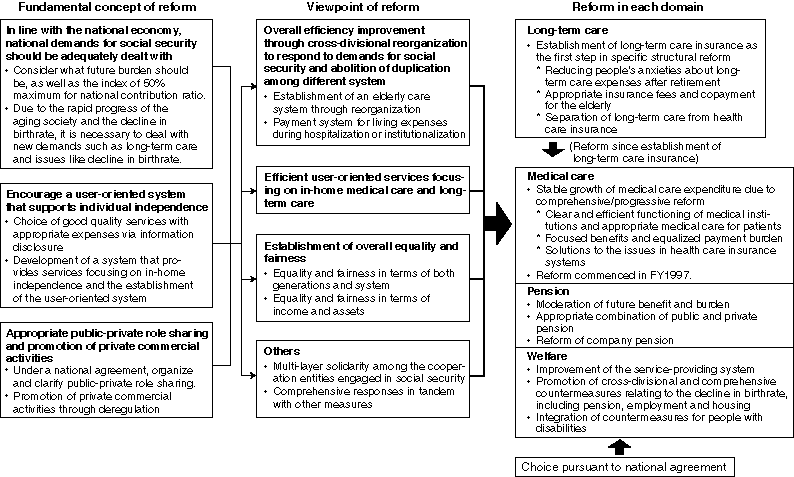
Detailed Data 1
Future Perspectives on the Benefits and Burdens for Social Security(compared to national income (NI))
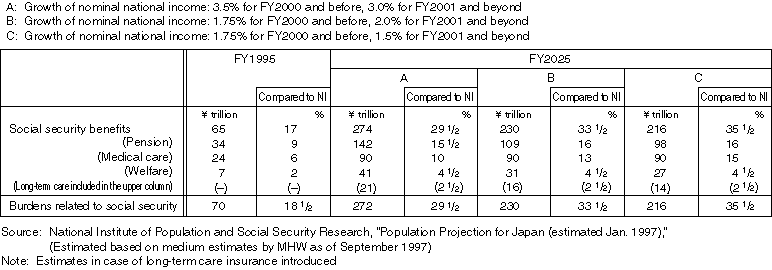
Detailed Data 2
Breakdown of the Social Security Benefit Expenditure by Sector
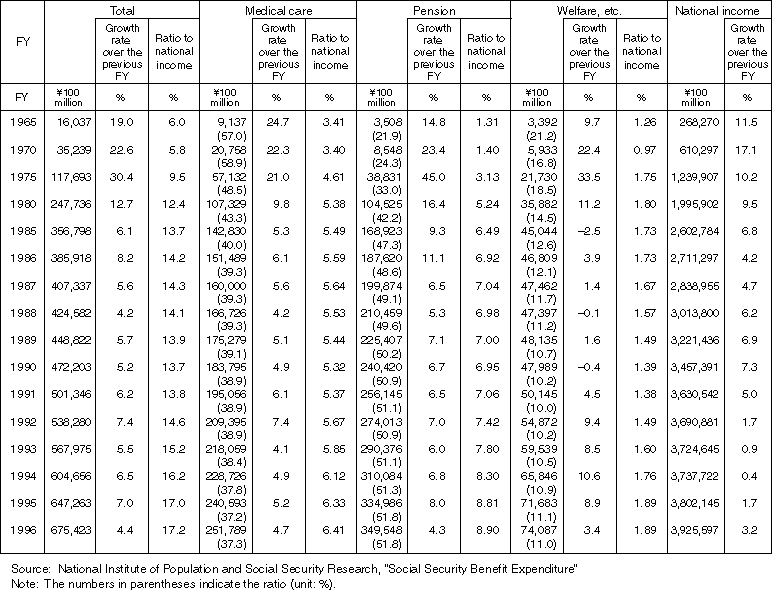
Detailed Data 3
Changes in the National Contribution Ratio (in terms of taxation and social security premiums)
Detailed Data 4
