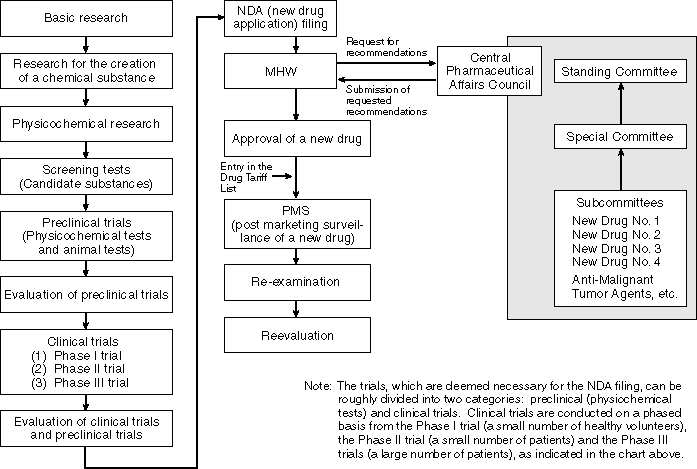
Overview
Flow of Examinations for the Approval of New Drugs

Examinations for the Approval of New Drugs
The quality, efficacy and safety of new drugs require an especially careful review. Therefore, a mechanism is in place in which the Central Pharmaceutical Affairs Council (an advisory organ to the Minister for Health and Welfare) composed of experts in the fields of medical science, pharmaceutical science, veterinary science and statistical science deliberates on these subjects based on many data derived from basic and clinical studies. This mechanism also includes the decision making process in which the Minister for Health and Welfare makes decisions on the approvals of new drugs based on the results of the deliberations of the council.
Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) for the implementation of animal testing (against toxity) among non-clinical tests and Good Clinical Practices (GCP) for the implementation of clinical tests are set forth. Each test is regulated by GLP and GCP so that it is conducted appropriately.
Licenses for the Manufacturing (Import and Sales) of Drugs, etc.
In issuing licenses for the manufacturing (imports and sales) of drugs, quasi-drugs and cosmetics, the structures/equipment of manufacturing companies (offices) and manufacturing control and quality control methods are examined to ensure compliance with standards and to confirm that applicants for licenses do not fall into any of the disqualification areas.
Prefectural governments have been authorized to issue these licenses except for some drugs which require sophisticated manufacturing technology, since April of 1995.
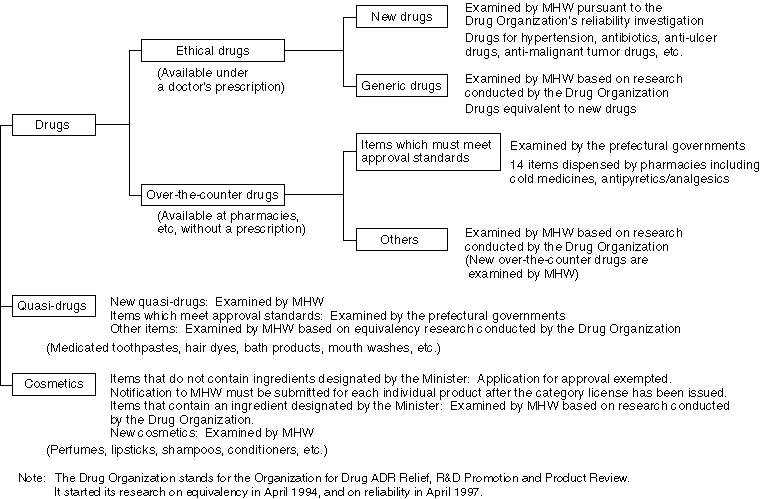
Examinations for the Approval of Products, Other Than New Drugs
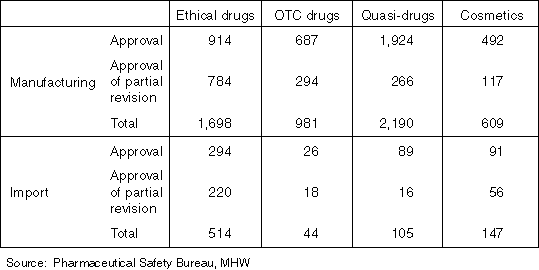
Detailed Data 1
The Number of Approvals (Licenses) in 1998
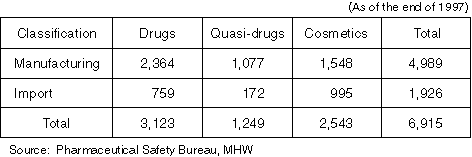
The Number of Manufacturer's (Importer's) Licenses for Drugs, etc.
