Overview
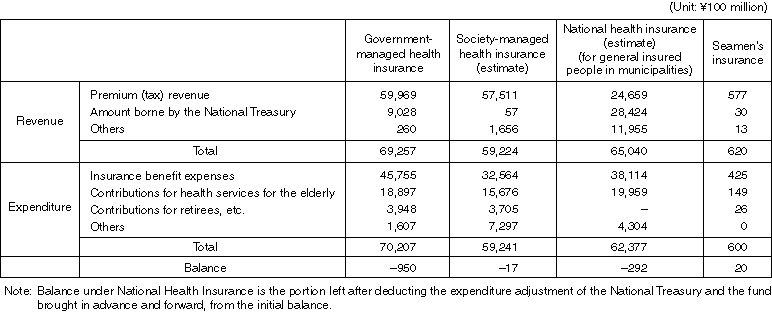
Status of the Finance of the Health Insurance System (FY1997)

Detailed Data 1
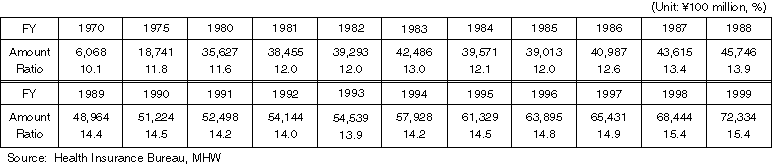
Ratio of the Health Expenditure Borne by the National Treasury to the National Government's General Expenditure
Overview
Outline of the Health Insurance System
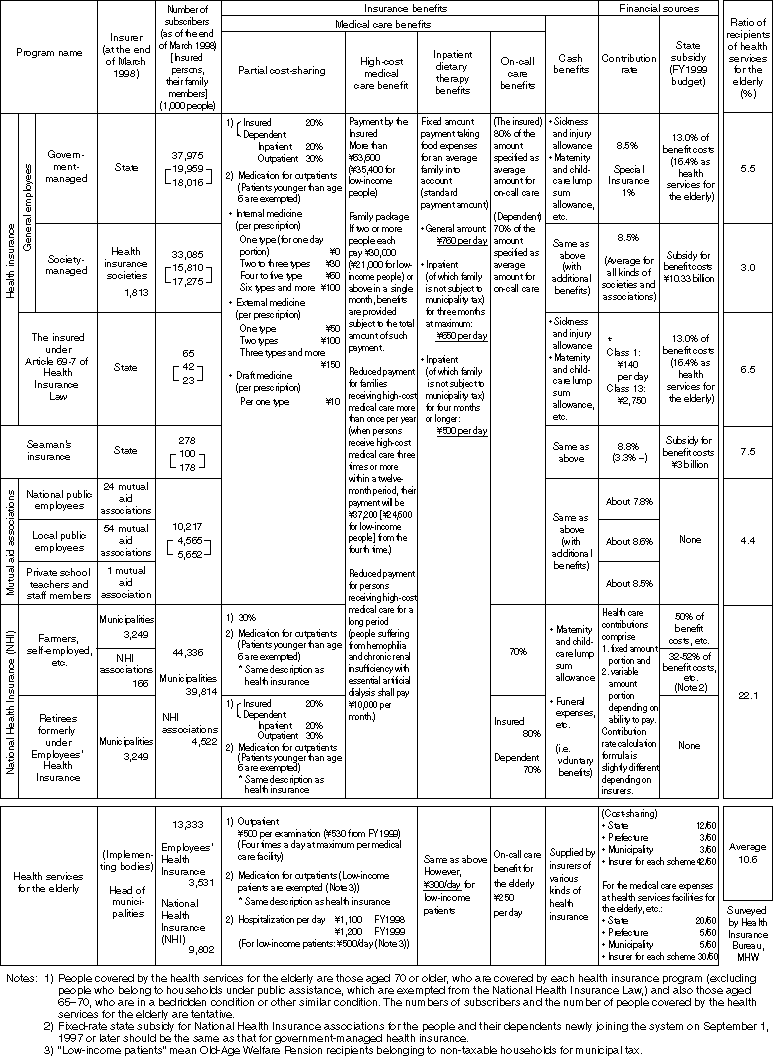
Detailed Information 1
History of the Health Insurance System
| 1905 | Kanebo and Yawata Iron and Steel Works established mutual aid associations. |
| 1922 | The Health Insurance Law was enacted. |
| 1927 | The Health Insurance Law was enforced in full scale (for factories and workplaces of mines and transportation industry with constantly employing at least ten employees). |
| 1934 | Amendment of the Health Insurance Law:
|
| 1938 | The Ministry of Health and Welfare was established. The National Health Insurance Law was enacted.