International Comparison in Social Security Benefits, and National Contribution Ratio (in terms of taxation and social security premiums)
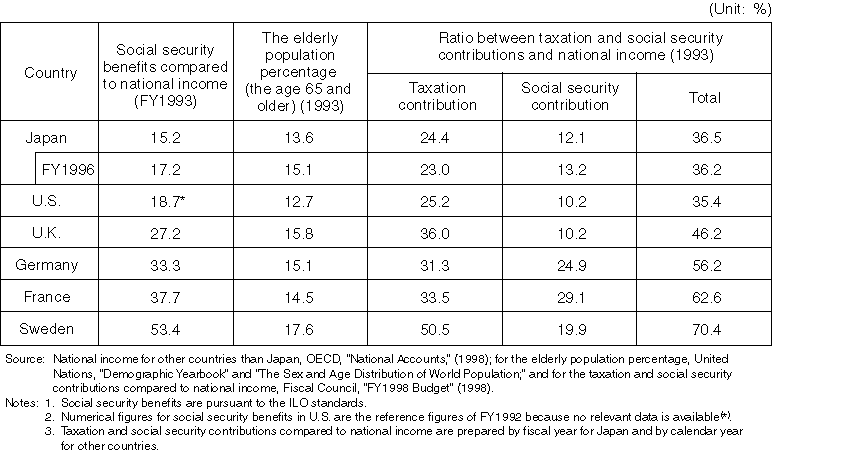
Detailed Data 5
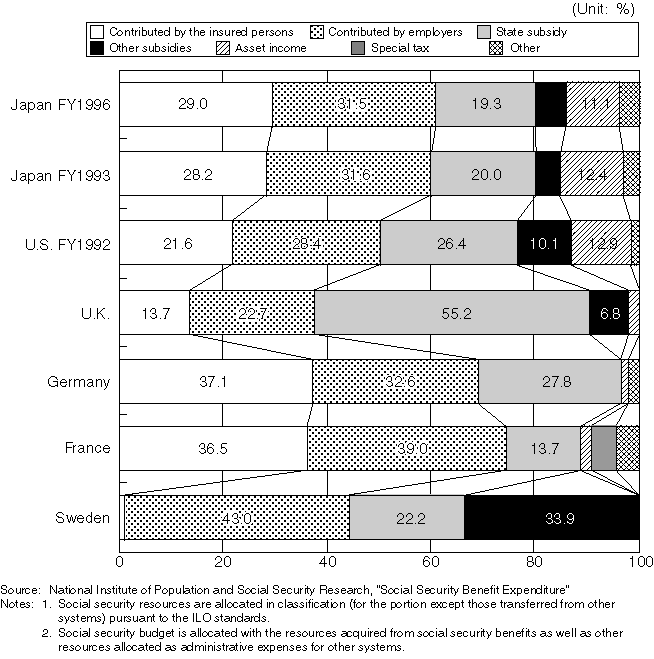
International Comparison in Social Security Resource Ratio (FY1993)
Medical Information System for Advanced Information Telecommunication Network
Integrated Information System of Medical Organizations