Overview
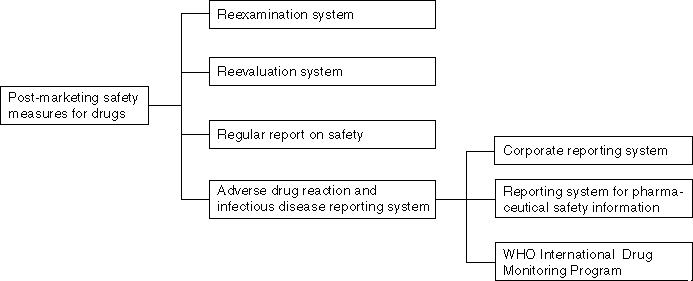
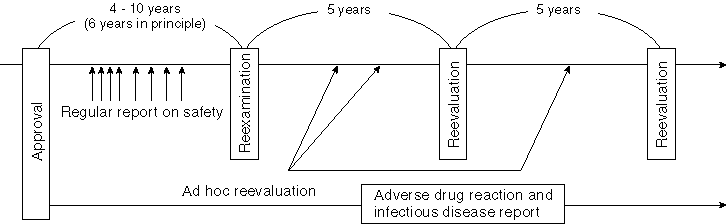
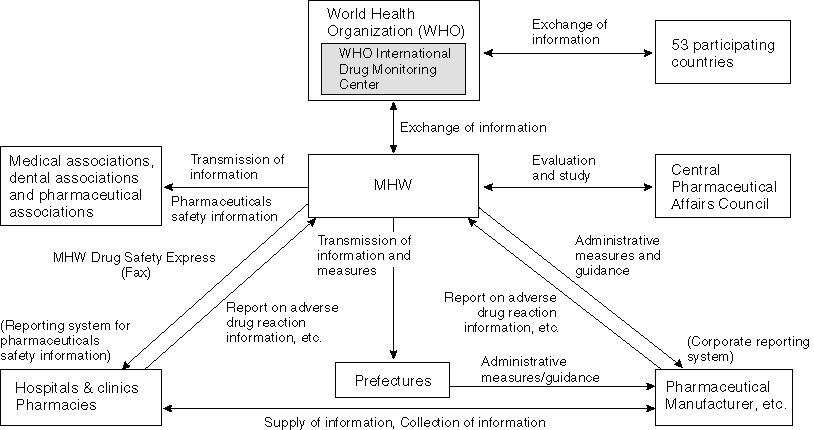
Detailed Data 1
List on the Results of Ethical Drug Reexaminations (up to December 31, 1997)

Detailed Data 2
List on the Results of Ethical Drug Reevaluations (up to December 31, 1997)
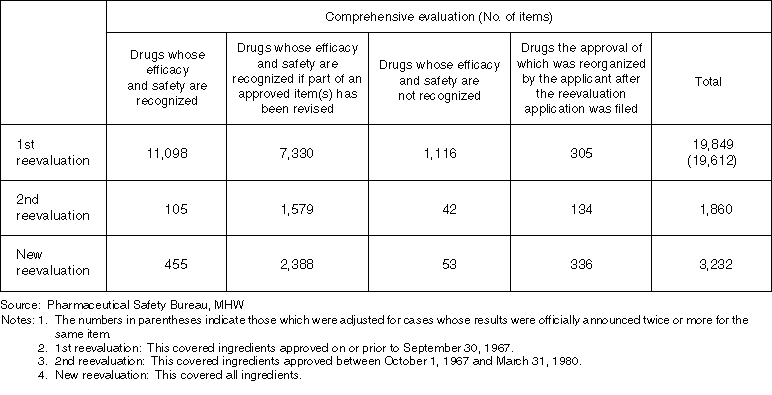
Detailed Data 3
Changes in the Number of Adverse Drug Reaction Reports, etc. in the Past 10 Years
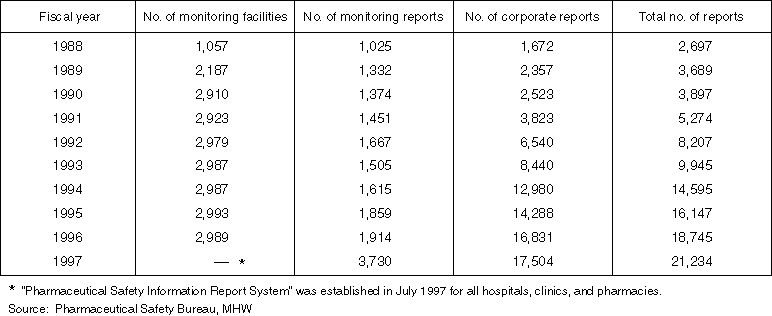
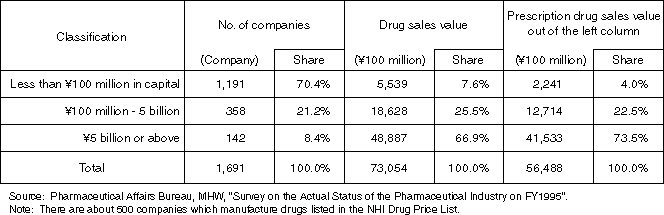
Detailed Data 1
Breakdown by Size of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