|
| 1939 | The Staff Health Insurance Law was enacted (for the employees working for companies and stores in specific municipalities). The Seamen's Insurance Law was enacted. Amendment of the Health Insurance Law: It was commenced to supply family benefits (voluntary benefits). |
| 1942 | Amendment of the Health Insurance Law: The Staff Health Insurance was merged (Copayment system was introduced). The Ministry of Health and Welfare Establishment Law was enacted.: Health Insurance Bureau was established. |
| 1944 | Amendment of the Health Insurance Law: Benefit supply period was extended to two years. |
| 1947 | The Workmen's Accident Compensation Insurance Law was enacted. Amendment of the Health Insurance Law: The benefits for occupational injures/diseases were abolished. |
| 1948 | The Social Insurance Medical Fee Payment Fund Law was enacted.
|
| 1953 | The Day Laborers' Health Insurance Law and the Private School Teachers and Employees Mutual Aid Association Law were enacted. Amendment of the Health Insurance Law:
|
| 1954 | The payment from the National Treasury was introduced for the first time to the government-management health insurance (\1 billion.) |
| 1956 | The Public Corporation and National Enterprise Employees Mutual Aid Association Law was enacted. |
| 1958 | Overall amendment of the National Health Insurance Law (promotion of universal coverage and 50% benefit coverage as the benefit for the insured) |
| 1961 | Universal coverage was achieved. |
| 1962 | The Social Insurance Agency was established. The Local Public Service Employees Mutual Aid Association Law was enacted. |
| 1963 | The restriction on the medical care benefit period was removed. |
| 1967 | The Special Exception Law on the Health Insurance was enacted (the creation of a copayment for drugs.) |
| 1968 | 70% benefit coverage was completely implemented. |
| 1969 | The copayment for drugs under the Health Insurance was abolished. |