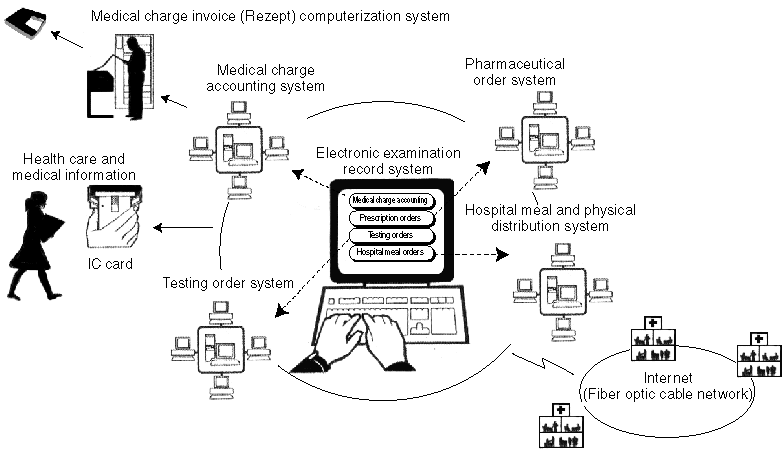
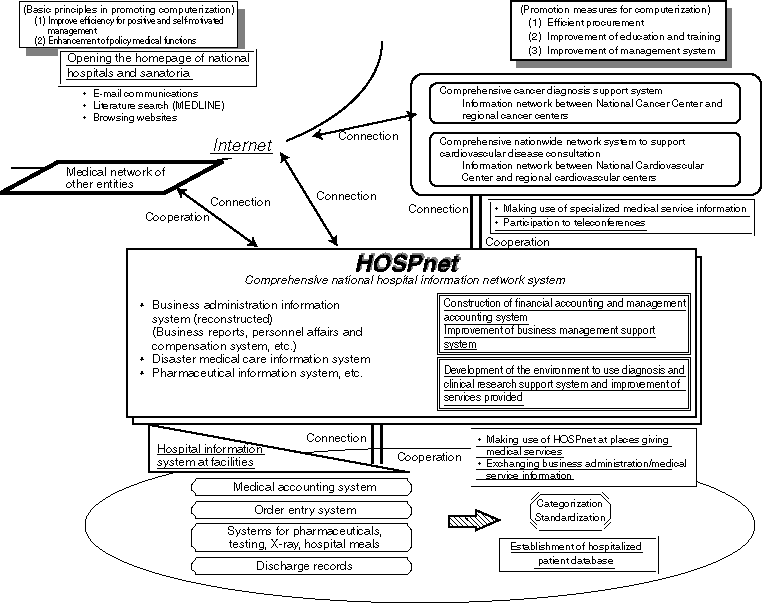
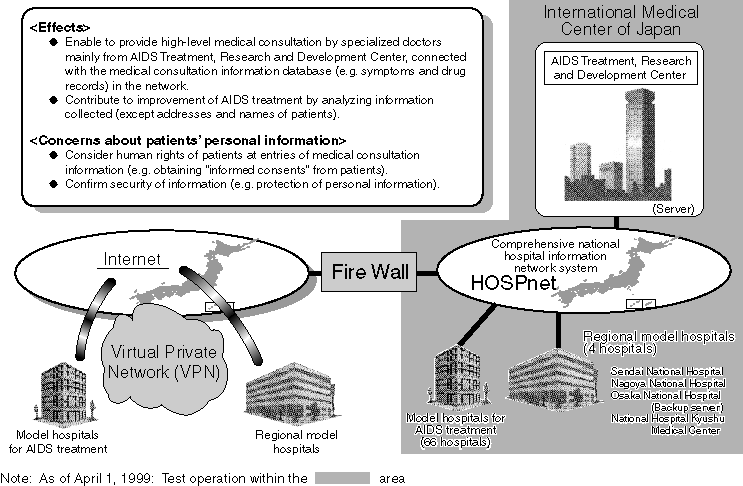
Overview
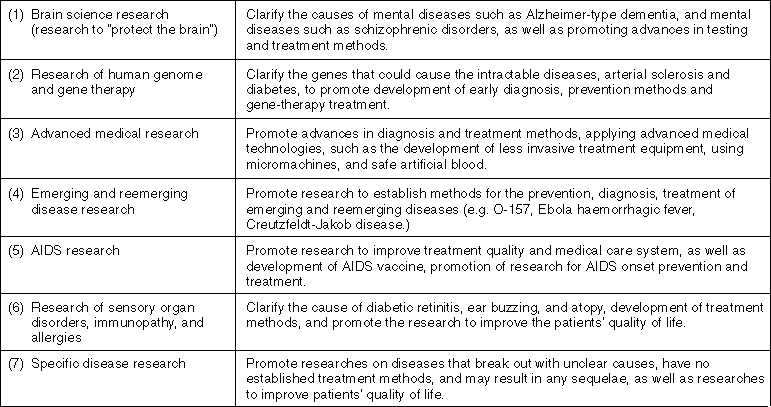
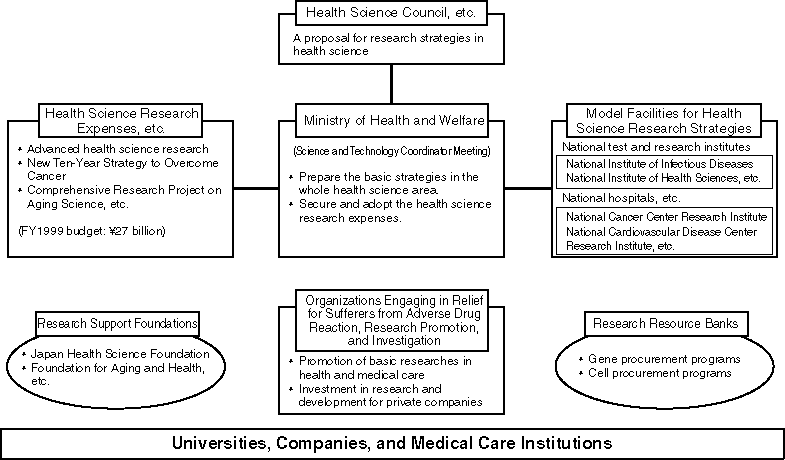
The "Science and Technology Basic Plan" was approved by the Cabinet in July 1996 pursuant to the Science and Technology Law to promote science and technology for the next decade. The aim is to establish the creative use of science and technology in Japan.