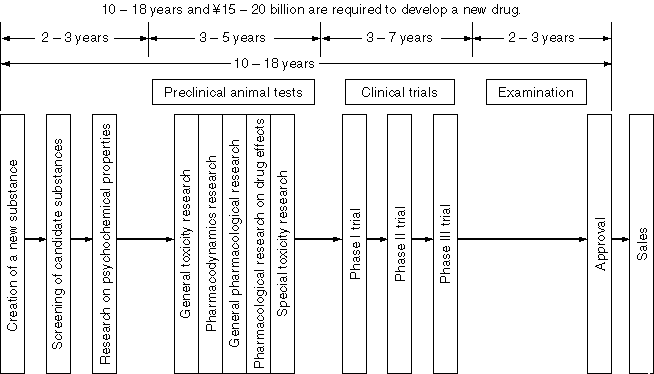
Detailed Information 1
Schematic Chart on the Research and Development of Drugs
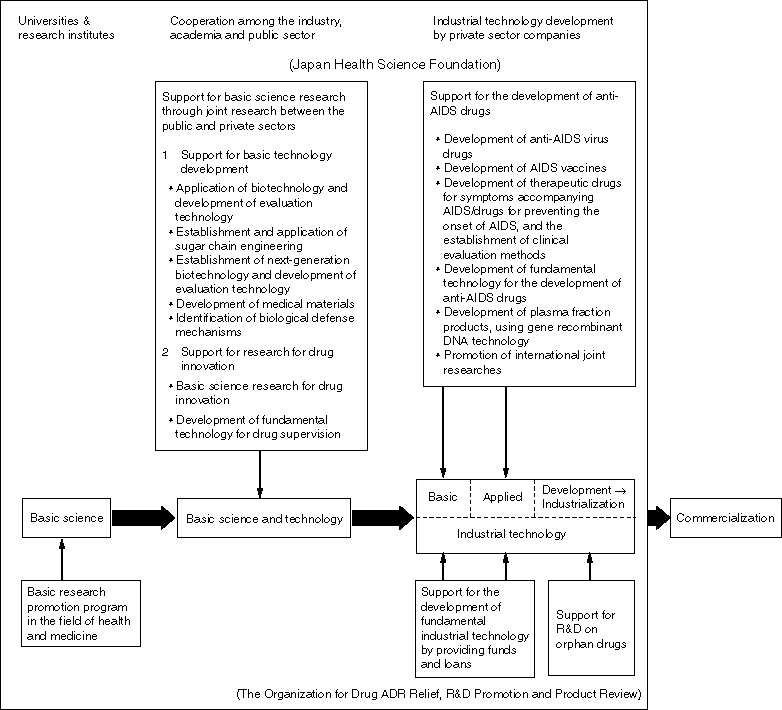
Overview
The Relief System for Sufferers from Adverse Drug Reactions
The purpose of this system is to provide various relief benefits and prompt relief to patients and their families, separately from civil liabilities, in relation to health damage caused by adverse reactions in spite of proper drug usage. This system is operated by the Organization for Drug ADR Relief, R&D Promotion and Product Review which was established upon approval of the Minister for Health and Welfare.