| 1972 | Amendment of the Welfare Law for the Elderly (the so-called "free of charge" medical care for the elderly) |
| 1973 | Amendment of the Health Insurance Law:
|
| 1977 | Amendment for the Health Insurance Law:
|
| 1980 | Amendment for the Health Insurance Law:
|
| 1982 | The Health and Medical Service Law for the Elderly was enacted. |
| 1984 | Amendment of the Health Insurance Law, etc.:
|
| 1986 | Amendment of the Health 2nd Medical Service Law:
|
| 1988 | Amendment of the National Health Insurance Law, etc.:
|
| 1990 | Amendment of the National Health Insurance Law, etc.:
|
| 1991 | Amendment of the Health and Medical Service Law for the Elderly:
|
| 1992 | Amendment of the Health Insurance Law, etc.:
|
| 1993 | Amendment of the National Health Insurance Law, etc.:
|
| 1994 | Amendment of the Health Insurance Law, etc.:
|
| 1995 | Amendment of the National Health Insurance Law, etc.:
|
| 1997 | Amendment of the Health Insurance Law, etc.:
|
| 1998 | Amendment of the National Health Insurance Law, etc.:
|
Overview
Changes in the National Health Expenditure
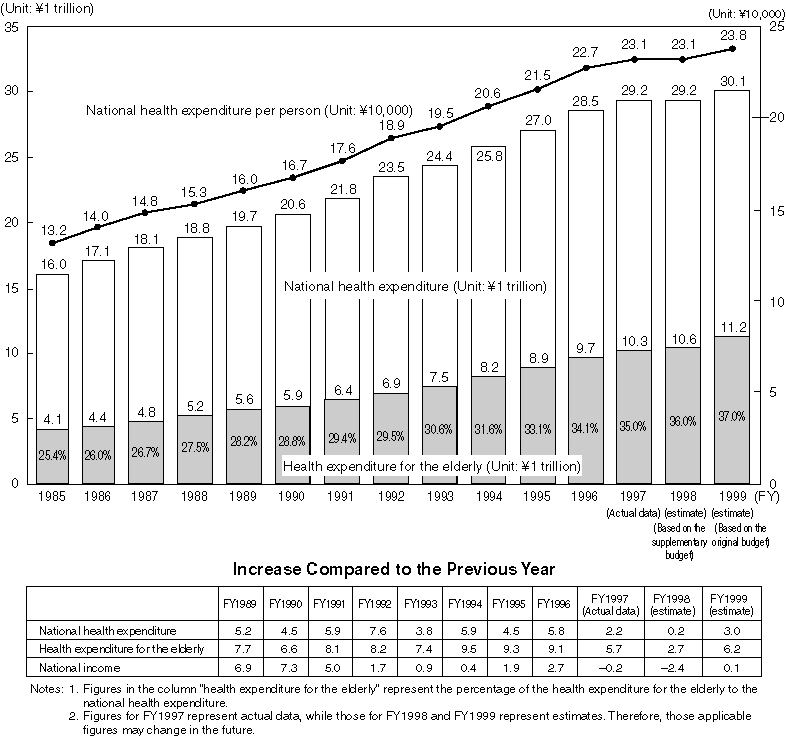
Overview
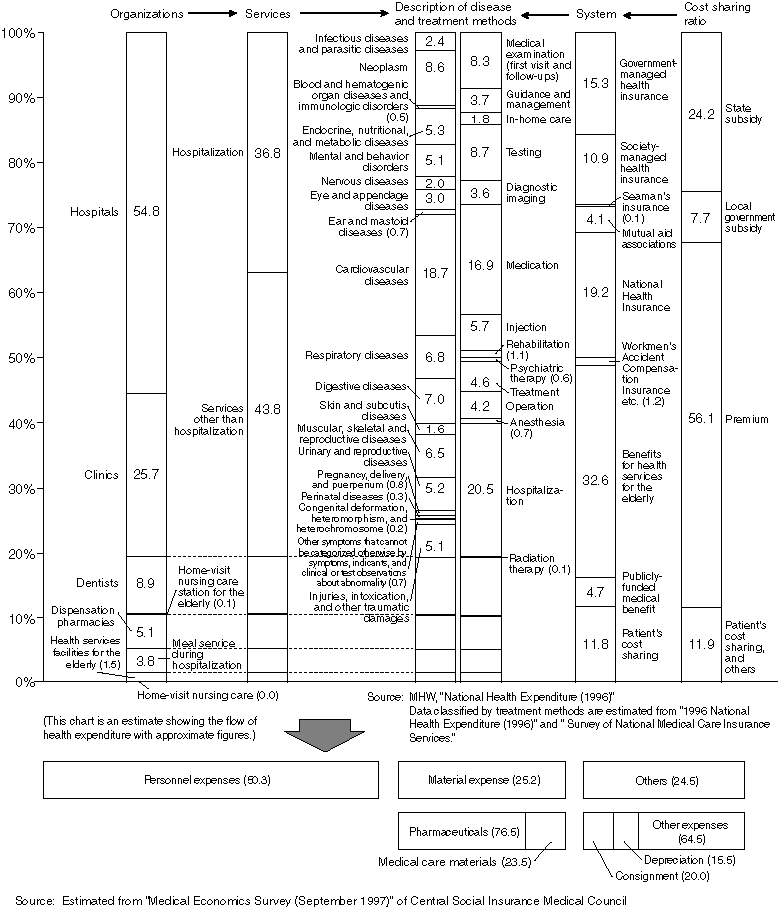
Conceptual Chart of Insured Medical Treatment
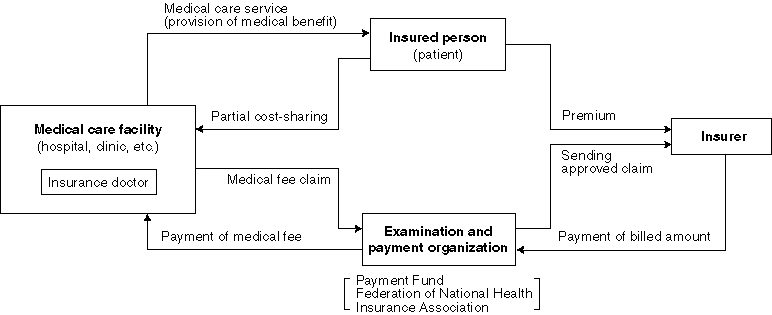
Medical fees are classified into three types: medical, dental and dispensing fees.
The medical fee is calculated by adding stipulated numbers of points for the individual medical activities provided (so-called "fee-for-service system"). The unit price for one point is \10. For a typhlitis hospitalization case, for example, the first visit fee, the hospitalization fee multiplied by the length of stay (days,) the typhlitis surgery fee (7,400 points,) the test fee and the drug fee are added to one another and the medical institution will receive the total amount less the patient's co-payment from the payment fund, etc.