The Ministry of Health and Welfare considers it important to promote health science, in order to approach the dream of health and long life through the application of state-of-the-art technology. In this context, health science has been promoted since 1997, focusing on the following seven areas:
Major Research Fields
Enhancement of Research Base
It is indispensable for promotion of health science research to enhance the research base. To promote and improve the reorganization of national research institutes, and so forth, it is important to provide incentive funds, and promote international contributions.
Improved Efficiency in Research Evaluation
"Guidelines for implementation methods in evaluation of health science research" are provided for evaluation of research agenda and institutions. Approaches to improve efficiency include 1) implementation of external evaluation, 2) presentation of evaluation results, 3) appropriate allocation of research and development resources for research expenses or other items.
|
Overview
"Gene therapy" refers to a new method of therapy in which genes or cells are transferred into the human body for treatment purposes. It is anticipated that the therapy will be an innovative treatment method for diseases (e.g. cancer, AIDS, congenital hereditary diseases) for which no effective treatment method is established at present. In the United States and other countries, clinical researches have already been conducted on more than 3,000 cases.
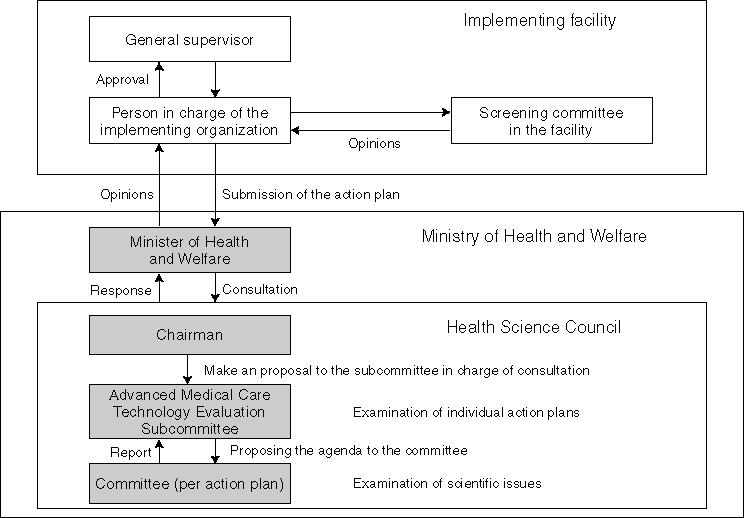
The Ministry of Health and Welfare, pursuant to the guidelines prepared by the Health Science Council in April 1993, established the "Official Guidelines for Clinical Research on Gene Therapy (the MHW Notice No. 23)" in February 1994. In the same month, the Ministry also established the "Central Evaluation Council for Clinical Research on Gene Therapy" for the purpose of comprehensively evaluating scientific safety and ethical appropriateness of research conducted in the field.
According to renewal of the Health Science Council in April 1997, this project was succeeded to the Council's Advanced Medical Care Technology Evaluation Subcommittee up to the present.