Types of Relief Benefits
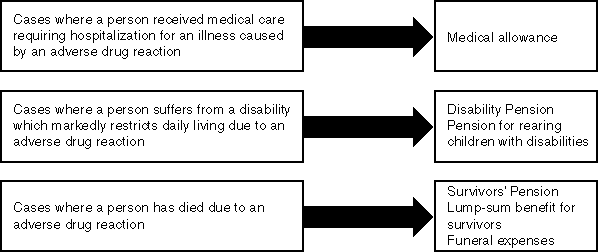
Activities on the Relief for Caused Damages
The Organization for Drug ADR Relief, R&D Promotion and Product Review is commissioned by pharmaceutical companies and the National Government to pay a health management allowance, etc. to SMON (subacute myelo-optico neuropathy) patients who have settled the lawsuit out of court.
The Relief Program for Patients, etc. of AIDS Caused by Blood Products, etc.
A variety of benefits are offered in accordance with the relief system for sufferers from adverse drug reactions if HIV (AIDS virus) carriers develop symptoms due to infection arising from blood products or if they die. Also, a survey and research program has been carried out since fiscal 1993. This program is intended to help HIV carriers, infected through the use of contaminated blood products and suffer from reduced immune functions, to prevent them from developing symptoms in daily living by providing health management expenses and requesting them to report their health status.
From 1996, assistance has been provided for the health management of people who developed AIDS and accepted the court settlement (e.g. reduction of costs incurred for health management after AIDS developed).