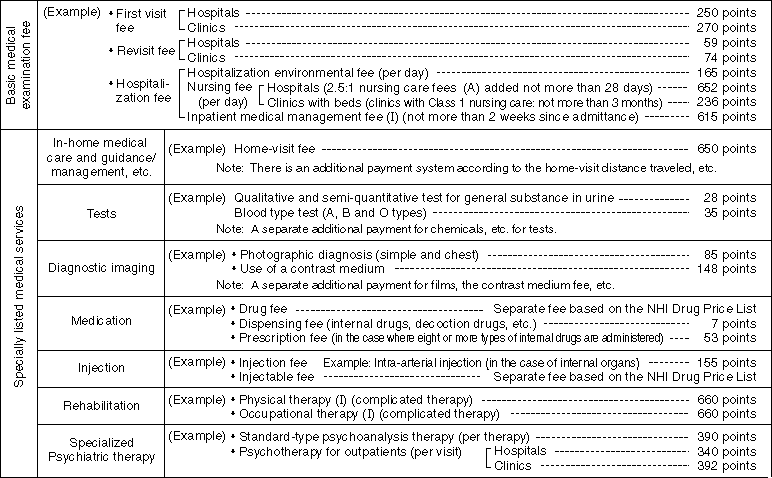
Detailed Information 1
Examples of Medical Fee Points !!(Unit price for 1 point is \10)
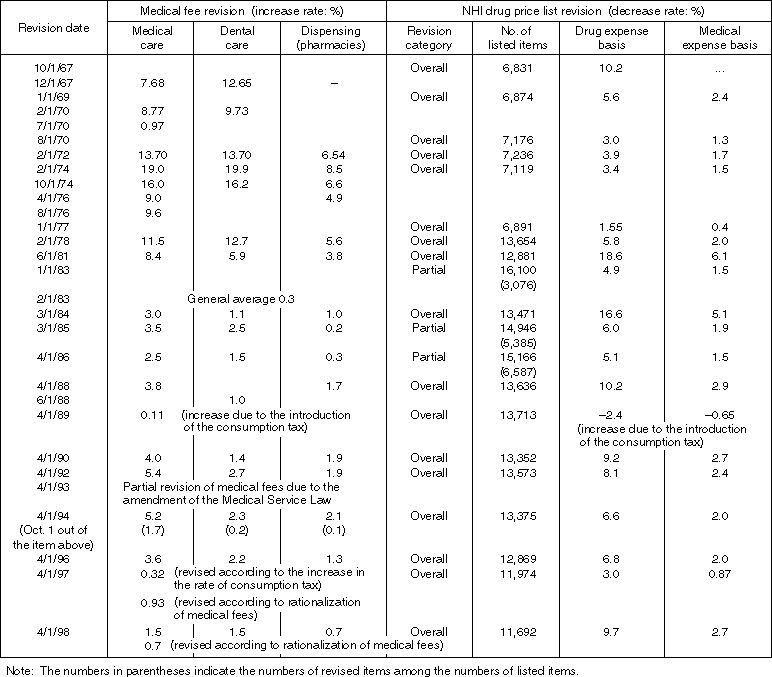
Detailed Data 1
Historical Development of the Revisions of Medical Fees and
the Drug Price List
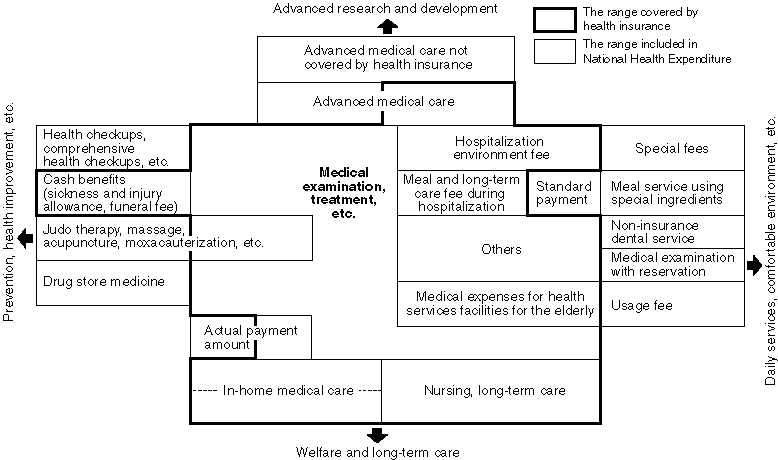
Detailed Information 2
Range of Medical Fees and Health Insurance Coverage (Conceptual-Chart)
Detailed Information 3
Health Expenditure Flow Chart