In August 1994, Japan's first action plan for clinical research on gene therapy for patients suffering the ADA (adenosine deaminase) deficiency was submitted by Hokkaido University to the Ministry of Health and Welfare. The clinical research started in August 1995 after the approval of the Minister of Health and Welfare as of February 13, 1995. Subsequent reports stated that the research made the given results and the follow-up is underway.
Subsequently, clinical research action plans about nephrocyte cancer were submitted by Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo and that about lung cancer by Okayama University, in December 1996. Those researches obtained approval for implementation by the Minister of Health and Welfare in July and September 1998, respectively.
At present, clinical research action plans are submitted by Chiba University (esophagus cancer), the Cancer Research Foundation (breast cancer), Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo (lung cancer), Nagoya University (brain tumor), The Jikei University School of Medicine (lung cancer). The Working Group for Clinical Research on Gene Therapy for Cancer established under the Advanced Medical Care Technology Evaluation Subcommittee is examining scientific issues.
For the purpose of promoting basic research and clinical research for gene therapy, the Ministry started a financial aid system for health science researches in 1993, and has been developing "human genome and gene therapy research" as one of major advanced health science research areas from 1997.
The Ministry of Health and Welfare comprehensively evaluates scientific safety and ethical appropriateness of research projects in the clinical stage. Furthermore, the Ministry is engaging in appropriate promotion of gene therapy research with financial aids to the research projects.
Overview
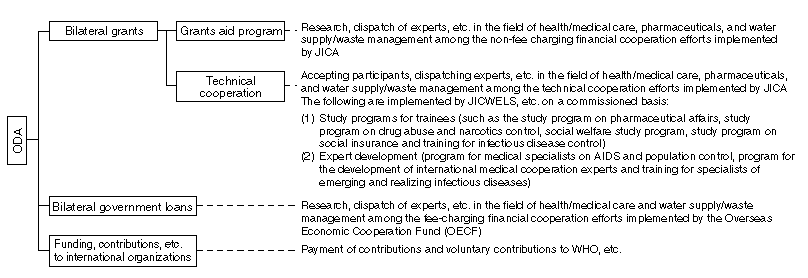
Present Situation of Japan's Official Development Assistance (ODA)
Japan's Official Development Assistance (ODA) reached \9,358 million in 1997, which is the highest in the world. The budget for fiscal 1998 is 1,389.1 billion, which is also among the world's highest figures.
The areas of health and medical services, water supply and population accounted for 13.1% of all bilateral cooperation in 1995 (committal basis: $1,926.77 million), demonstrating that these areas are a mainstay of Japan's ODA.
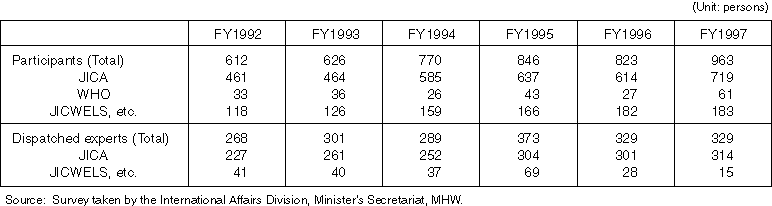
Detailed Data 1
Changes in the Number of Received Participants and Dispatched Experts in Health Care, Medical Care and Welfare Cooperation Activities of MHW
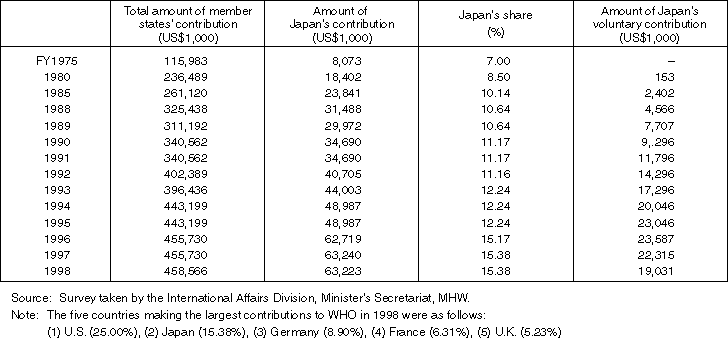
Detailed Data 2
Changes in Japan's Financial Contribution to WHO
|