Detailed Data 1
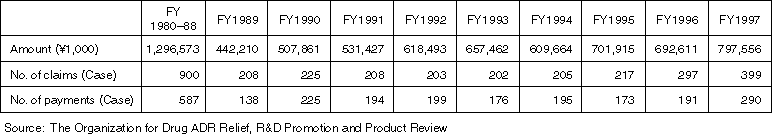
Annual Changes on the Status of Adverse Drug Reaction Relief (as of the End of Each FY)
Overview
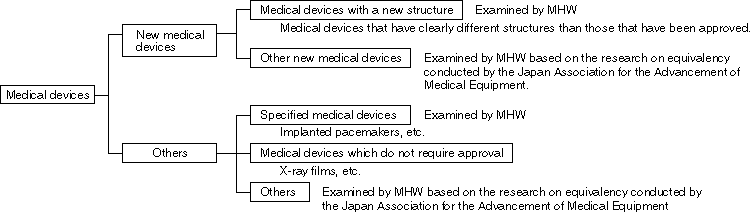
Classification of Examinations for the Approval of Medical Devices
Detailed Data 1
The Number of Approvals (Licenses) in 1998

The Number of Manufacturer's (Importer's) Licenses for Medical Devices

Overview
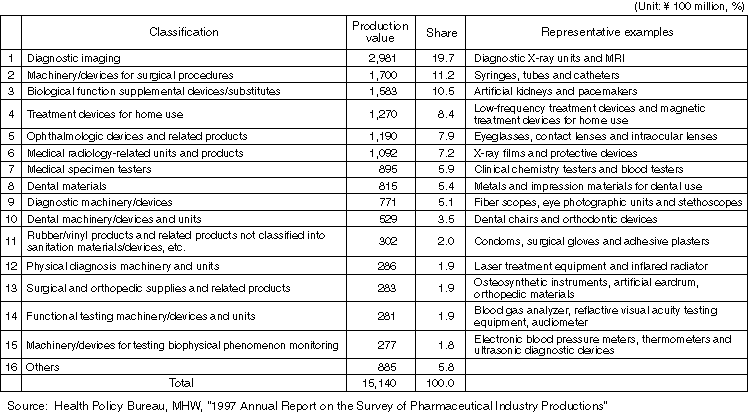
Production Value, etc. of Medical Devices
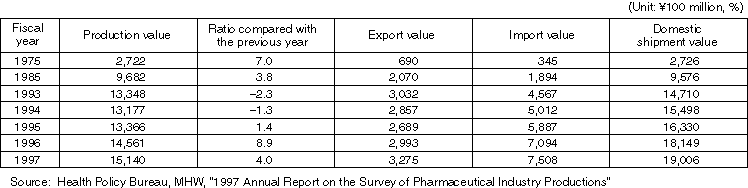
Detailed Information 1
Production Value by Medical Device Type
Overview
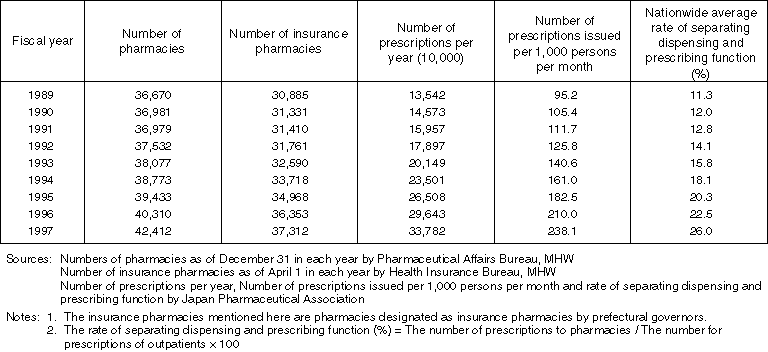
The System of Separating Dispensing and Prescribing Functions
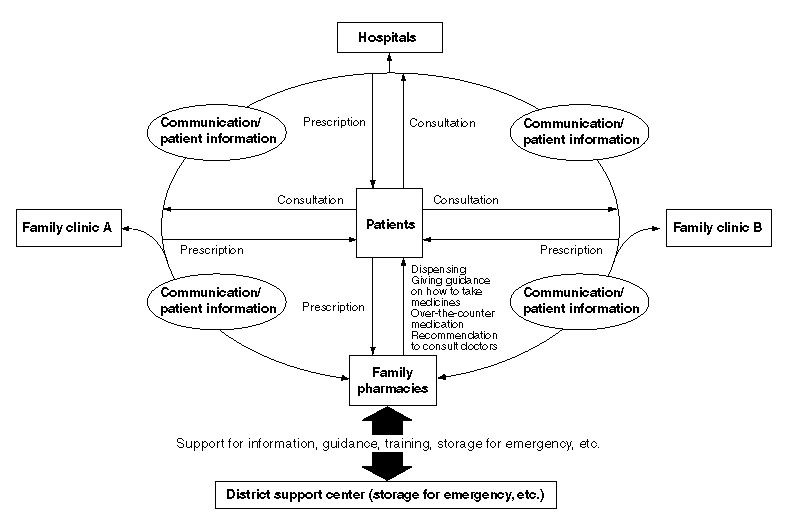
Advantages of the Separation of Dispensing and Prescribing Drugs
Overview
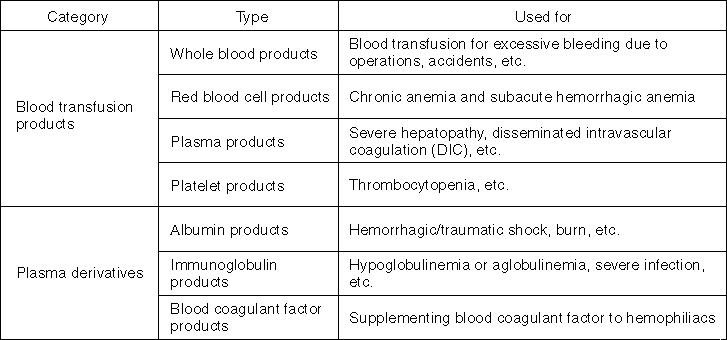
Blood Products
"Blood products" refer to all the pharmaceutical products which are derived from human blood, and are categorized into: blood transfusion products and plasma derivatives. All of the blood transfusion products are supplied through blood donations.
On the other hand, though blood coagulant factor products are supplied domestically except for a few special products, other plasma derivatives, namely albumin products and immunoglobulin products, are mostly imported from overseas, and questions have been raised from the viewpoint of ethics, safety, and supply stability. The Ministry of Health and Welfare is planning to develop a system that can secure the domestic supply of all blood products including plasma derivatives.
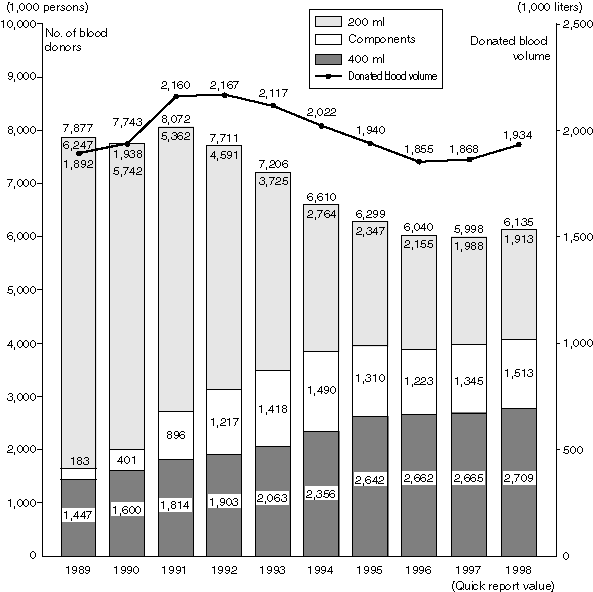
Status of Blood Donations
Introduction of 400ml blood donation and pheresis in addition to conventional 200ml blood donation led annual increase in the number of people for 400ml blood donation and pheresis. Since FY1999, the maximum age limit for blood donation is to be revised from the age 64 to 69.
Detailed Data 1
Annual Changes in the Number of Blood Donors and Donated Blood Volume
Overview
Structural Chart of Countermeasures to Narcotics and Stimulants Abuse
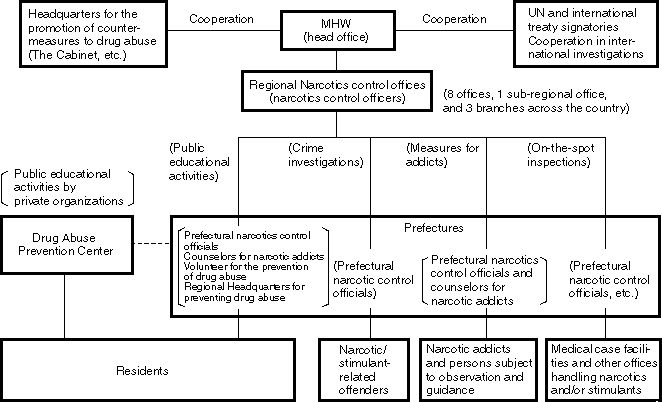
Narcotics which are used, for example, as analgesics for cancer patients and psychotropic agents, such as hypnotics and tranquilizers, serve medically important roles. On the other hand, when they are abused, they not only damage the health of abusing individuals, but also can have significantly negative effects on the entire society.
For this reason, we try to stabilize the supply and demand of narcotics for medical use. We are also promoting nationwide countermeasures such to control narcotics and stimulants abuse, focusing mainly on the following three countermeasures: strict law enforcement, public education activities for abuse prevention, and treatment and after-treatment care for addicts.
Supply and Demand Status on Narcotics for Medical Use
Japan has been importing opium, which serves as a raw material for opium alkaloid-based narcotics, from India. The volume of opium imports have been increasing in recent years. This is because the consumption of codeine and dihydrocodeine which are used as narcotics for home medications has been rising. Consumption of morphine which is used for the purpose of pain relief for terminal cancer patients has also been increasing to 11.8 fold compared with ten years ago. This tendency seems likely to continue in the future.
An Outline of Narcotic and Stimulant Offenses
The number of stimulant offenders, previously stable at around 15,000, has recently increased dramatically since 1995. On the other hand, the number of arrested cannabis offenders, which followed stimulant offenders in number, continuously decreased since 1995.